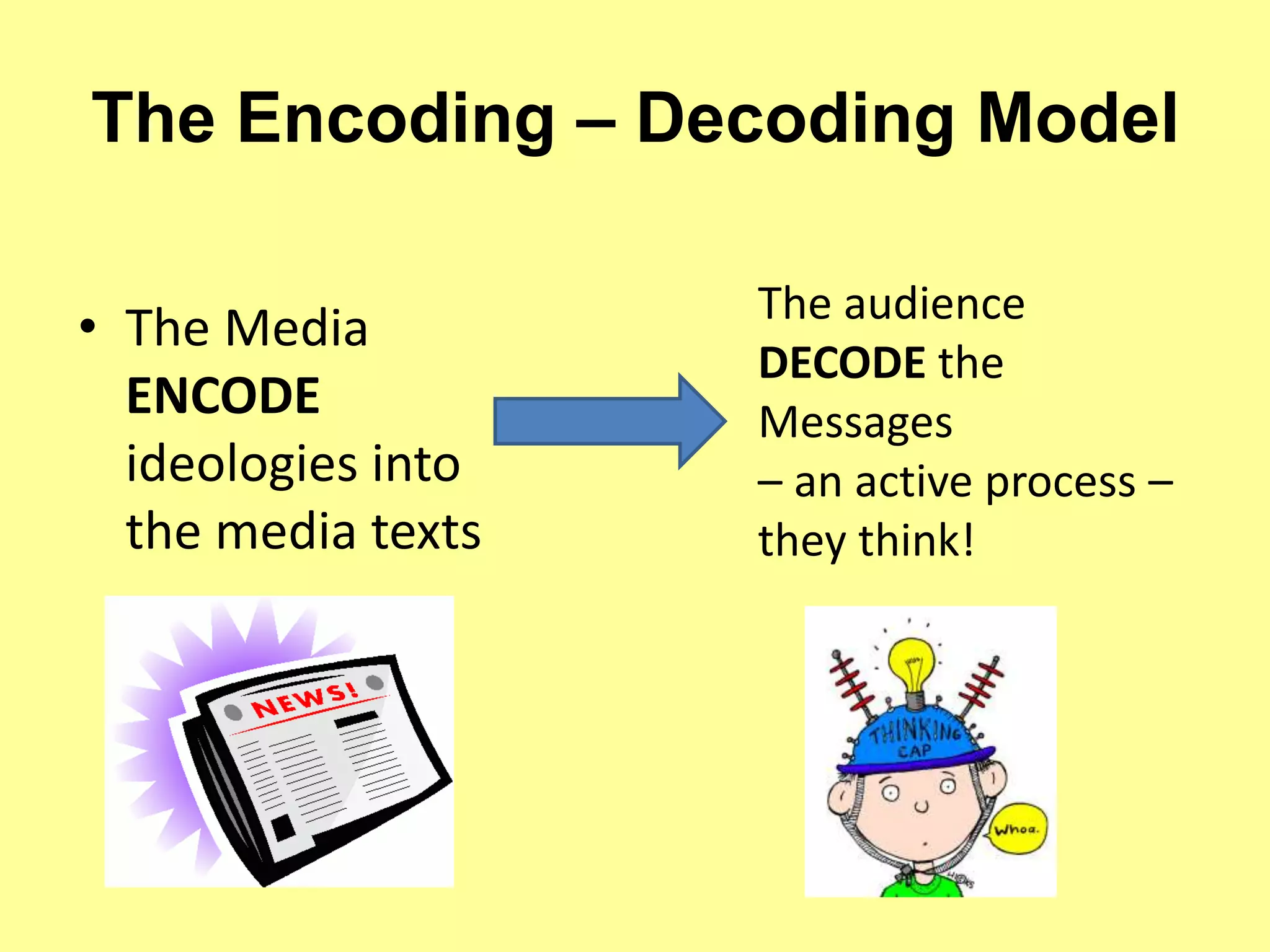
This document discusses theories about how audiences engage with media texts. It describes the passive audience theory, which views audiences as believing everything they are told. It notes criticisms of this theory and the development of active audience theories. The encoding/decoding model is discussed, which sees audiences actively interpreting messages depending on their identity and views. Reception theory focuses on different readings audiences can have. Other theories covered include uses and gratifications, two-step flow, and the pick and mix approach viewing audiences as actively selecting media.