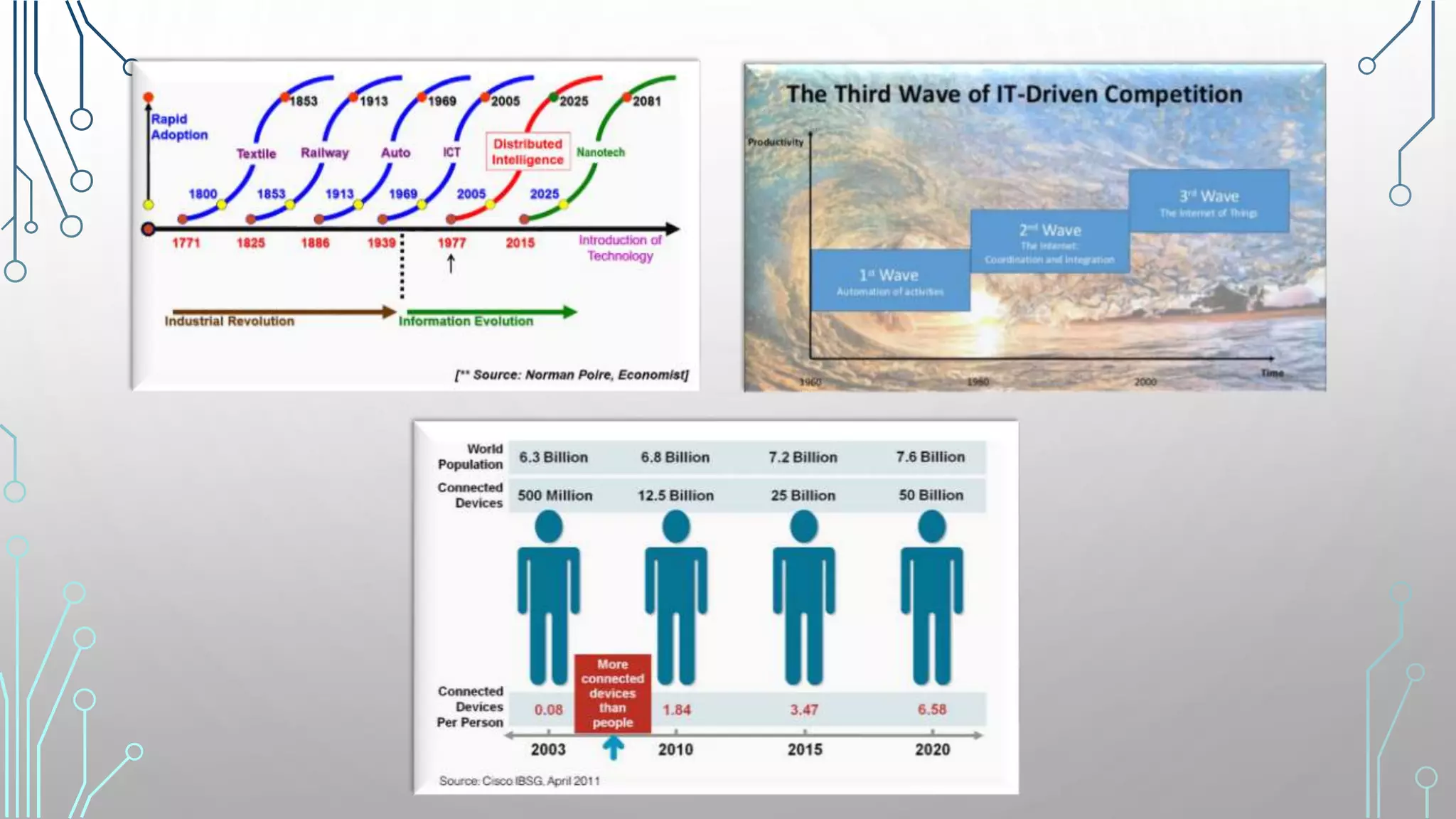
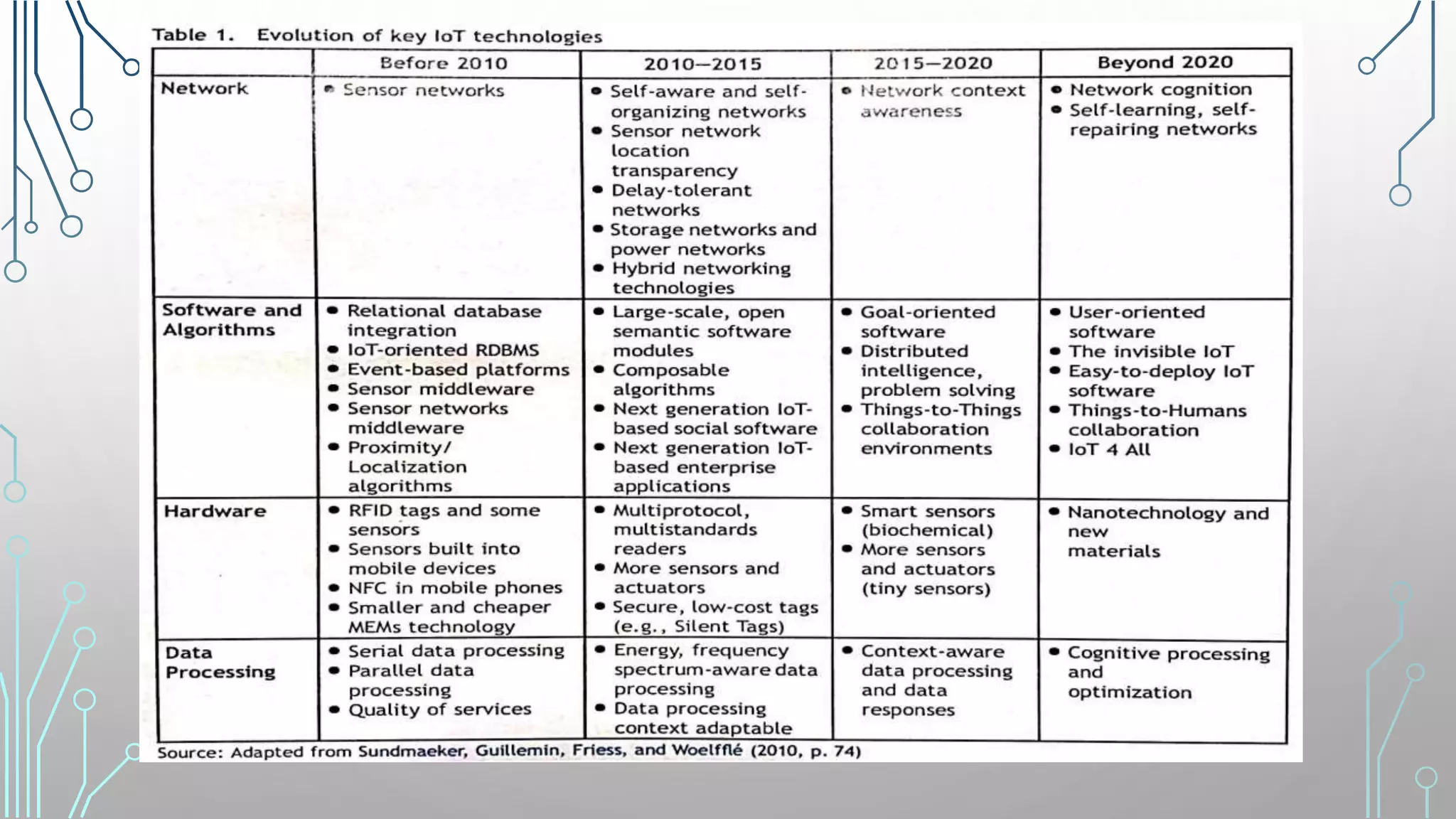
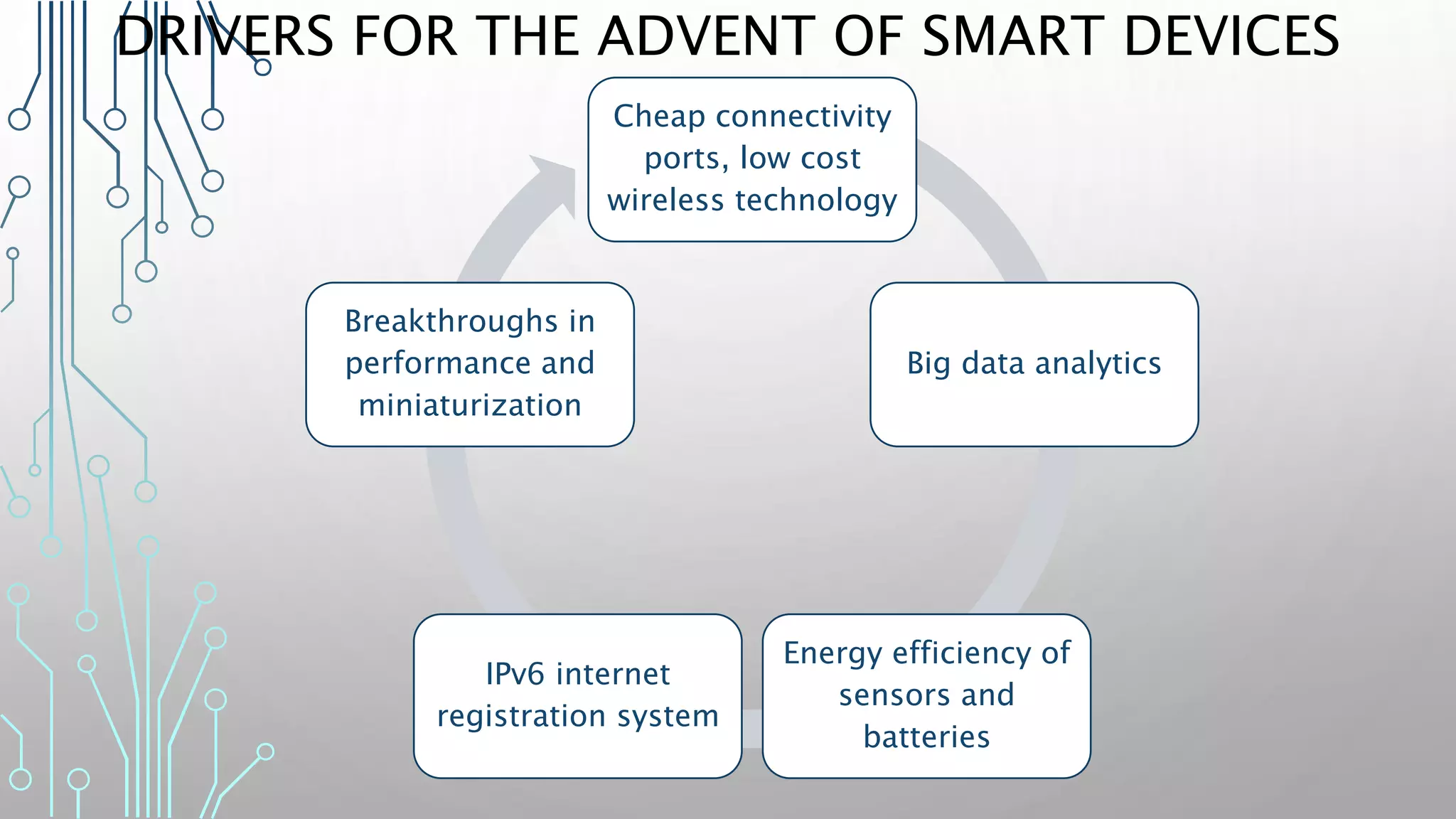
