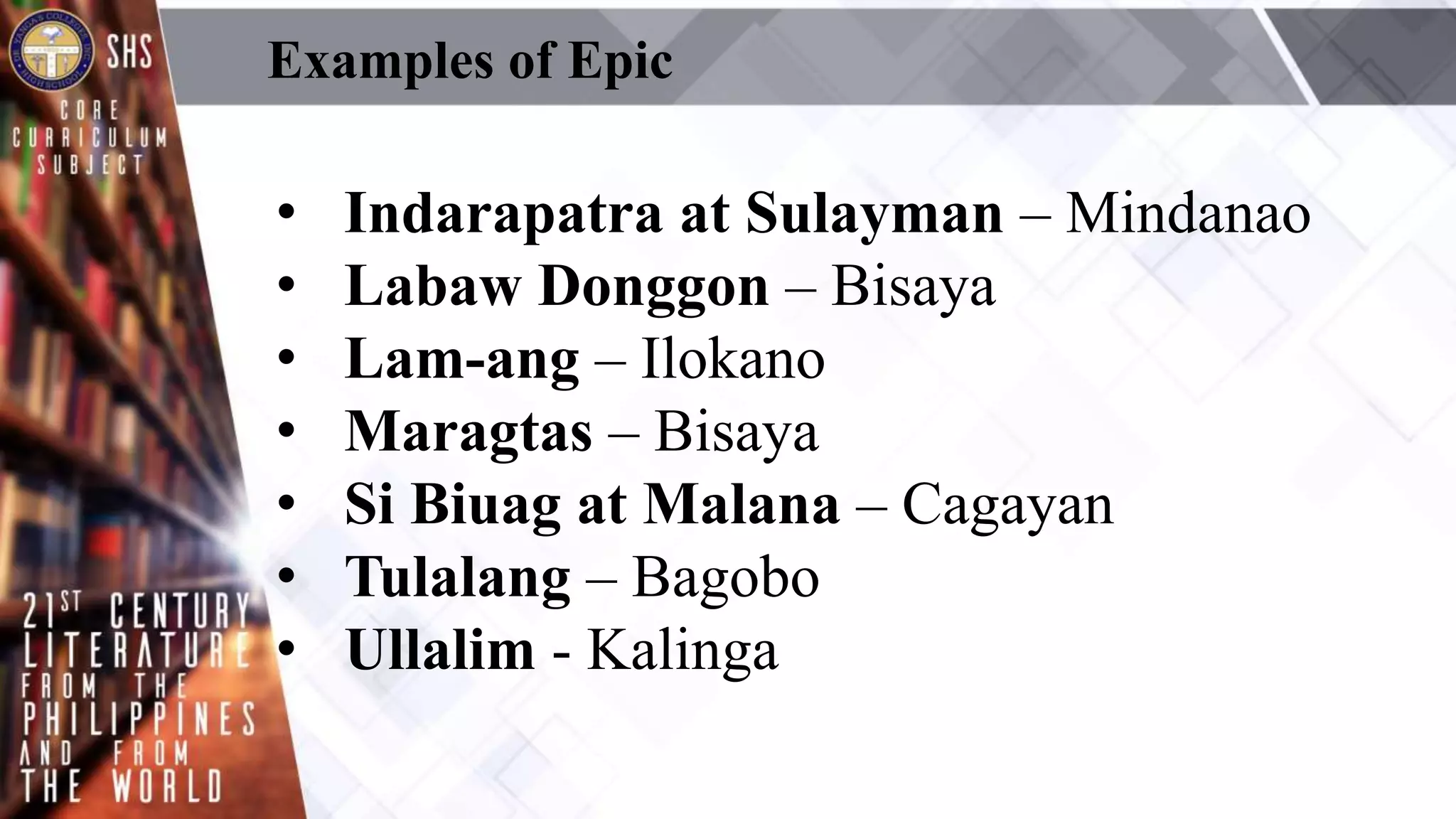
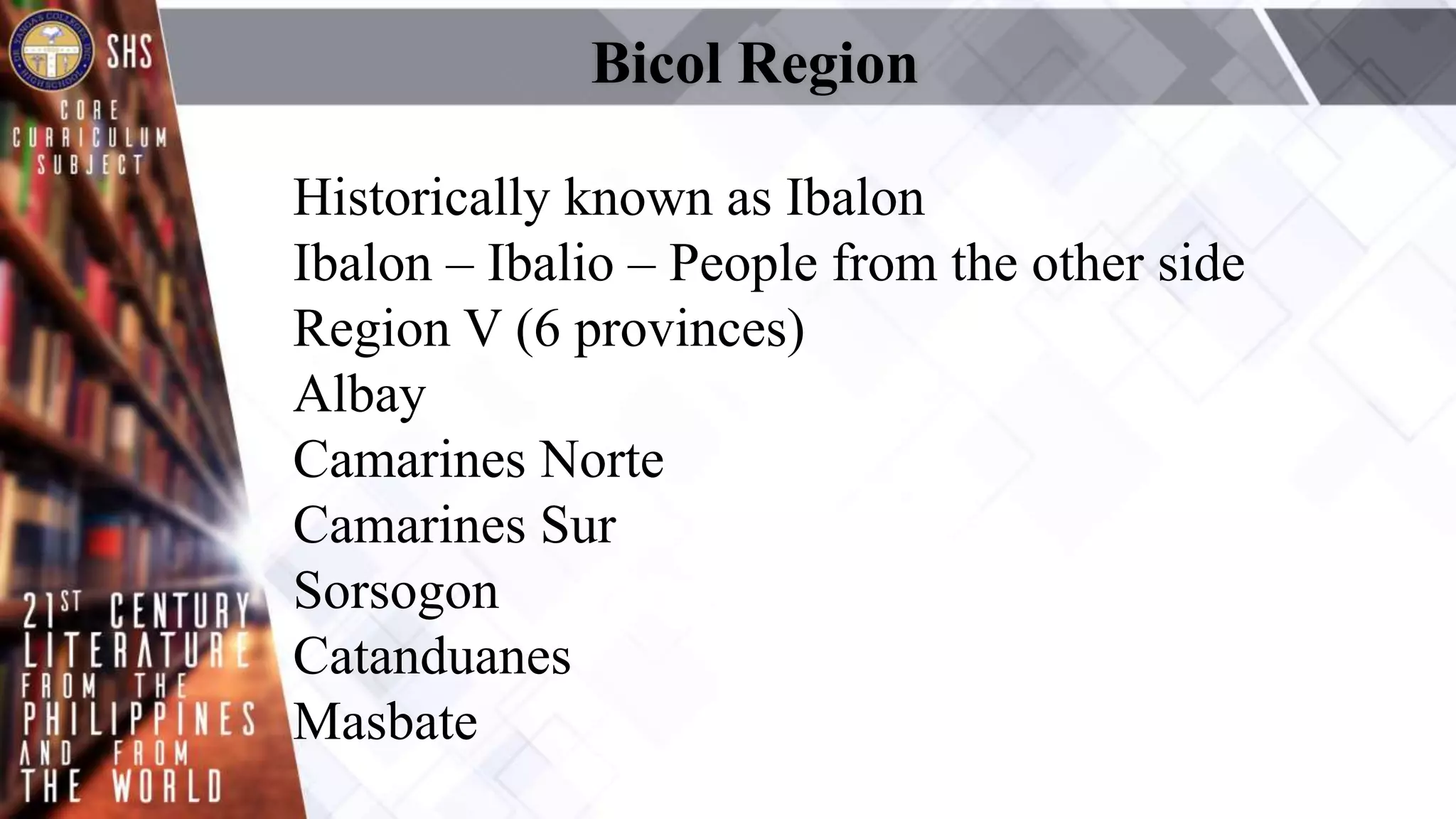
This document provides an overview of Philippine literature from pre-Hispanic times to the present day. It discusses the main poetic forms that developed during the pre-Spanish era, including folk songs, riddles, proverbs and epics. The arrival of the Spanish is noted for popularizing the Pasyon. During the American period, English became dominant and new poetic styles like free verse emerged. The document also summarizes the characteristics of literature from the Bicol region, and highlights some notable Bikolano writers.