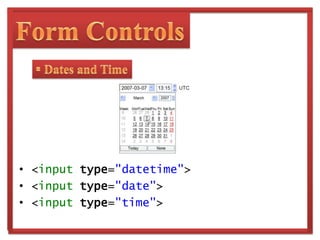
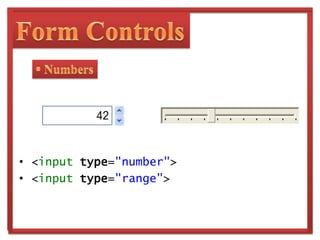
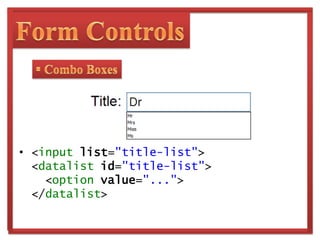
The document discusses HTML5, the next major revision of HTML, and its development by the WHATWG and W3C. It highlights key features such as semantic elements, new form controls, and multimedia support, which aim to improve web application design and functionality. Additionally, it notes the evolutionary timeline for HTML5's acceptance and browser support.