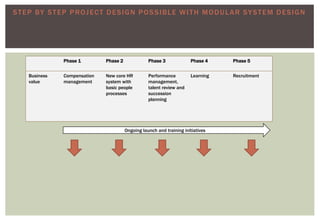
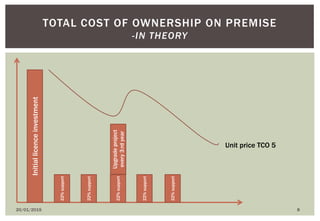
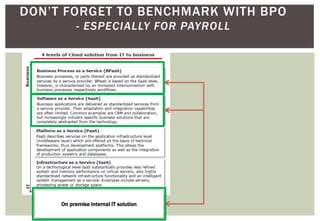
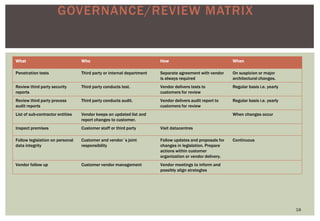
The document discusses the business case and lessons learned for moving an organization's HR systems to a consolidated SaaS/cloud solution. It notes that many companies have a mix of legacy on-premise systems and various standalone modules that need to be consolidated. Adopting a consolidated SaaS model can help achieve unified global HR processes, lower IT costs, and allow the HR department to focus on strategic initiatives rather than system maintenance. The document outlines considerations for the implementation process and governance of cloud solutions to ensure security, data privacy, and regulatory compliance.