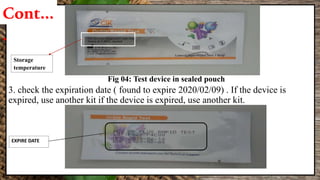
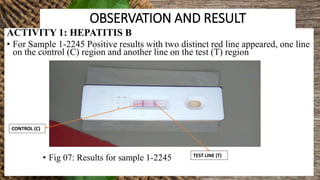
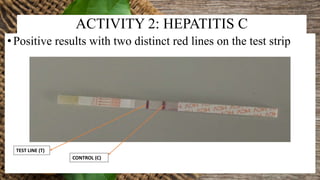
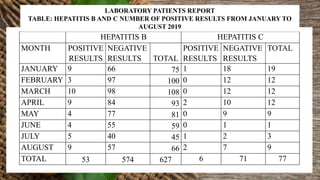
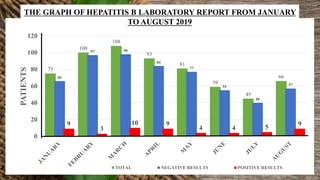
This document summarizes a student's research project on diagnosing hepatitis B and C at Amana Referral Hospital. The student conducted laboratory tests to diagnose samples for hepatitis B and C. For hepatitis B, two samples tested positive and one negative. For hepatitis C, one sample tested positive. From January to August 2019, the laboratory detected 53 positive hepatitis B cases and 6 positive hepatitis C cases out of a total of 627 and 77 patients, respectively. The highest number of positive hepatitis B cases was in March while no cases of hepatitis C were found in February, March, May and June.













![REFERENCES
• Viral Hepatitis, Fourth Edition by Howard C. Thomas ,Anna S.F. Lok, Stephen
A. Locarnini, Arie J. Zuckerman :26 July 2013
Viral Hepatitis: 1985 Update Saul Krugman, Pediatr Rev, 1985
CDC. Updated US Public Health Service guidelines for the management of
occupational exposures to HBV, HCV, and HIV Rep. 2001 Jun
Abara WE, Qaseem A, Schillie S, McMahon BJ, Harris AM. Hepatitis B
vaccination and screening Ann Intern Med. 2017.
Johnson DF, Leder K, Torresi J. Hepatitis B and C infection in international
travelers. J of Trop Med. 2013 May–Jun;2015
UK Essays. November 2018. Hepatitis B infection: An overview. [online].
Available from: https://www.ukessays.com/essays/medical/hepatitis-b-
infection.php?vref=1 [Accessed 20 November 2019].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepatitisbandc1-200129211426/85/HEPATITIS-B-AND-C-PRESENTATION-20-320.jpg)