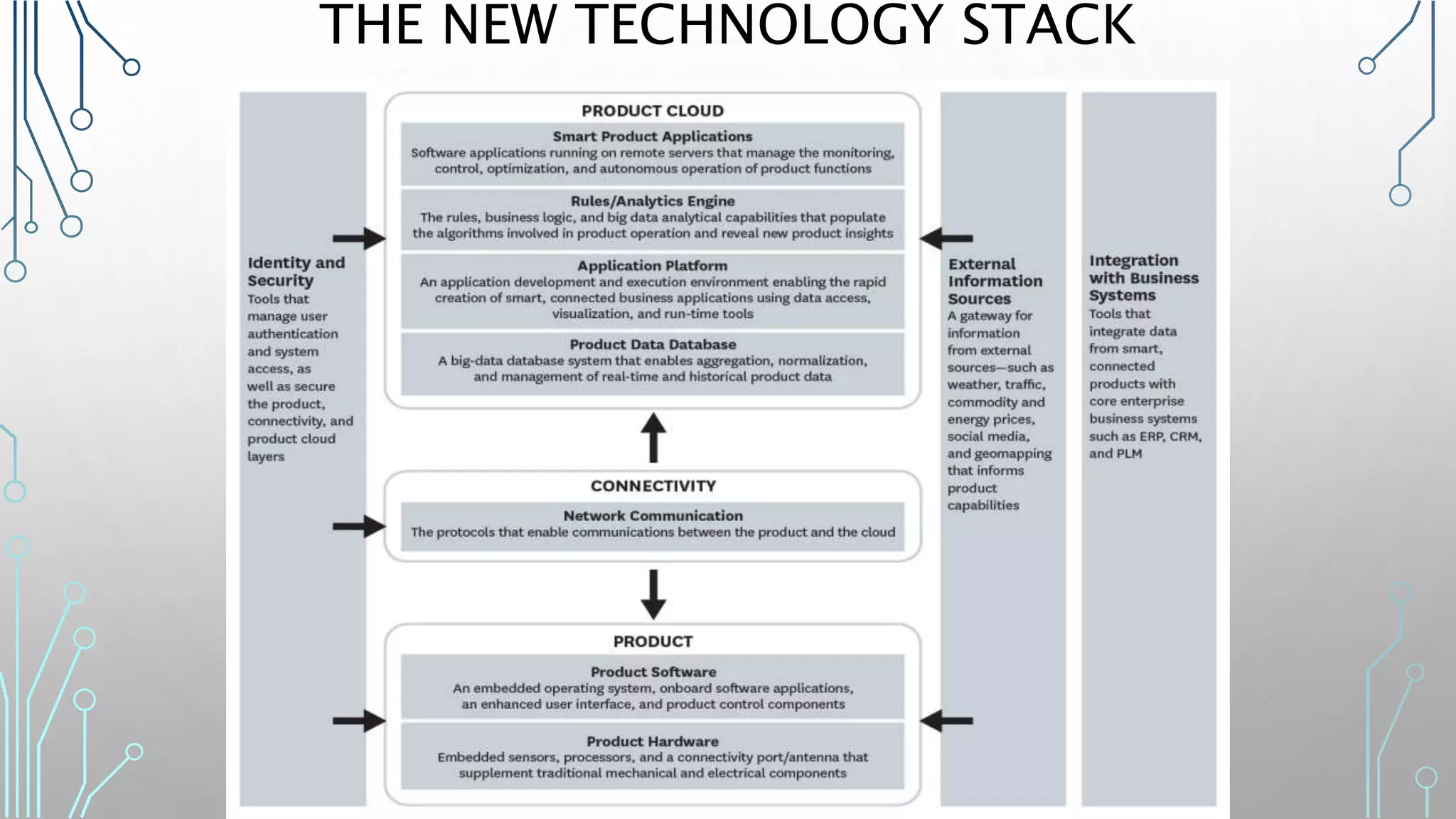
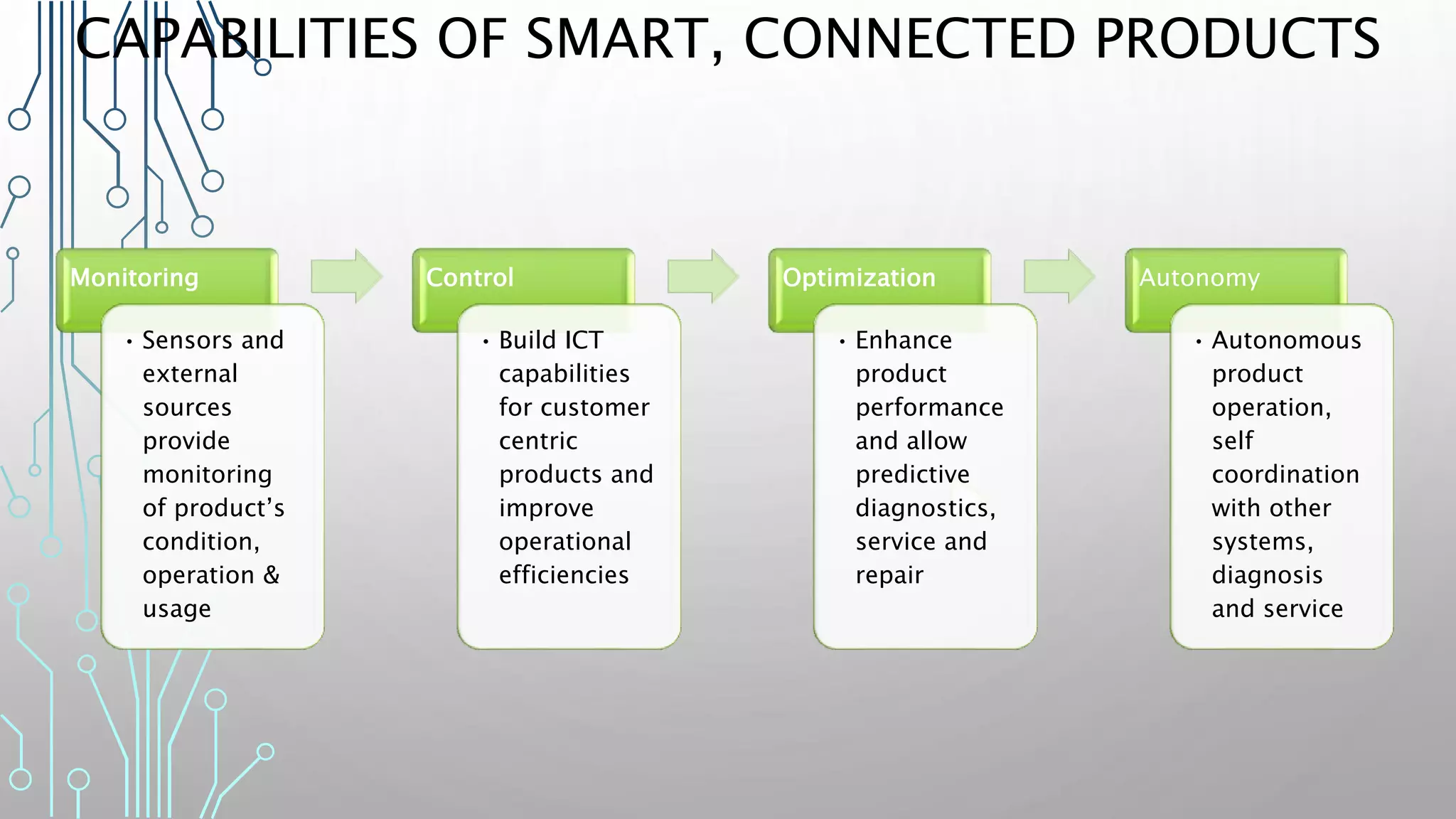
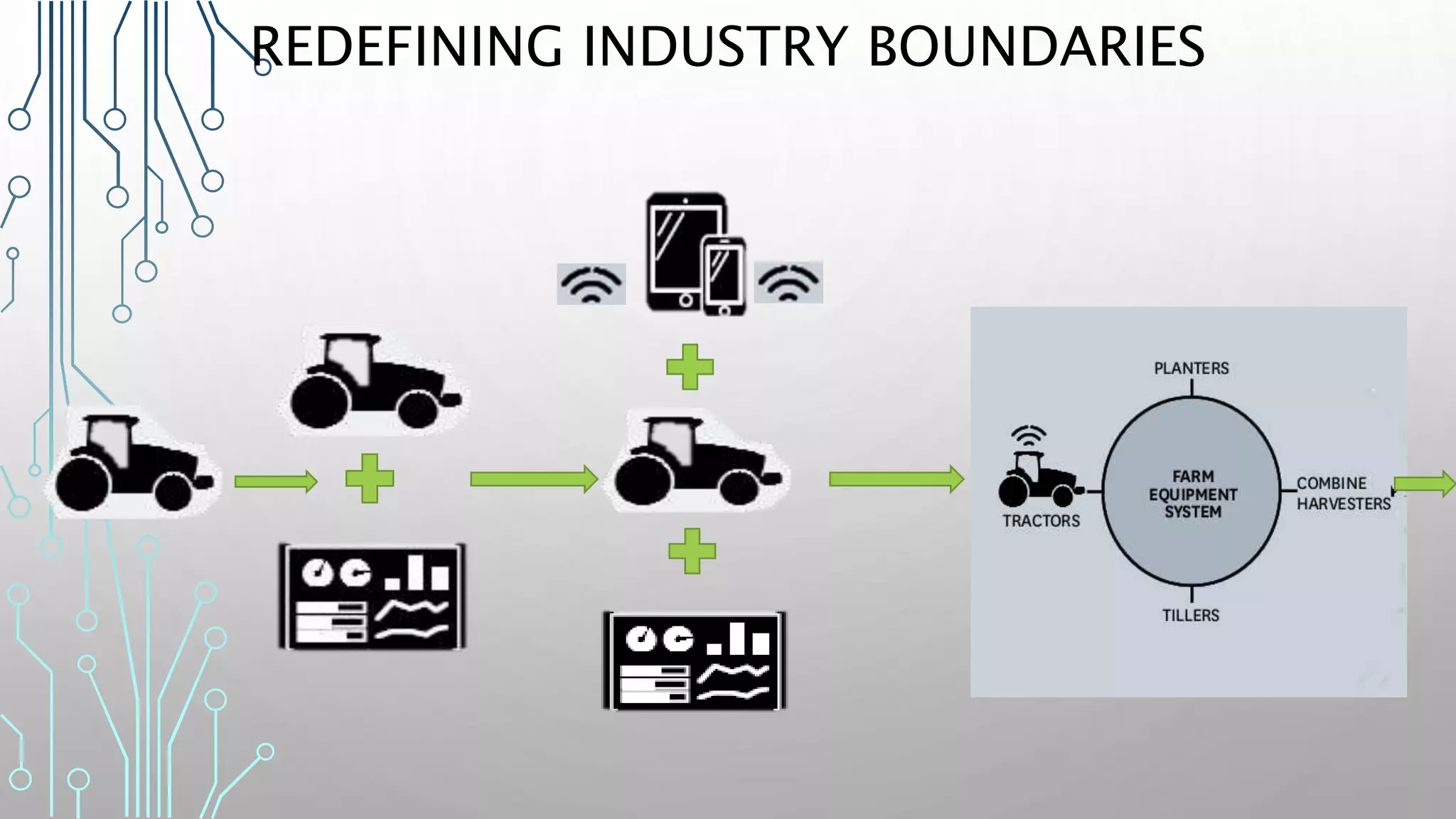
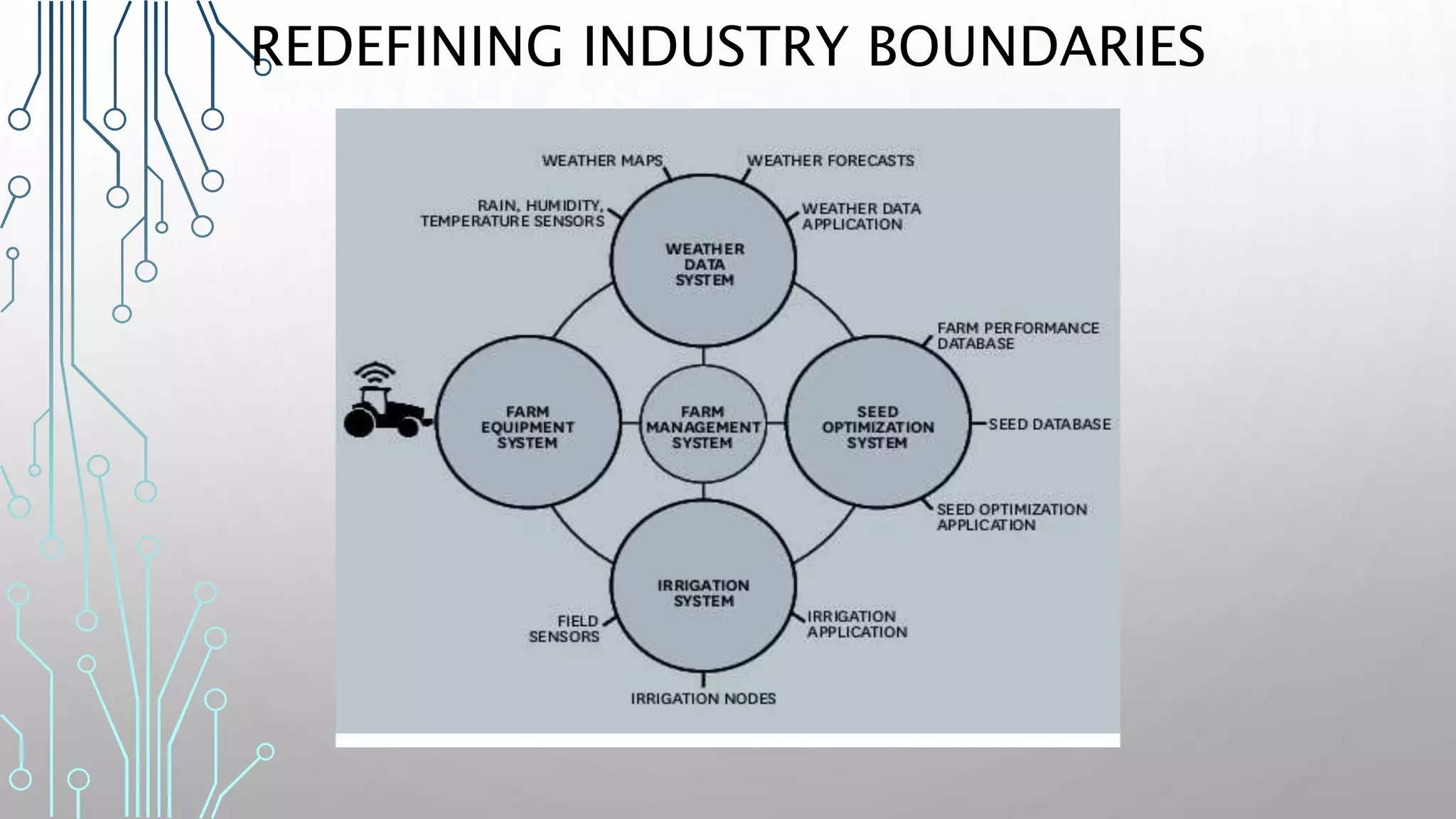
