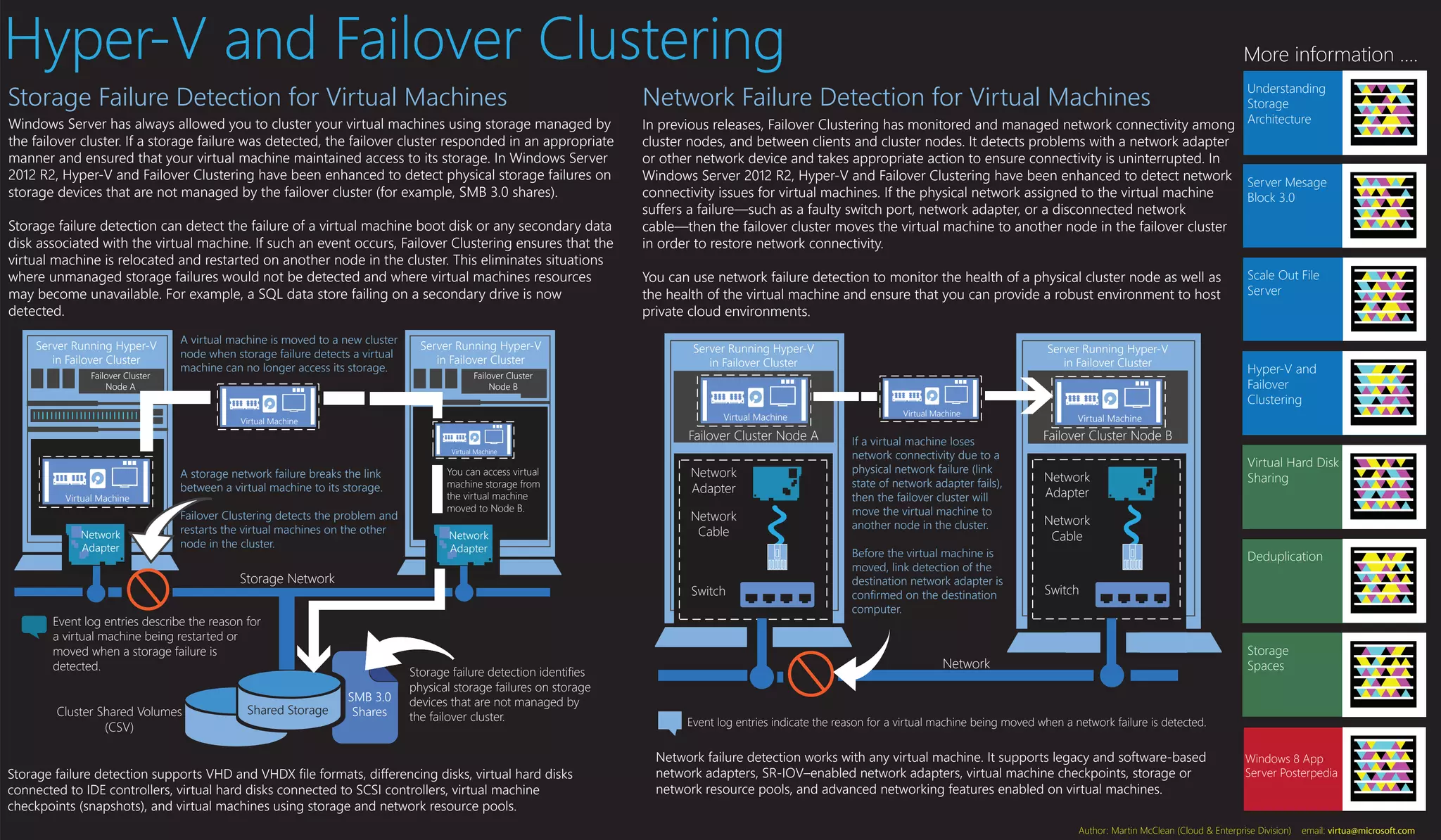
Windows Server 2012 R2 enhances Hyper-V and Failover Clustering by adding the ability to detect physical storage and network failures that impact virtual machines. Storage failure detection can now identify failures on devices not managed by the failover cluster, such as SMB 3.0 shares, and ensure virtual machines restart on another cluster node. Network failure detection monitors virtual machine network connectivity and will move a virtual machine if the physical network fails. These enhancements provide high availability for virtual machines even if the storage or network is not cluster-managed.