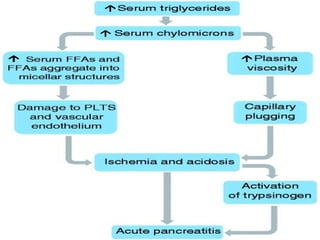
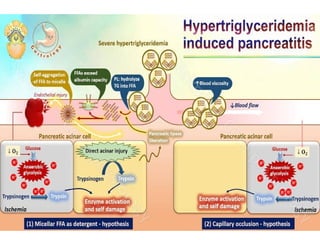
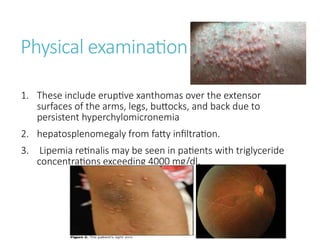
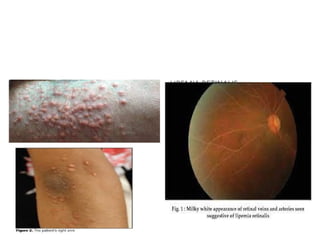
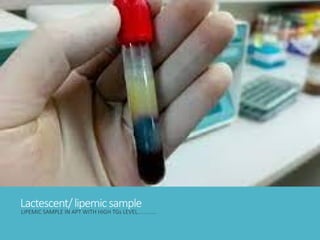
Hypertriglyceridemia (HTG) is a significant risk factor for acute pancreatitis, especially when triglyceride levels exceed 1000 mg/dl, with demographic differences in patients with HTG-induced pancreatitis compared to other causes. Management involves treating acute pancreatitis, reducing triglyceride levels with apheresis and insulin, and implementing long-term strategies such as pharmacotherapy and lifestyle changes to prevent recurrence. Monitoring triglyceride and glucose levels is crucial during treatment, with therapeutic interventions tailored according to the severity of the condition.



![Types of hypertriglyceridemia
1. Both primary (genetic) and secondary disorders of
lipoprotein metabolism are associated with hyper-
triglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis (HTGP).
2. Primary hyper-triglyceridemia — Types I (high chylomicrons),
IV (high very low-density lipoprotein [VLDL]), and V (high
chylomicrons and VLDL) dys-lipidemias are associated with
severe hypertriglyceridemia (HTG) and an increased risk of
acute pancreatitis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypertriglyceredemiainducedpancreatitis-241017141127-6958c570/85/HYPERTRIGLYCEREDEMIA-INDUCED-PANCREATITIS-pptx-5-320.jpg)