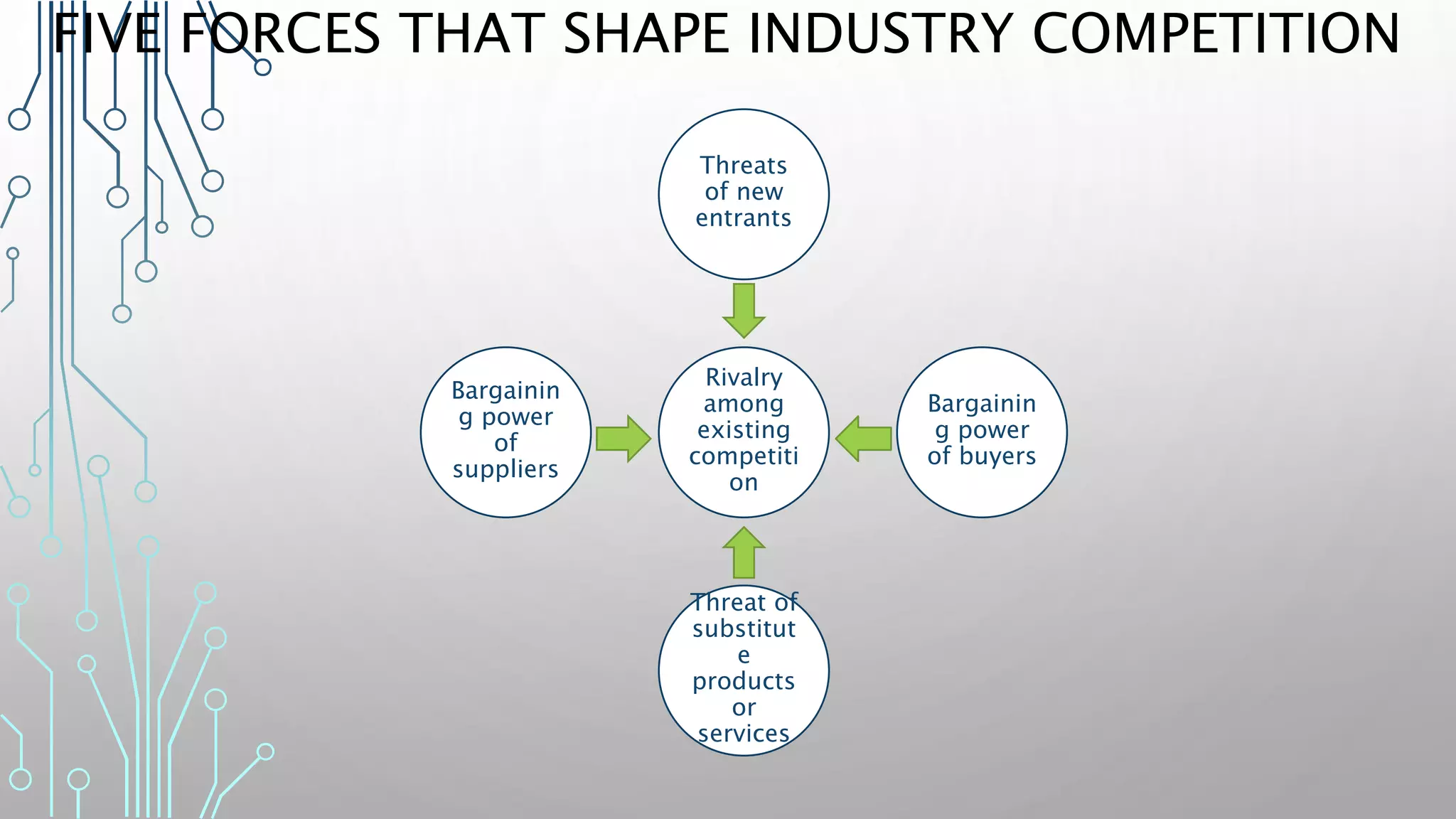
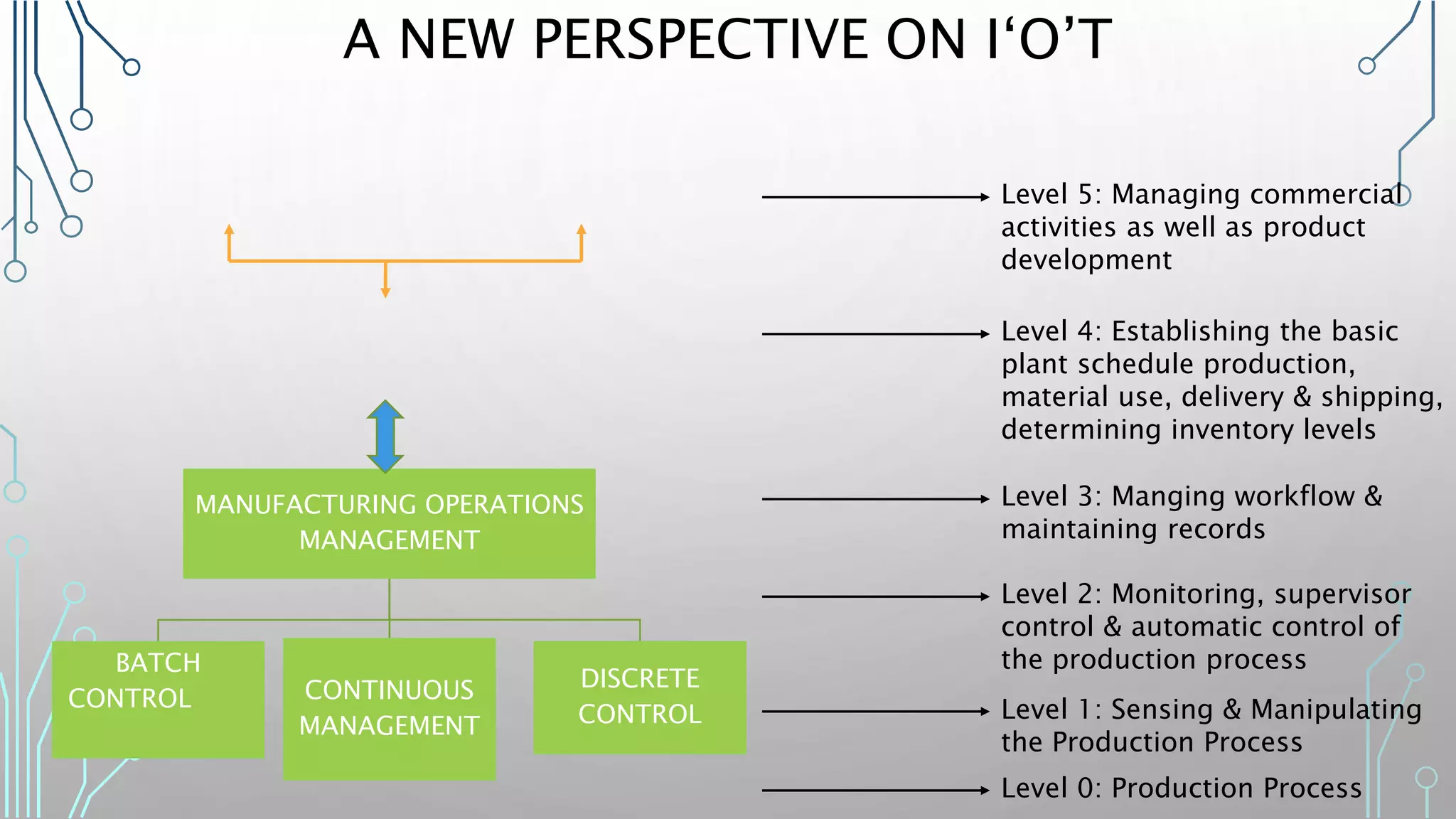
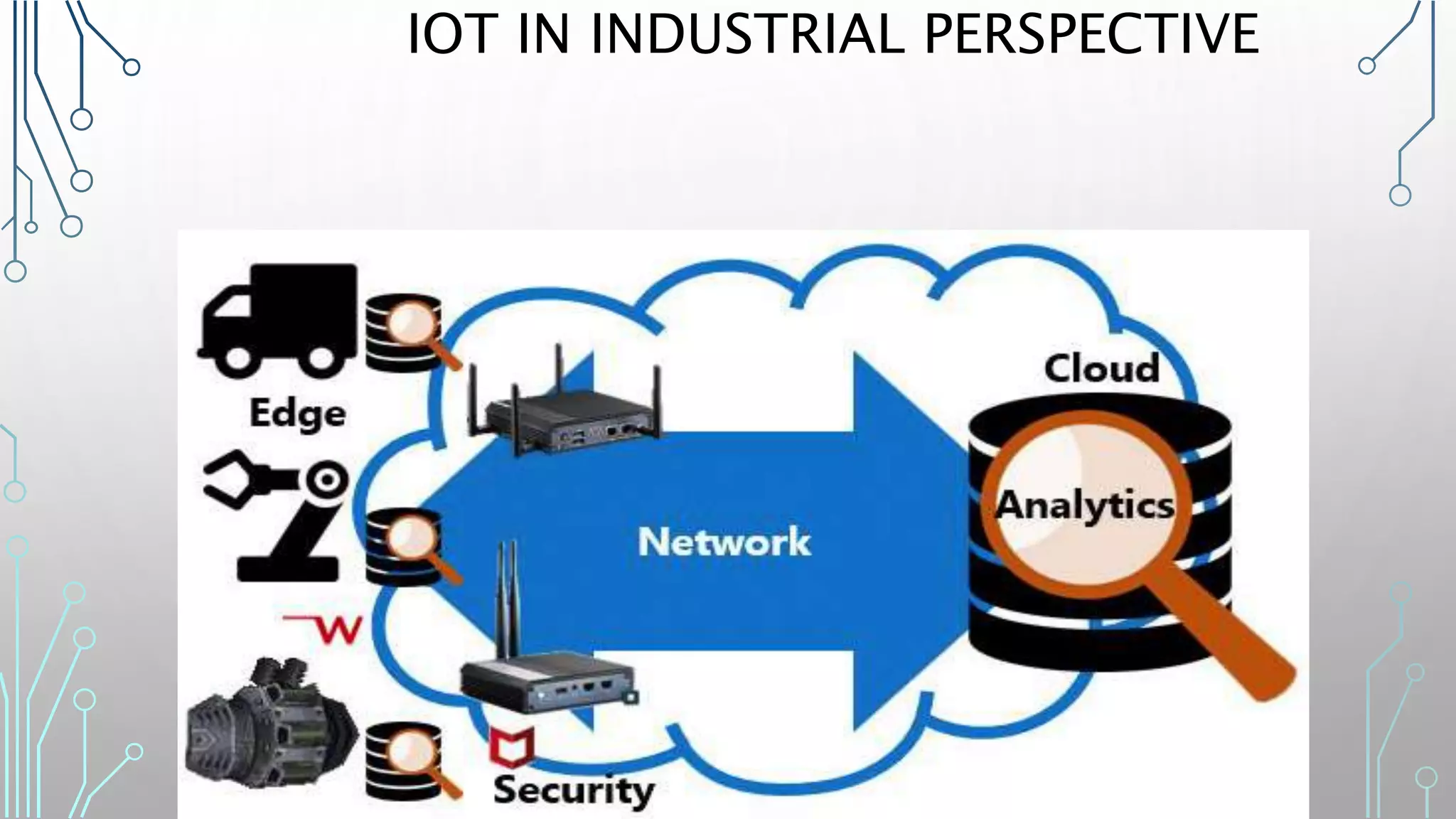
