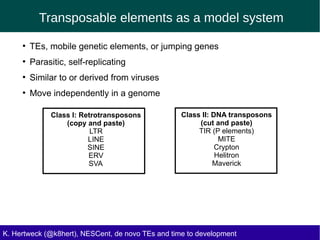
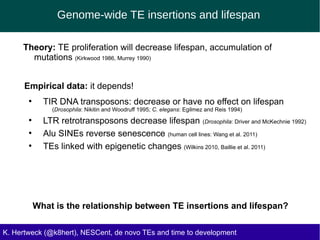
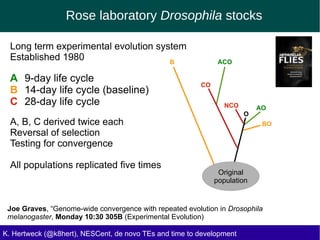
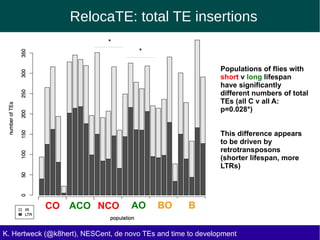
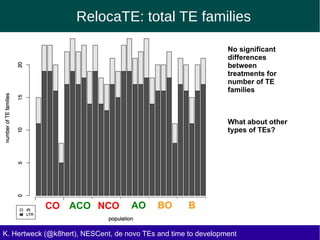
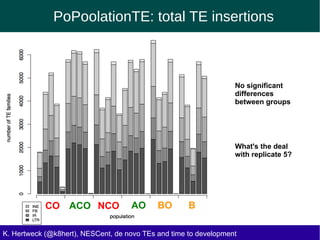
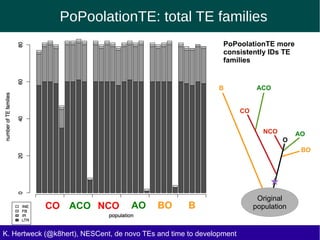
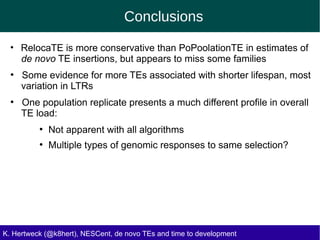
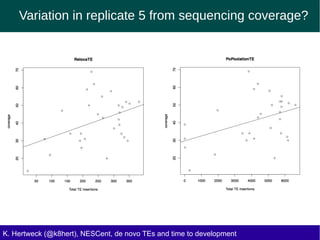
This document discusses the relationship between transposable elements (TEs) and aging, highlighting how different types of TEs can influence lifespan in various organisms, particularly in Drosophila. Empirical data indicate that certain TEs may reduce lifespan, while others show varied effects based on their type and genomic context. The study employs various bioinformatics methods to analyze TE insertions in response to selective pressures and aims to understand the implications of these findings for evolutionary biology.