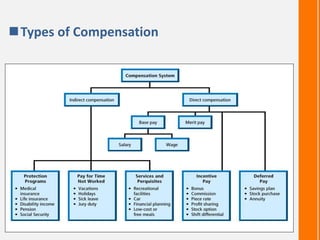
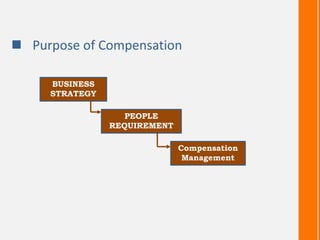
This document discusses compensation structure and comparison. It defines compensation as monetary and non-monetary benefits provided to employees in exchange for work. Compensation objectives include increasing morale, recruiting/retaining employees, and rewarding performance. Compensation is important for attracting/retaining talent and motivating better performance. Types of compensation include direct compensation like salary and benefits, and indirect compensation like paid leave. Factors affecting compensation include job requirements, responsibility level, market rates, and organizational affordability.