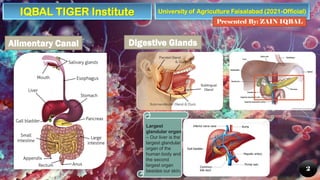
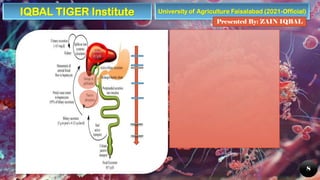
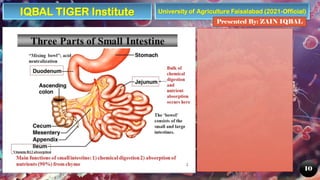
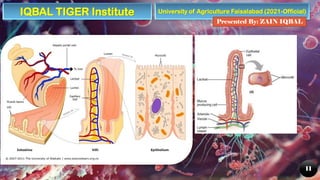
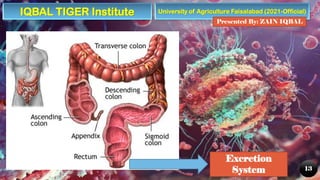
The document provides an overview of the human digestive system, detailing its components, including the alimentary canal and digestive glands, and describing the processes of digestion and nutrient absorption. It explains the roles of different organs like the mouth, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine in breaking down food and extracting nutrients. Additionally, the document highlights the importance of digestive health and offers tips for maintaining it.