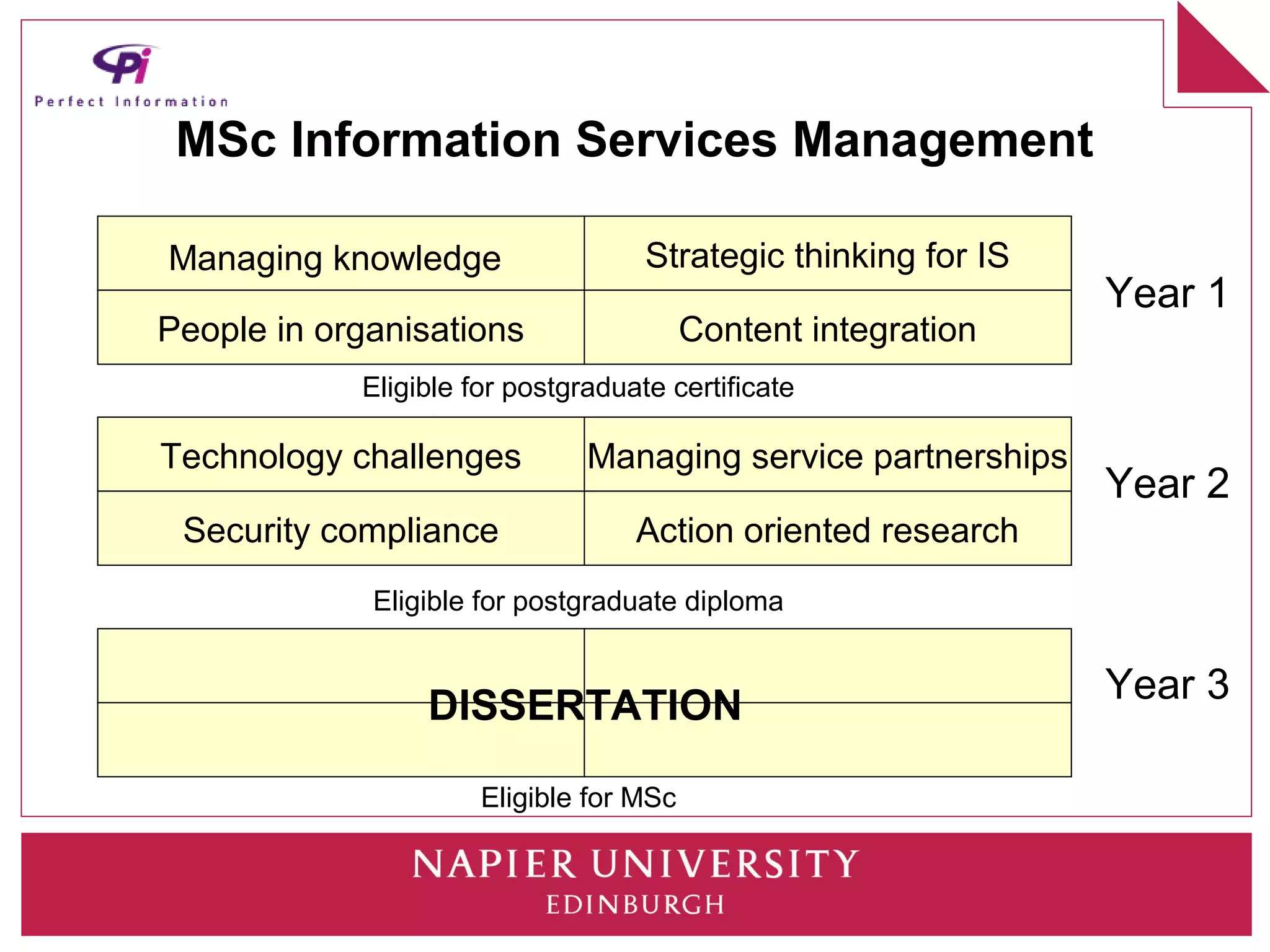
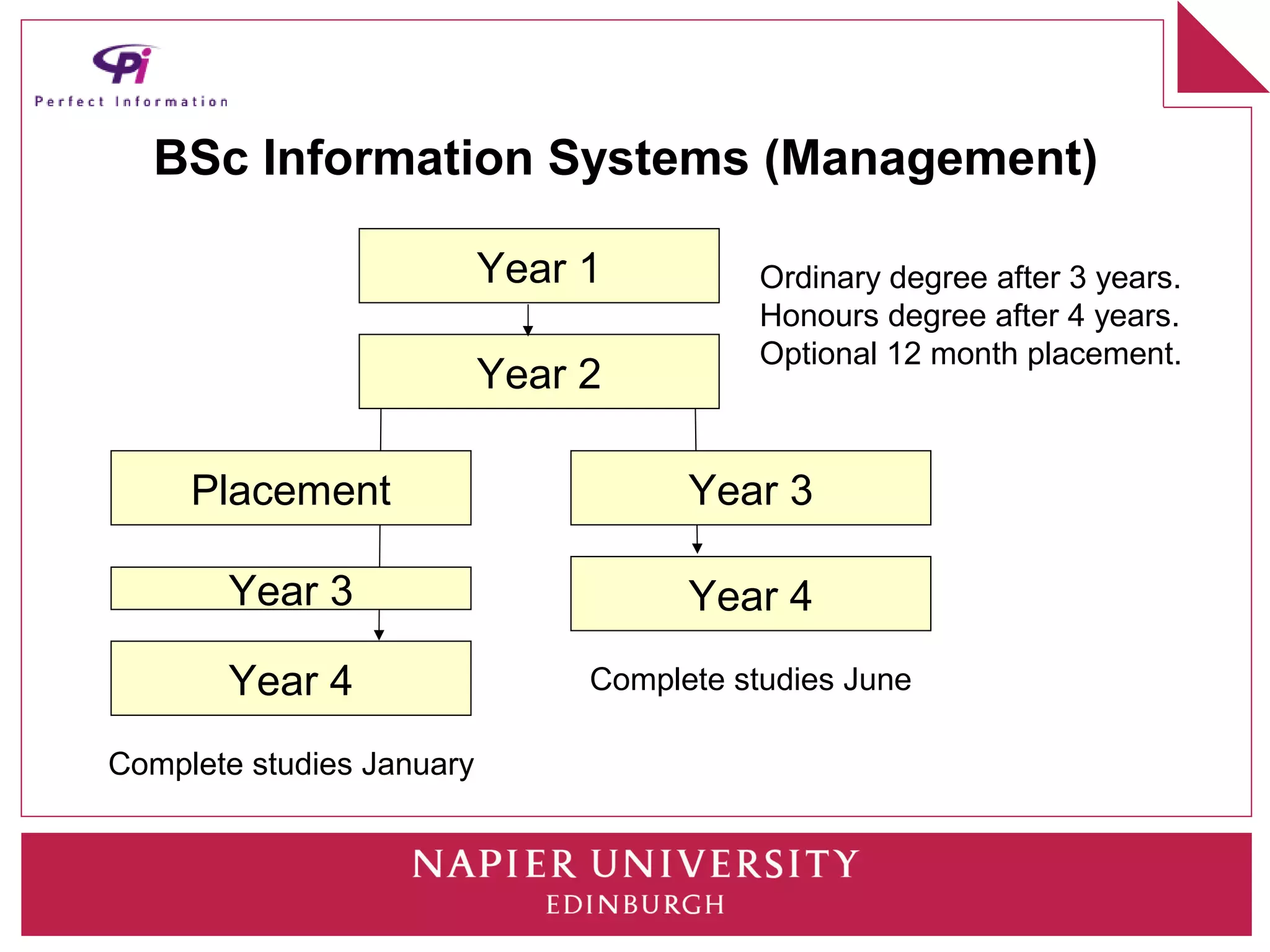
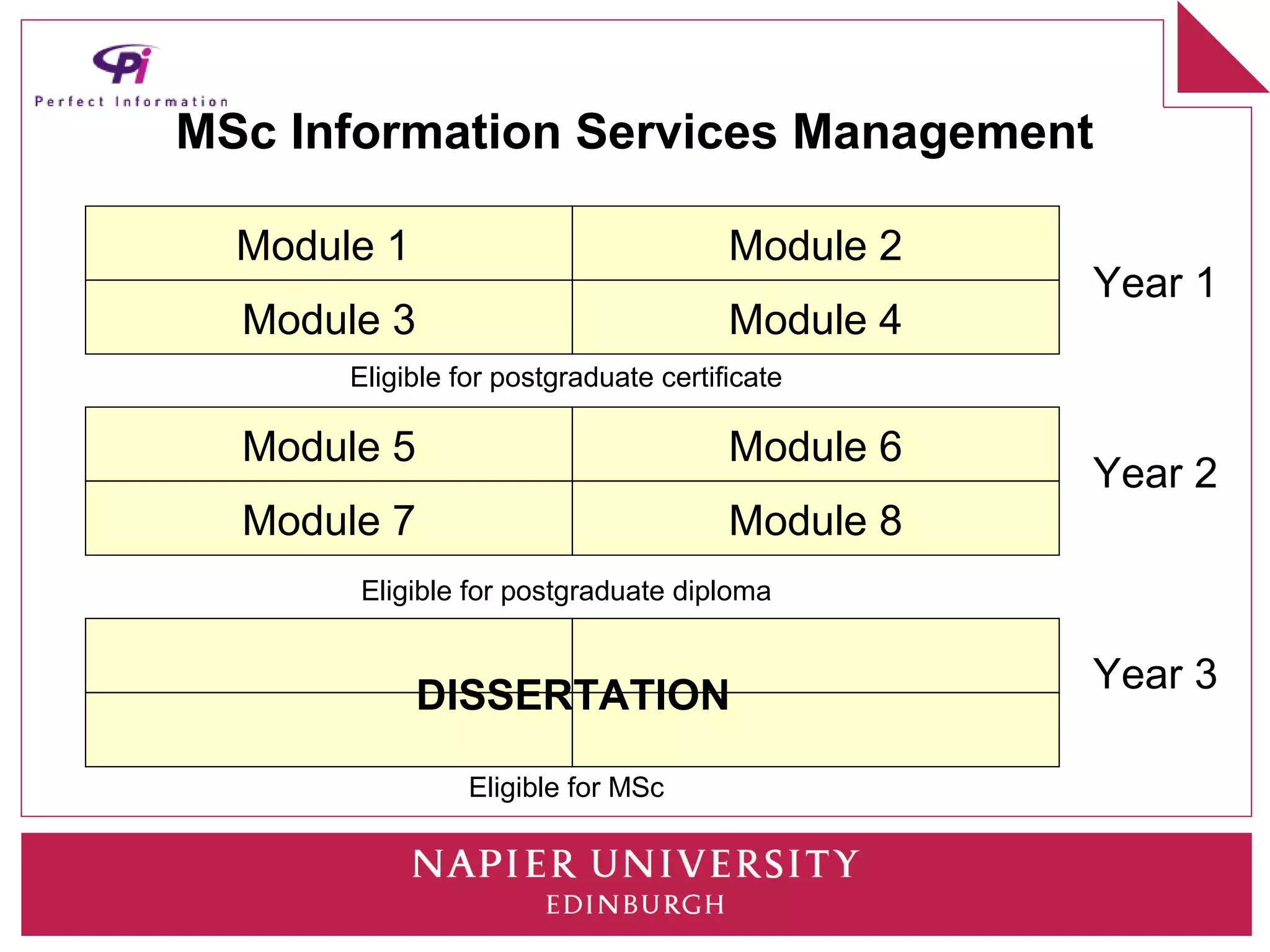
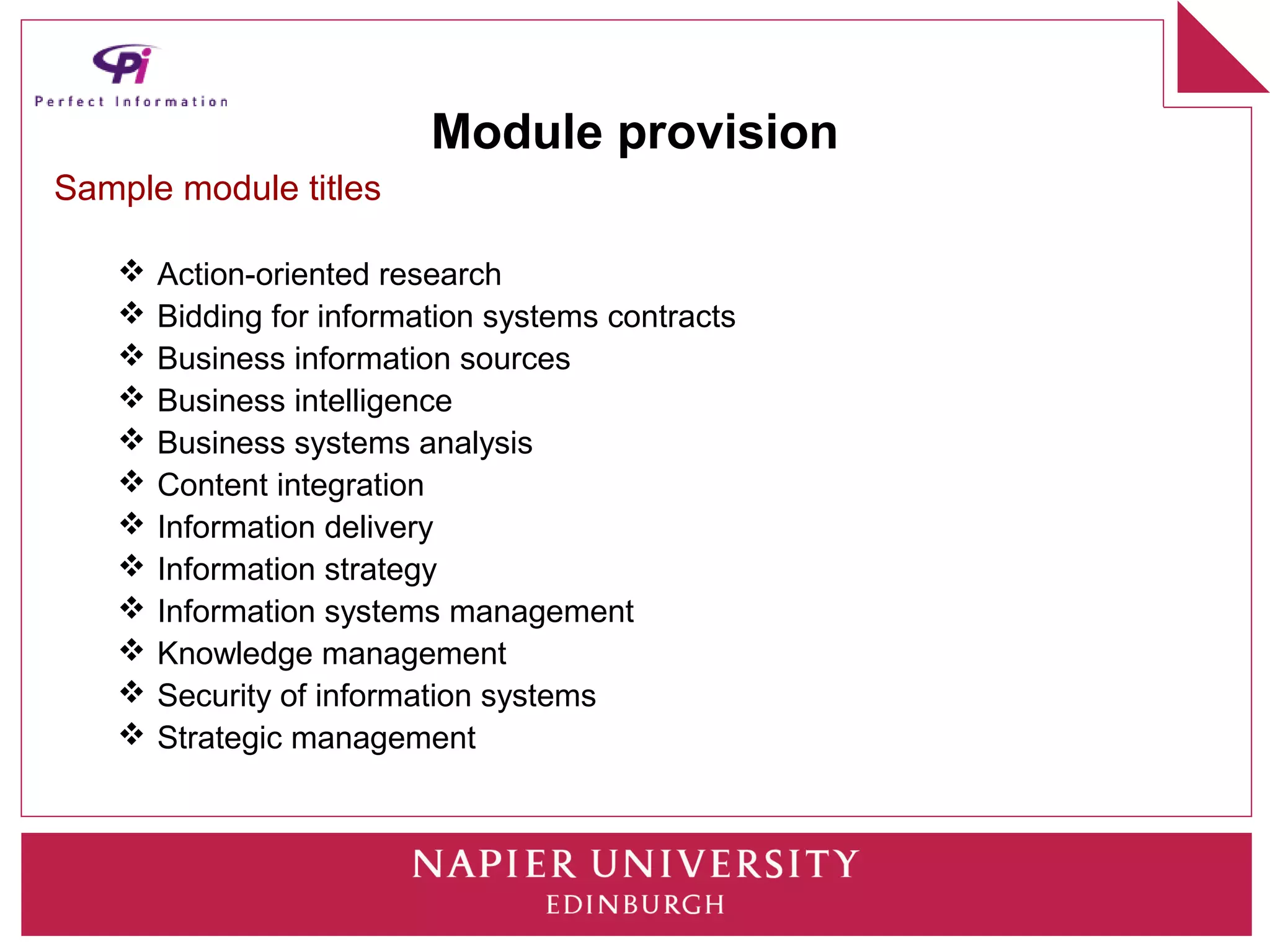
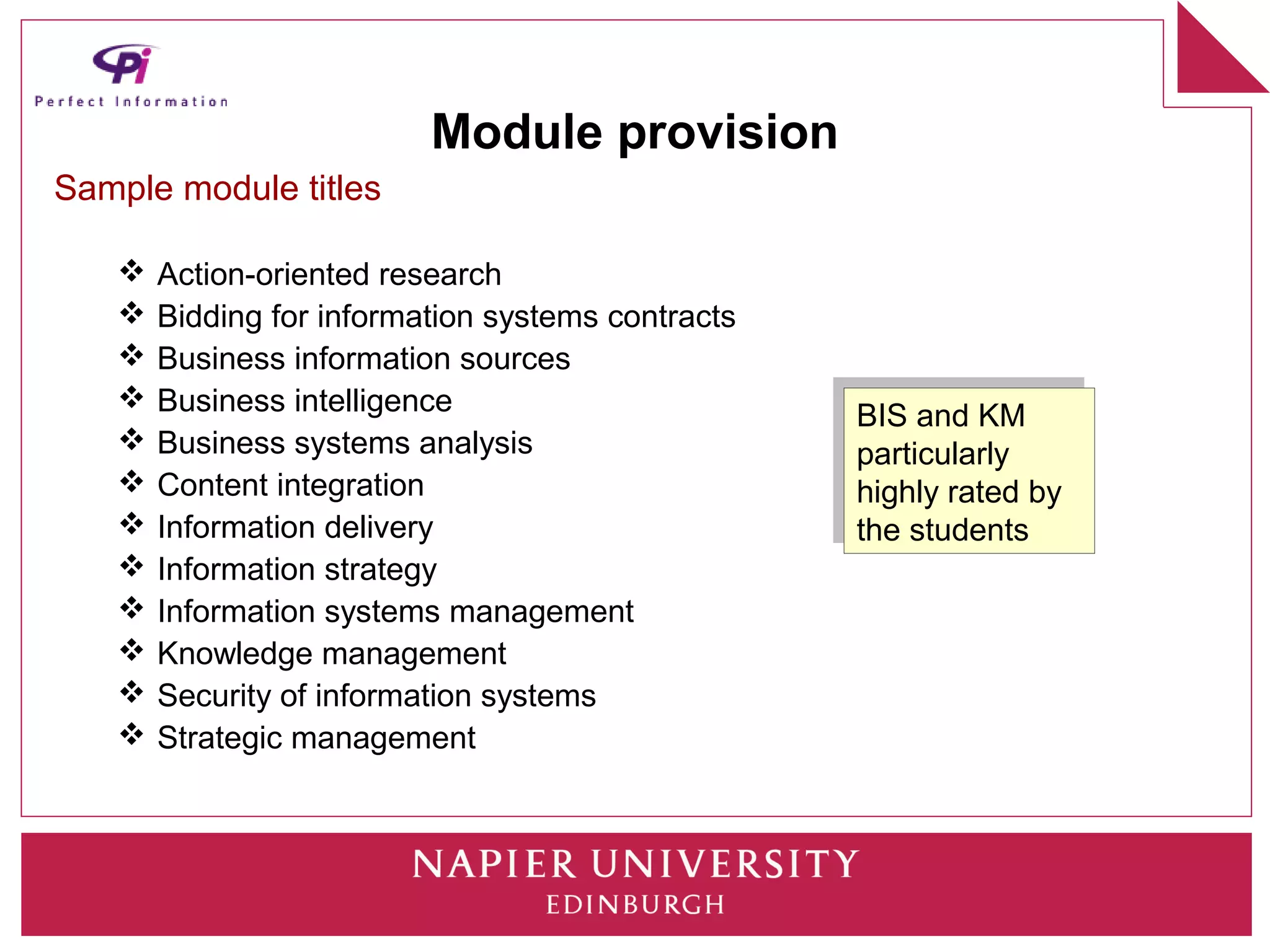
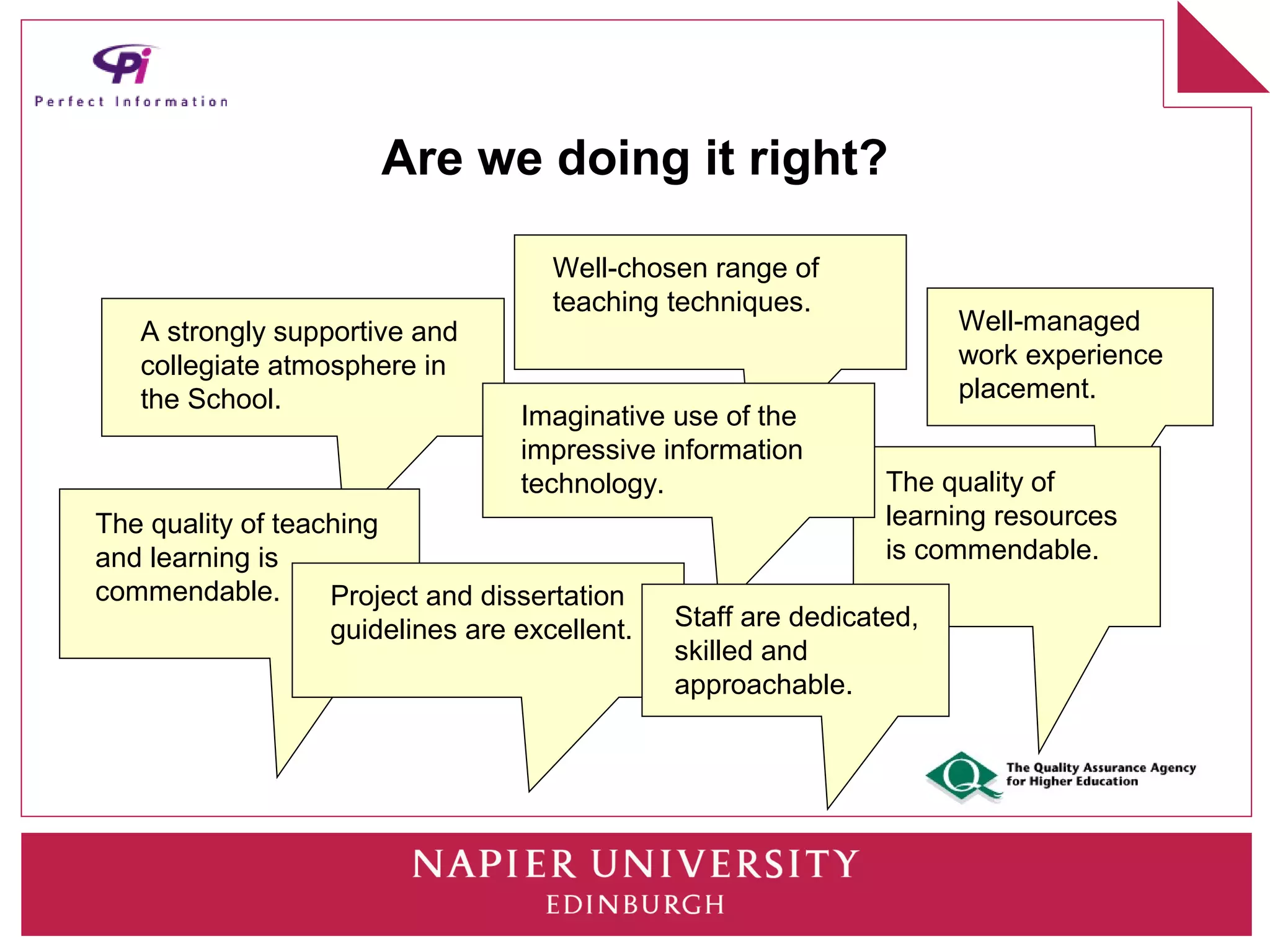
