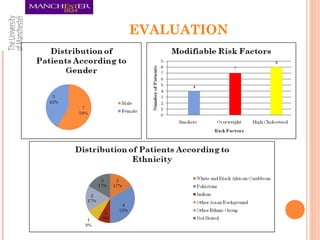
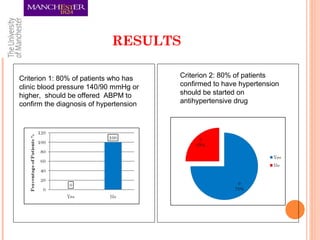
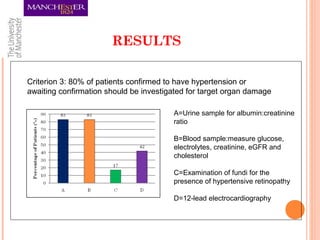
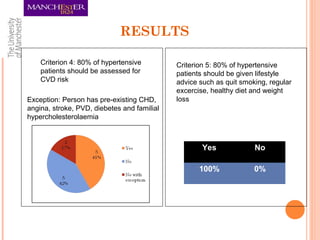
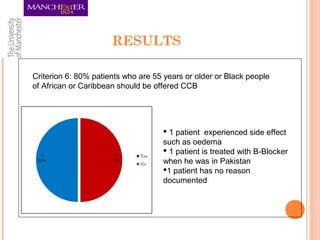
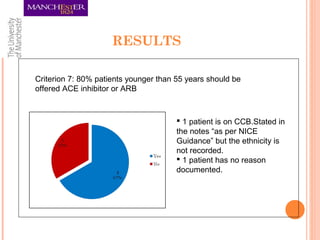
This document summarizes an audit on the management of hypertension in newly diagnosed patients. The audit evaluated 12 newly diagnosed hypertensive patients based on 7 criteria from NICE guidance and Quality and Outcomes Framework. The results found that most criteria were met for over 80% of patients, except for confirming the diagnosis with ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and documenting reasons for medication choices. The audit limitations included its small sample size and some patients previously being treated abroad. Recommendations include re-auditing with a larger sample, improving documentation of patient details and test/risk results, and documenting medication reasons.