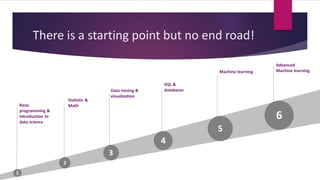
1) The document provides guidance on how to start a journey as a data scientist. It outlines basic steps to take including learning basic programming, statistics, data mining and visualization, SQL, and machine learning.
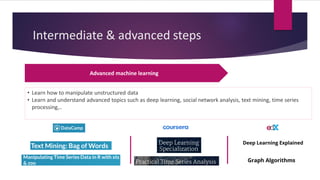
2) The document emphasizes that learning in data science is non-linear and involves gaining skills in multiple areas over time. It recommends starting with online courses and practicing on datasets.
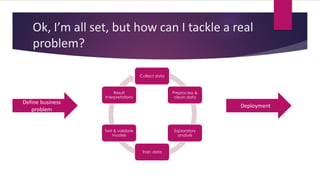
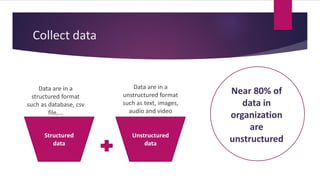
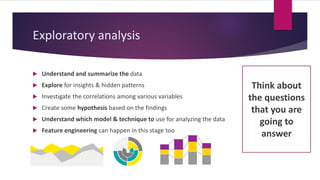
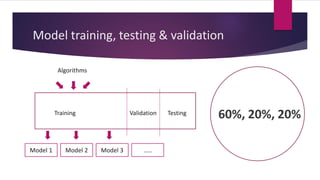
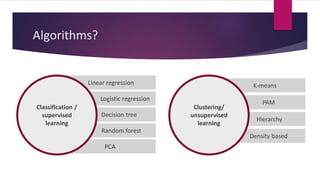
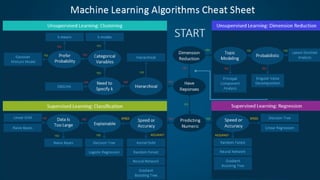
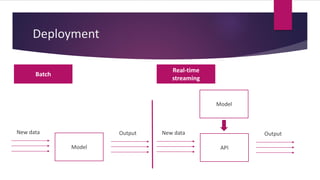
3) Applying what you learn to real problems is important. The document outlines a process for tackling a real business problem including defining the problem, collecting and preprocessing data, exploratory analysis, model training and validation, and deployment.