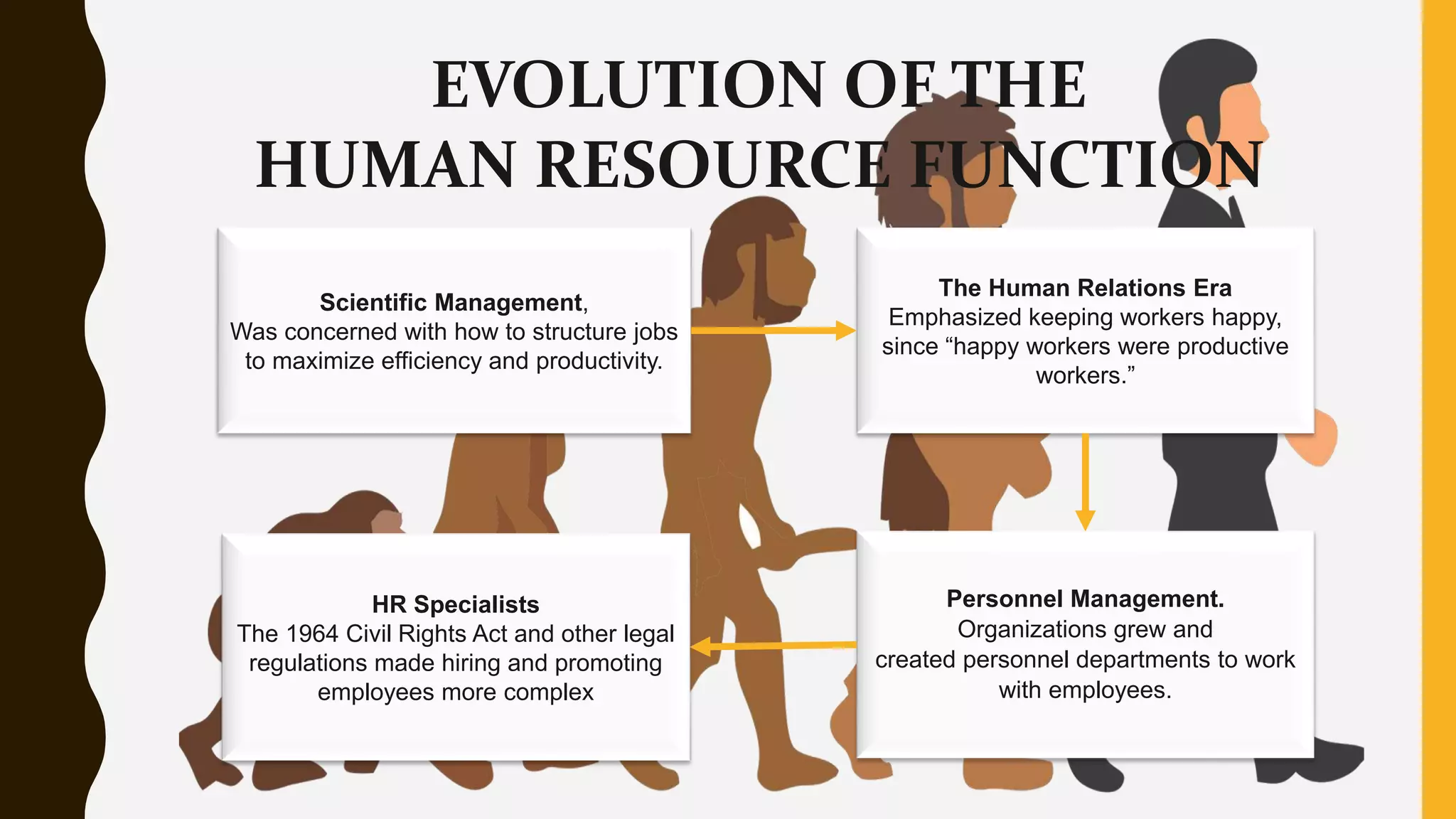
Human resource management has evolved from focusing on scientific management and keeping workers happy to becoming a strategic function within organizations. The contemporary perspective recognizes people as a source of competitive advantage and balances legal/ethical concerns with business needs. HR managers facilitate organizational competitiveness through activities like selecting and developing talent, enhance productivity and quality, ensure compliance with employment laws and social obligations, and promote individual growth.