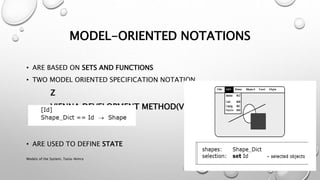
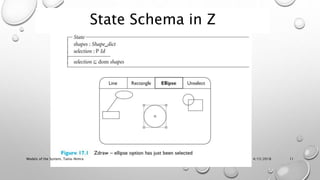
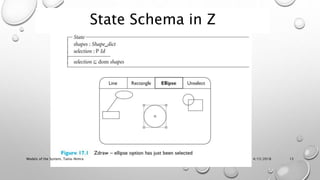
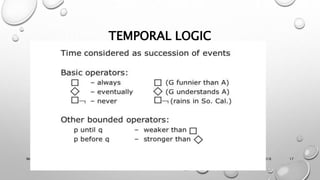
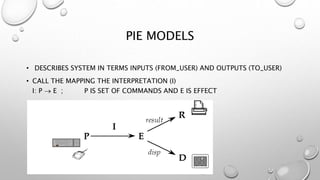
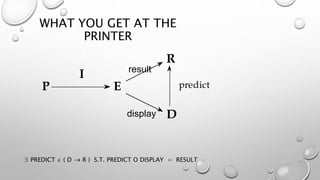
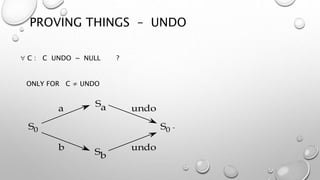
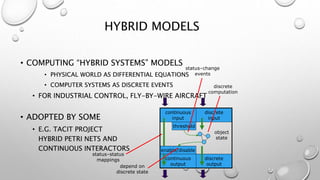
This document discusses different models for representing interactive systems, including formal models from software engineering like Z notation, algebraic specifications, temporal logic, and interaction models like PIE models. It also covers dealing with continuous behaviors like mouse movement using status-event and hybrid models that combine discrete and continuous aspects. The models can be used for communication, analysis, and proving properties about a system's usability.