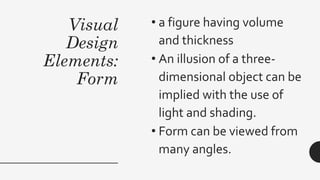
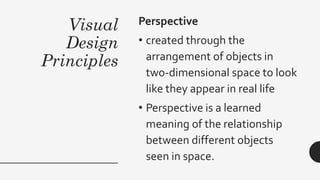
This document discusses visual information and media. It defines visual media as materials that aid learning through visual images. The types of visual media include photography, videography, infographics, and more. Visual media can be formally or informally produced. The primary purpose of visual information is to gain attention, create meaning, and facilitate retention. The document then outlines and describes various visual design elements like line, shape, value, texture, color, and form. It concludes by explaining principles of visual design such as consistency, center of interest, balance, harmony, contrast, directional movement, rhythm, and perspective.