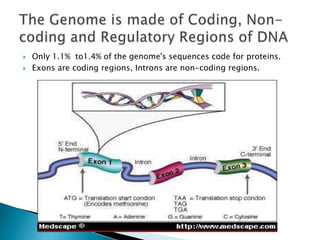
The human genome contains around 3 billion base pairs that make up DNA organized into 23 chromosome pairs. Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins, and can range in size from 1,000 to over 1.5 million base pairs. The human genome project mapped all human genes, finding around 20,000-25,000 genes, with only 1.1-1.4% of the genome actually coding for proteins. Genetic variations like single gene mutations or multiple gene effects can cause inherited diseases or influence disease risk.