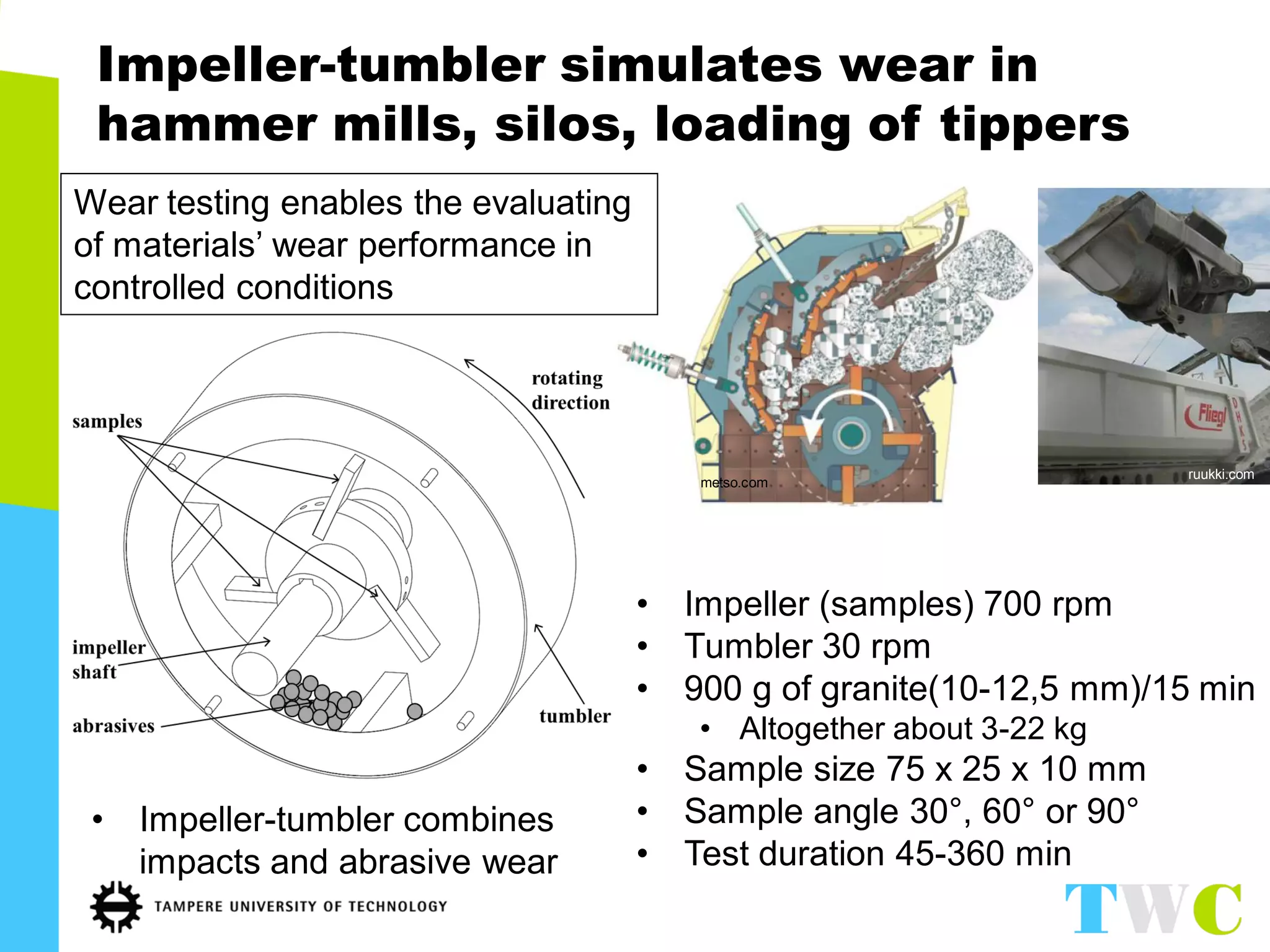
