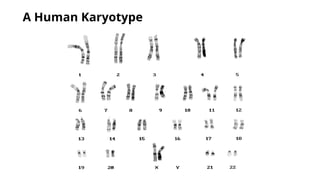
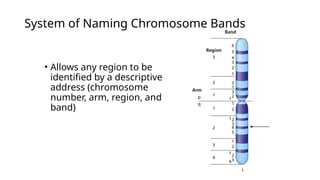
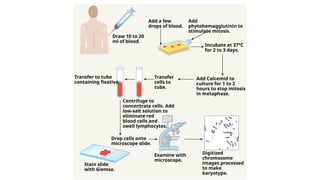
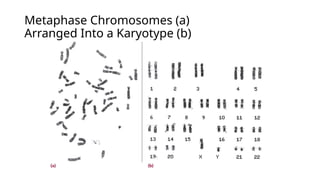
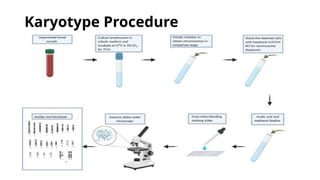
A human karyotype allows identification of chromosomal regions through a systematic naming convention. The procedure involves stimulating mitosis from blood samples, fixing, and staining to analyze chromosomal structure and number for abnormalities. Karyotype analysis has historical significance, such as the discovery of Down syndrome related to an extra chromosome 21.