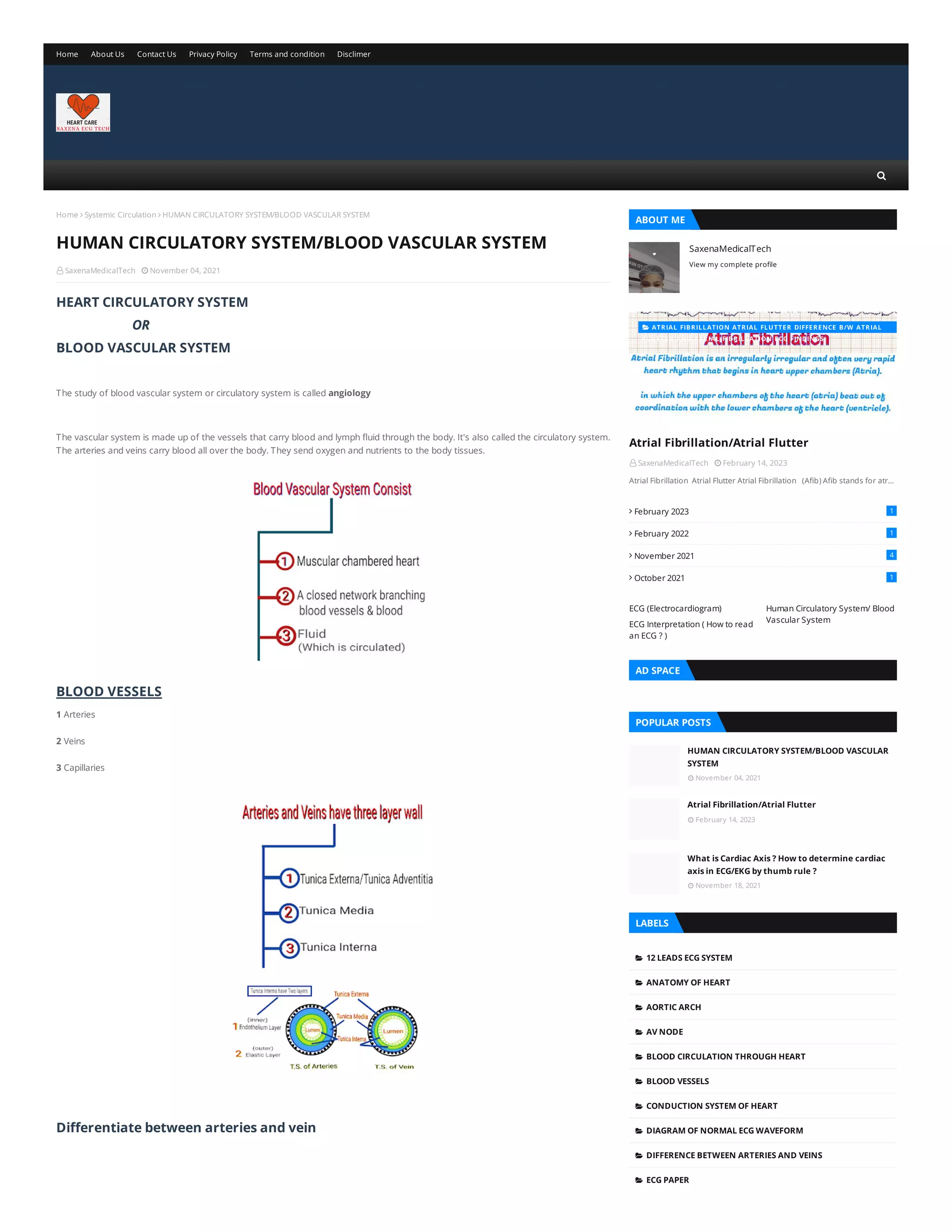
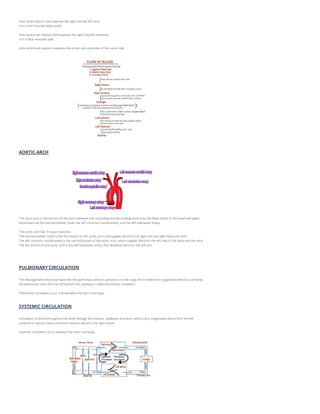
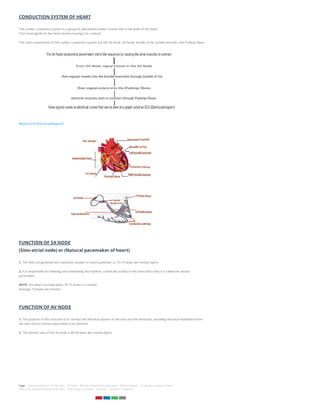
The document discusses the human circulatory system, also known as the blood vascular system, which involves the arteries, veins, and capillaries that transport blood and lymph fluid throughout the body. It details the structure and function of the heart, including its chambers and the conduction system, while also comparing pulmonary and systemic circulation. Additionally, it covers the significance of key components like the sinoatrial node and atrioventricular node in regulating heart rhythm.