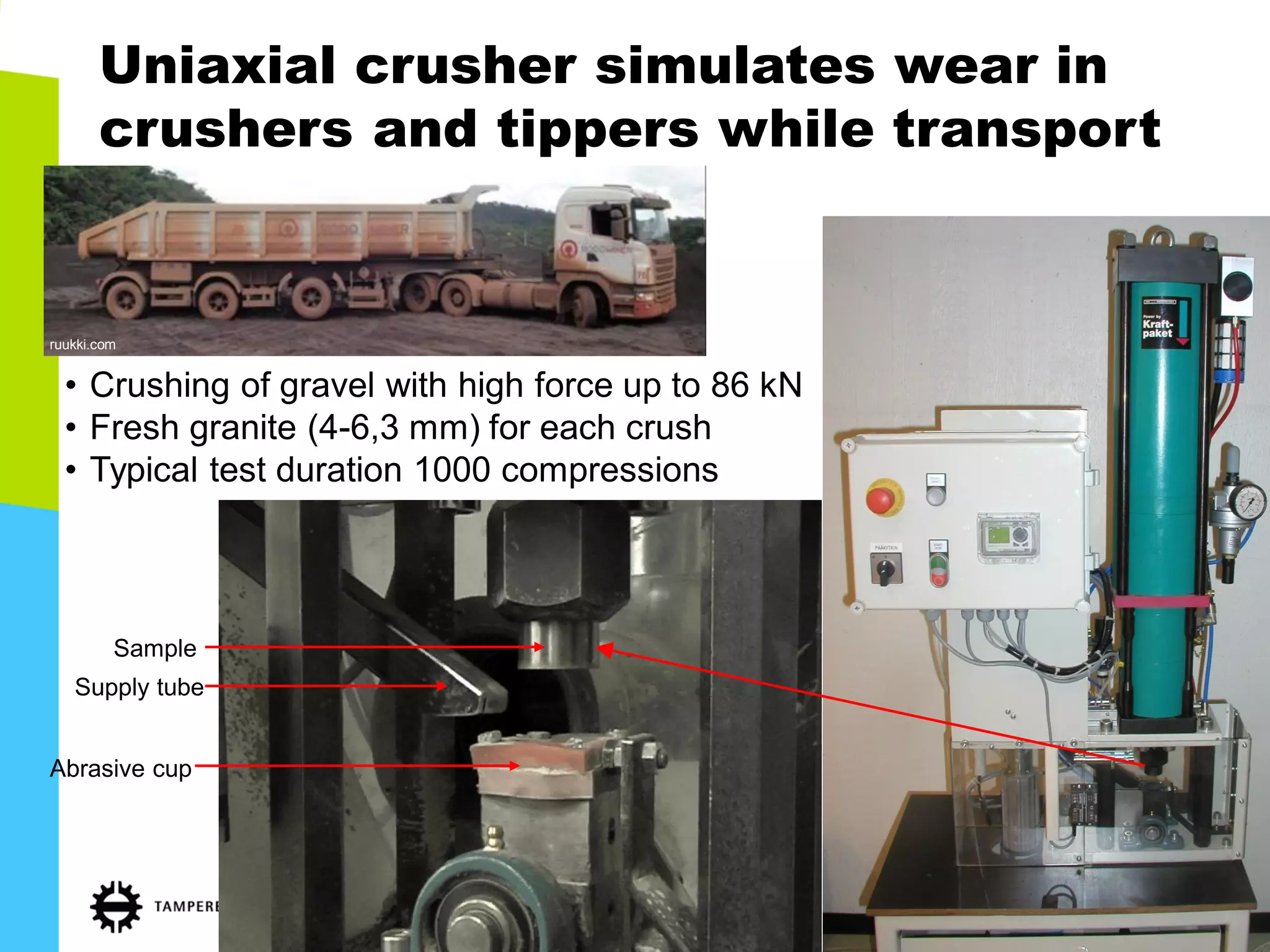
