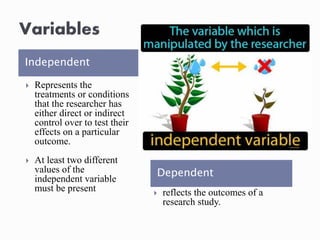
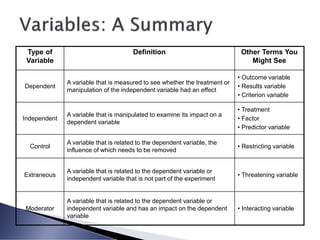
The document discusses the definition and categorization of variables in research, including independent, dependent, control, extraneous, and moderator variables. It explains the significance of hypotheses, distinguishing between null and research hypotheses, and the implications of their relationships within a study. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of precise measurement for better utility of variables and the impact of various factors on research outcomes.