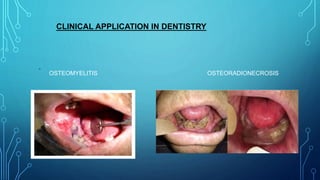
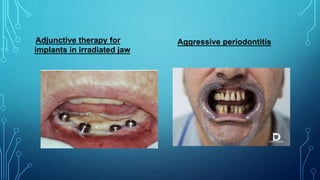
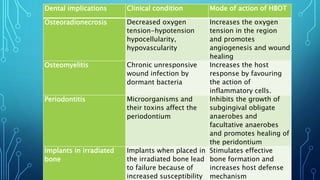
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy involves patients breathing 100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber at higher than normal atmospheric pressure. This results in increased oxygen levels in tissues and blood. The therapy has several beneficial effects including anti-ischemic, anti-infective, and wound healing properties. It is used to treat conditions like carbon monoxide poisoning, decompression sickness, osteomyelitis, osteoradionecrosis, and compromised grafts or flaps where normal healing is impaired. Treatment involves repeated sessions in monoplace or multiplace hyperbaric chambers at specific pressures and durations depending on the condition.