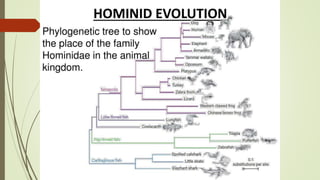
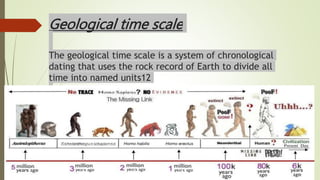
This document provides an overview of human evolution. It discusses how humans are classified within the animal kingdom and fall under the Hominidae family along with apes. The document outlines some of the key events in human evolution, such as humans descending from primitive ape ancestors between 200,000-300,000 years ago and acquiring the ability to speak around 50,000 years ago. It also discusses paleontological evidence that is used to investigate the biological and cultural aspects of early humans, including artifacts, fossilized bones, and the environments in which specimens are found.