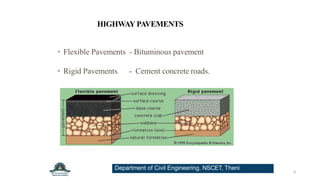
This document provides an overview of a presentation on highway engineering. It discusses evaluating and maintaining pavements, including pavement distress in flexible and rigid pavements. It also lists common types of failures for flexible pavements such as alligator cracking caused by repeated heavy loads, rutting from temperature variations, and cracking from swelling or shrinking of subgrade layers.