- New quantization algorithm called HAWQ-V3 that uses only integer multiplication, addition, and bit shifting for inference, with no floating point operations or integer division
- Achieves higher accuracy than prior work, including up to 5% higher than Google's integer-only method, with no accuracy degradation for INT8 quantization
- Proposes a novel ILP formulation to find optimal mixed precision of INT4 and INT8 that balances model size, latency, and accuracy
- Implementation in TVM demonstrates up to 1.5x speedup for INT4 quantization compared to INT8 on Nvidia T4 GPU tensor cores



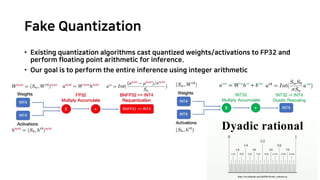


![Mixed Precision and Integer Liner
Programming
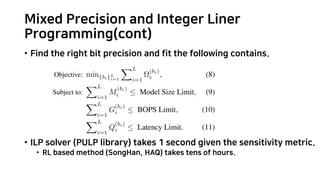
Integer Linear Programming (ILP) problem
Search space: 𝐵!
• 𝐵 choices for quantizing each layer:
INT4 or INT8
• 𝐿 layers
Assume the perturbations for each layer ar
e independent of each other [1,2].
• Ω = ∑"#$
!
Ω"
(&!)
• The i-th layer’s perturbation with b_i bit
[1] ICCV2019, HAWQ
[2] NeurIPS 2020, HAWQ-V2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dyadicquantization-211015002054/85/HAWQ-V3-Dyadic-Neural-Network-Quantization-8-320.jpg)
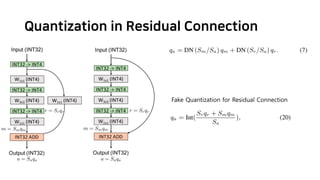
![Mixed Precision and Integer Liner
Programming(cont)
[1] ICCV2019, HAWQ
[2] NeurIPS 2020, HAWQ-V2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dyadicquantization-211015002054/85/HAWQ-V3-Dyadic-Neural-Network-Quantization-10-320.jpg)

![Results
• HAWQv3 achieves higher accuracy than the integer-only work [google, CVPR18]
• Uniform 4bit Quant is the first outcome reported in the literature
• Distillation helps most for mixed-precision quantization except uniform ones
• Comparable accuracy to prior methods that use non-standard bit precision and FP32
operation (PACT, RVQuant, OneBitwidth, HAQ)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dyadicquantization-211015002054/85/HAWQ-V3-Dyadic-Neural-Network-Quantization-12-320.jpg)




