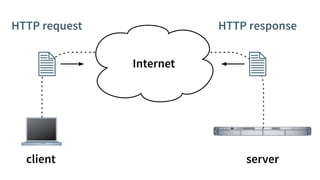
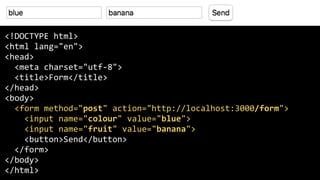
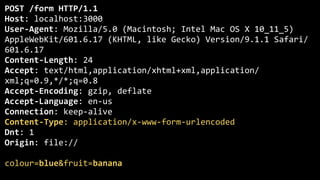
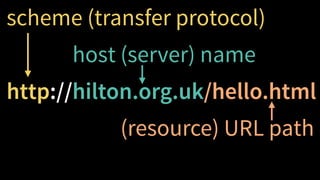
HTTP is a protocol for transmitting hypertext documents across the internet. It was introduced in 1989 along with HTML to allow hypertext documents to be fetched via the internet. HTTP works by having clients make requests to servers using methods like GET and POST, and servers respond with status codes and headers along with content in the response body. Key aspects of HTTP include URLs, requests, responses, status codes, headers, and common mistakes around character encodings, caching, and cookies.








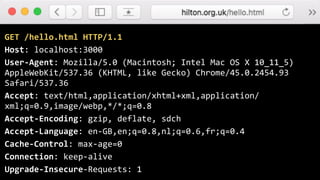
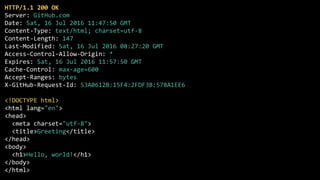
![$ telnet hilton.org.uk 80
Trying 192.30.252.153...
Connected to hilton.org.uk.
Escape character is '^]'.
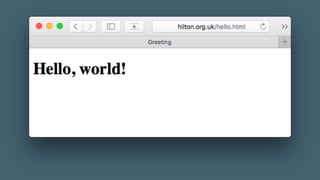
GET /hello.html HTTP/1.1
Host: hilton.org.uk
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: GitHub.com
Date: Sat, 16 Jul 2016 09:20:27 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 147
Last-Modified: Sat, 16 Jul 2016 08:27:20 GMT
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpdemystified-160717092352/85/HTTP-demystified-for-web-developers-12-320.jpg)