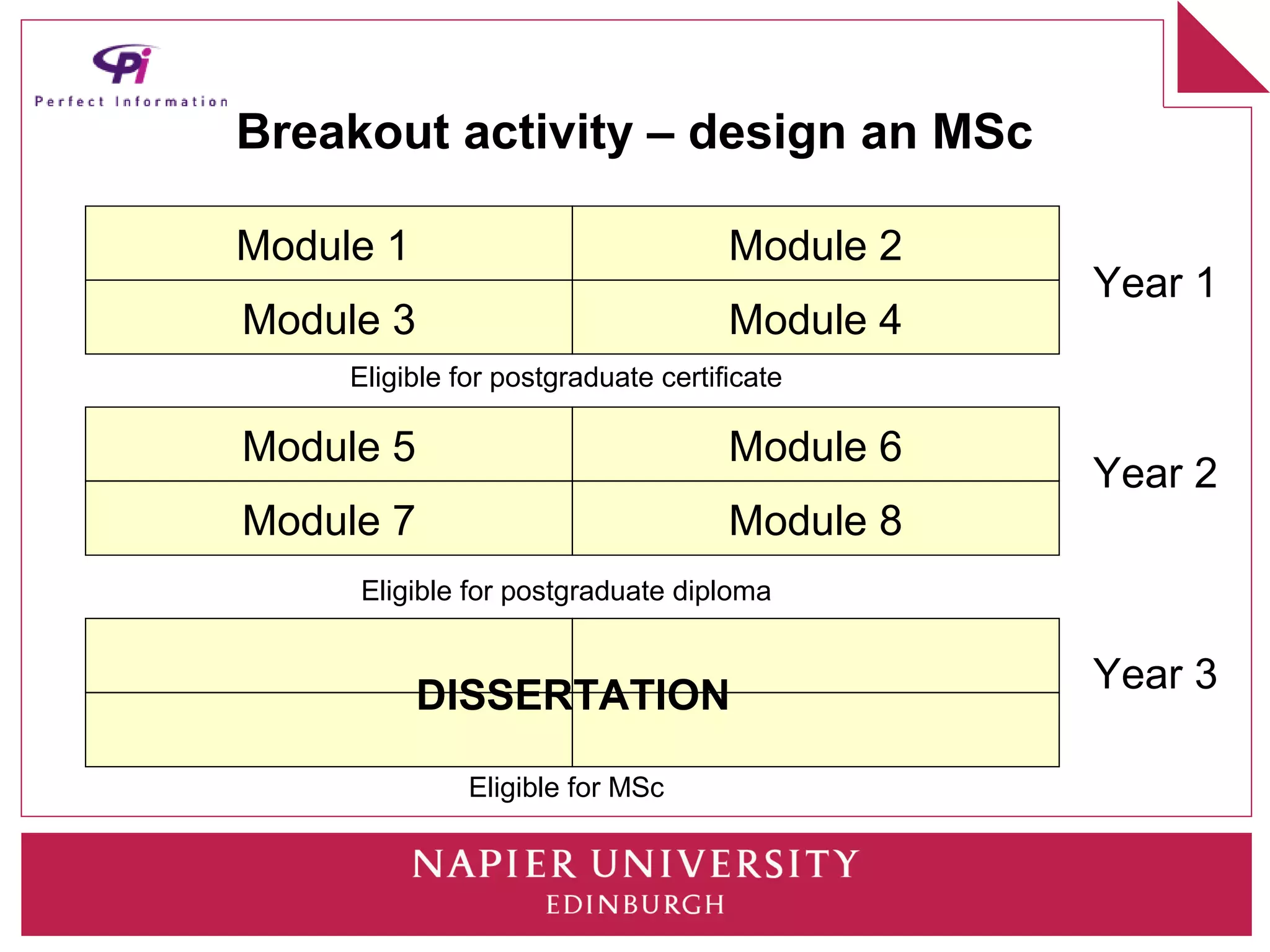
This document discusses how universities can better prepare information graduates for careers. It outlines the current state of library and information science programs in the UK, including the types of courses offered and their focuses. It also describes the curriculum structure of sample undergraduate and postgraduate programs at Napier University. The document notes challenges in attracting students and meeting employer needs. It proposes ways for industry professionals to contribute their expertise to university programs through advisory boards, module content, placements, and dissertation topics. The breakout session is intended to have participants collaboratively design a sample Masters program.












![Discussion points
For each module
Decide a title
List learning outcomes (4 maximum). Use the wording:
On completion of this module the student will be able to…[explain
the general principles of X/critically assess/evaluate…]
Describe the module content (6 sentences maximum)
Suggest how the module might be assessed, giving both the
assignment format and “question”:
For example, a 3000 word report on X
For the dissertation module
Suggest some dissertation topics
And if time allows…
Devise a marketing plan for your new degree](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2007hallgradsworkingworldpibath-130108112833-phpapp02/75/How-should-universities-prepare-information-graduates-for-the-working-world-21-2048.jpg)