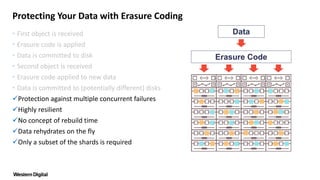
Erasure coding protects data by segmenting it into shards that are parity encoded and distributed across various storage locations, ensuring resilience against multiple failures. It allows for data access without rebuild time even during hardware failures and provides protection at a lower cost than traditional mirroring. This method emphasizes data protection over hardware concerns, needing only a subset of shards to restore the original data.