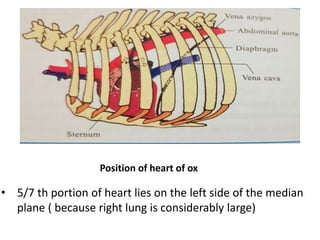
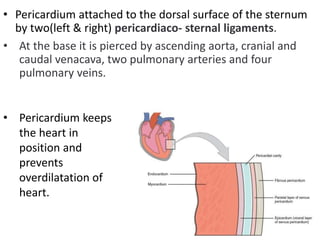
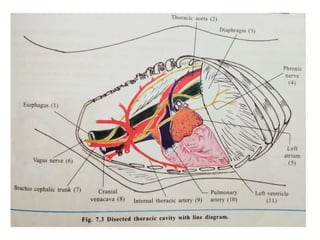
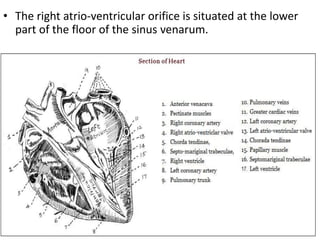
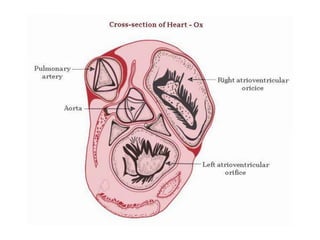
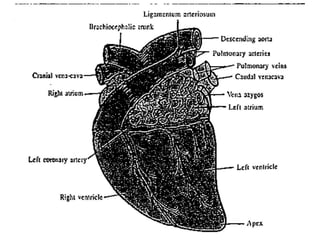
The heart is a hollow muscular organ that acts as the central pump of the circulatory system. It has four chambers - two atria that receive blood and two ventricles that pump blood out. The heart is located in the middle mediastinum in the chest cavity. It has a fibrous pericardium covering and is protected by the pericardial sac that contains serous fluid. The heart has right and left sides, each with an atrium and ventricle, and valves that ensure one-way blood flow.