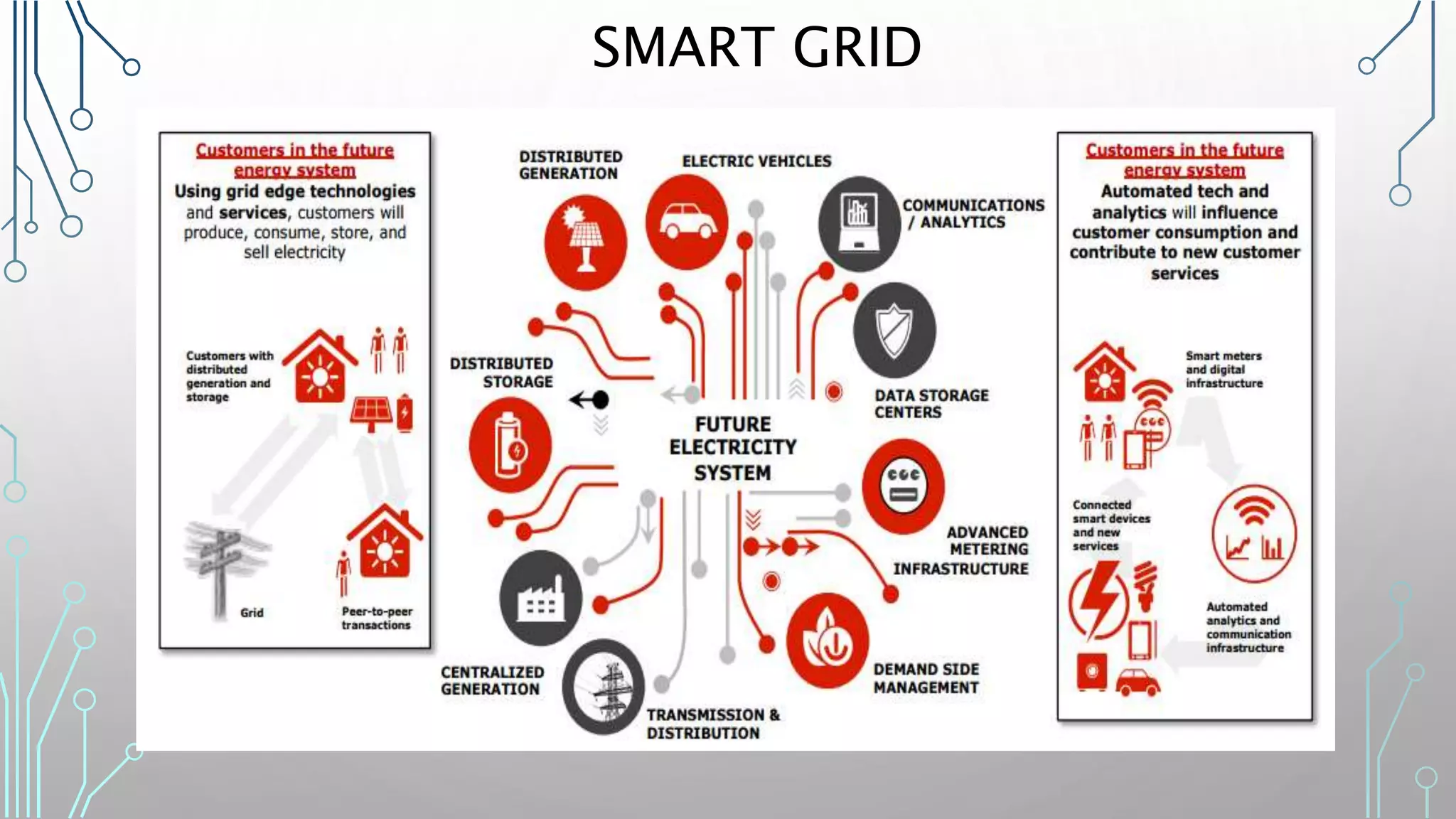
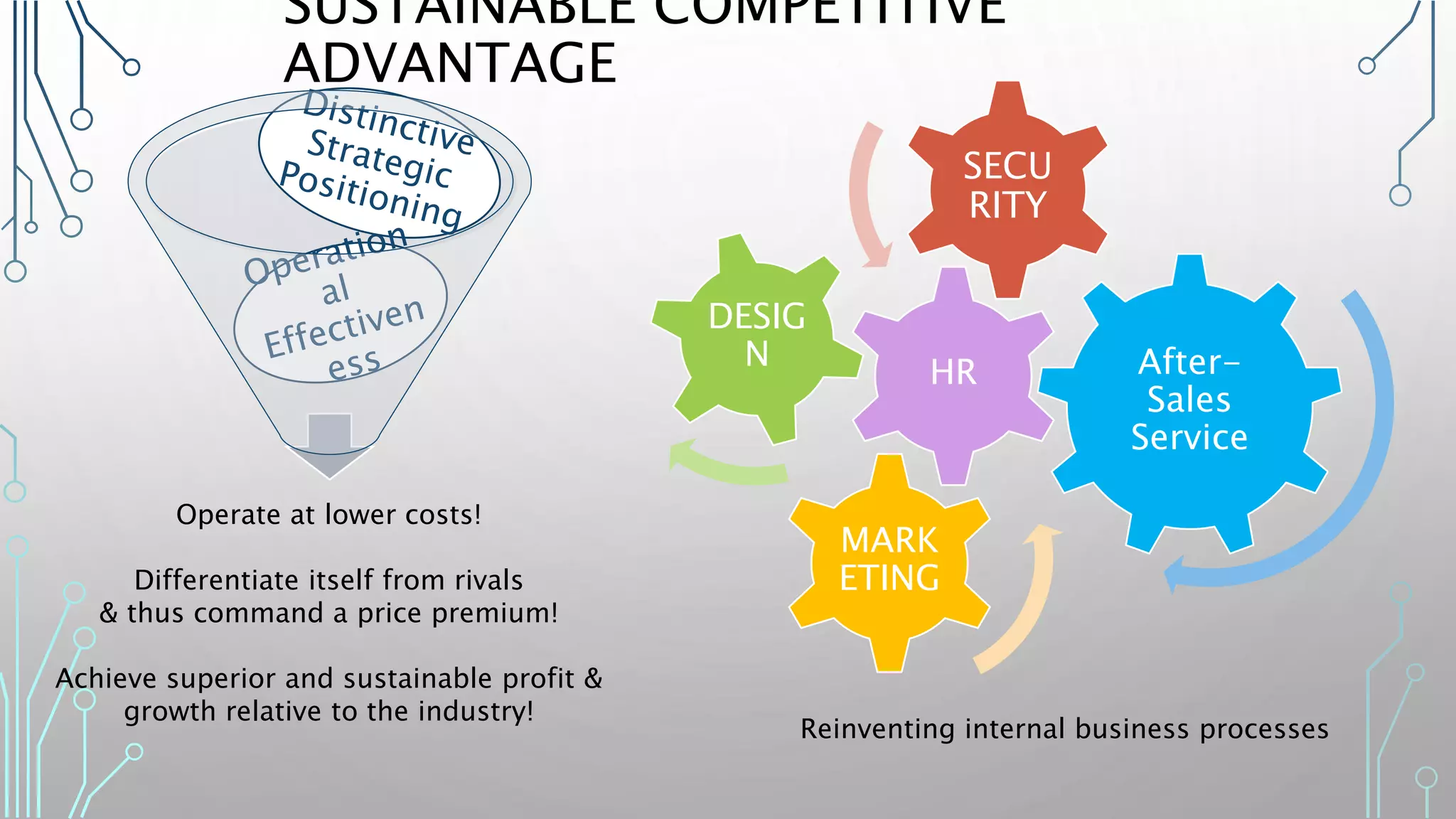
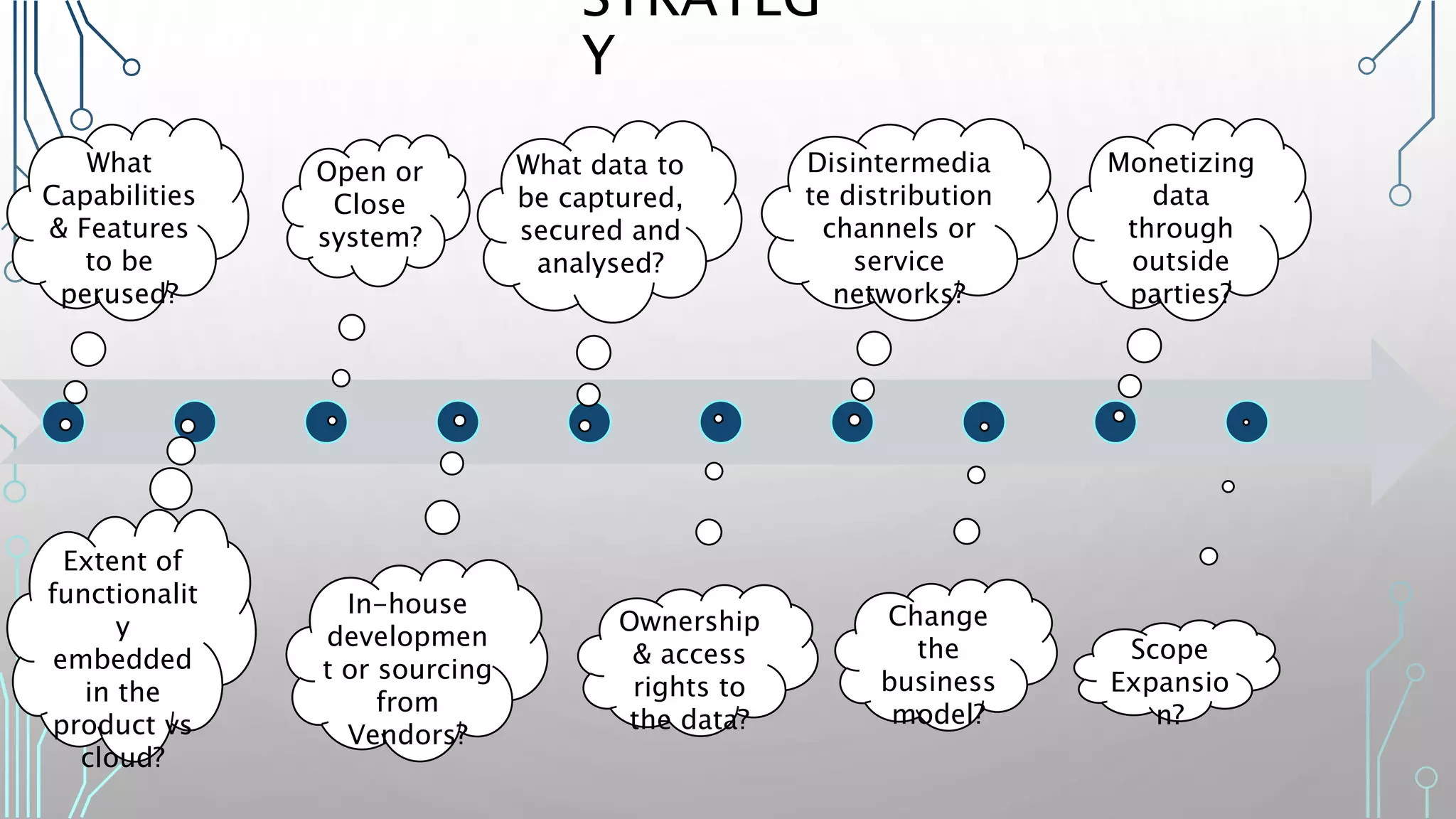
The document discusses how smart, connected products are reshaping competition, driven by advancements in Internet of Things (IoT) technology, including improved monitoring, control, and optimization capabilities. Challenges and strategic considerations for implementation in various industries, particularly energy and utilities, are highlighted alongside the need for organizational and technological harmonization. The potential of IoT to transform business models and create sustainable competitive advantages is emphasized, with references to significant industry examples.