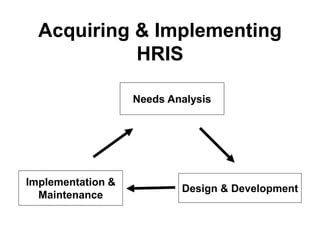
The document defines Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) as a systematic approach for managing data related to an organization's human resources, including data collection on payroll, performance, and recruitment. It outlines the components of HRIS, its implementation process, and its applications in strategic HRM and reporting. Additionally, it addresses ethical and evaluation issues associated with HRIS and hints at future topics such as job analysis.