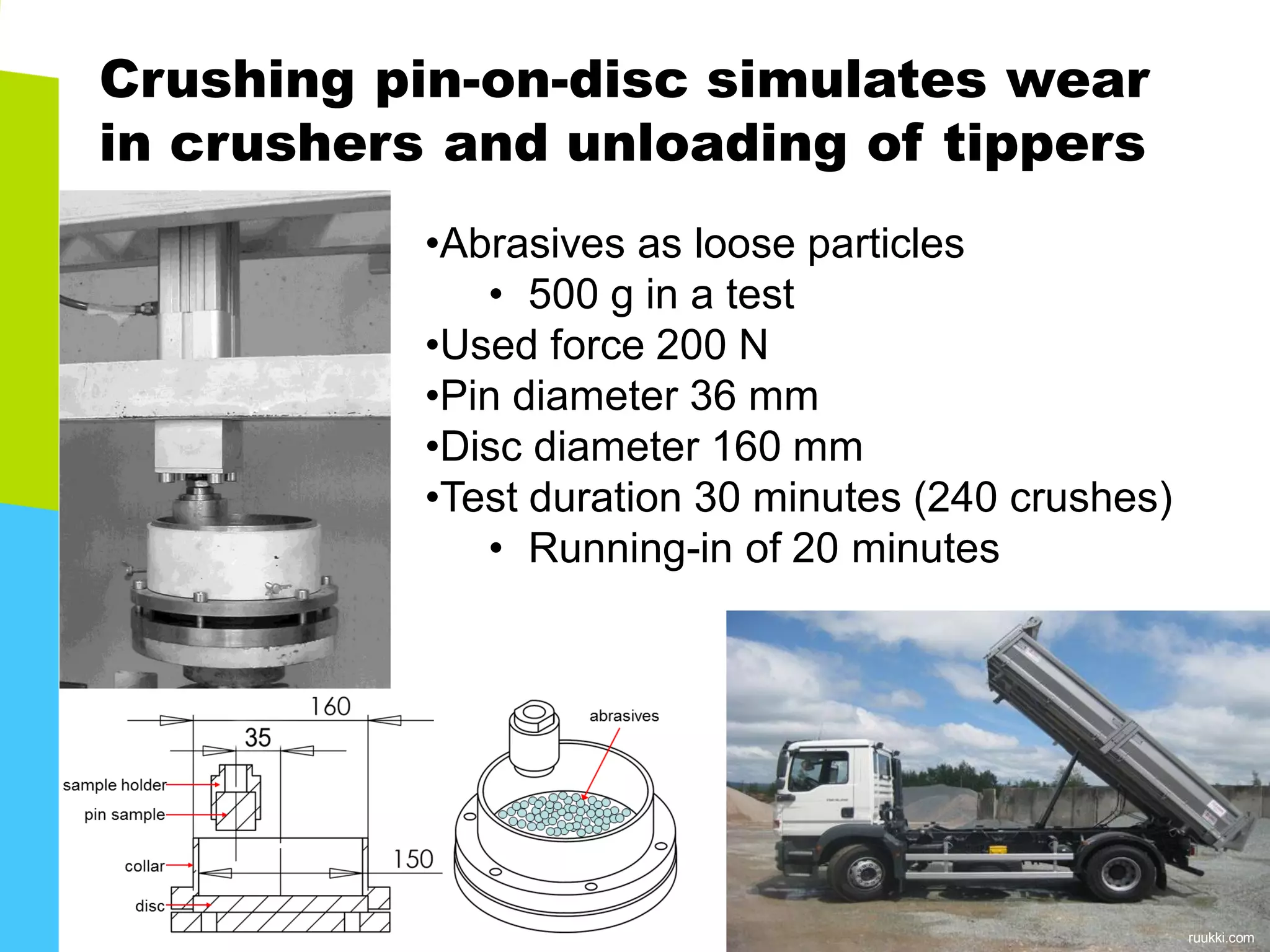
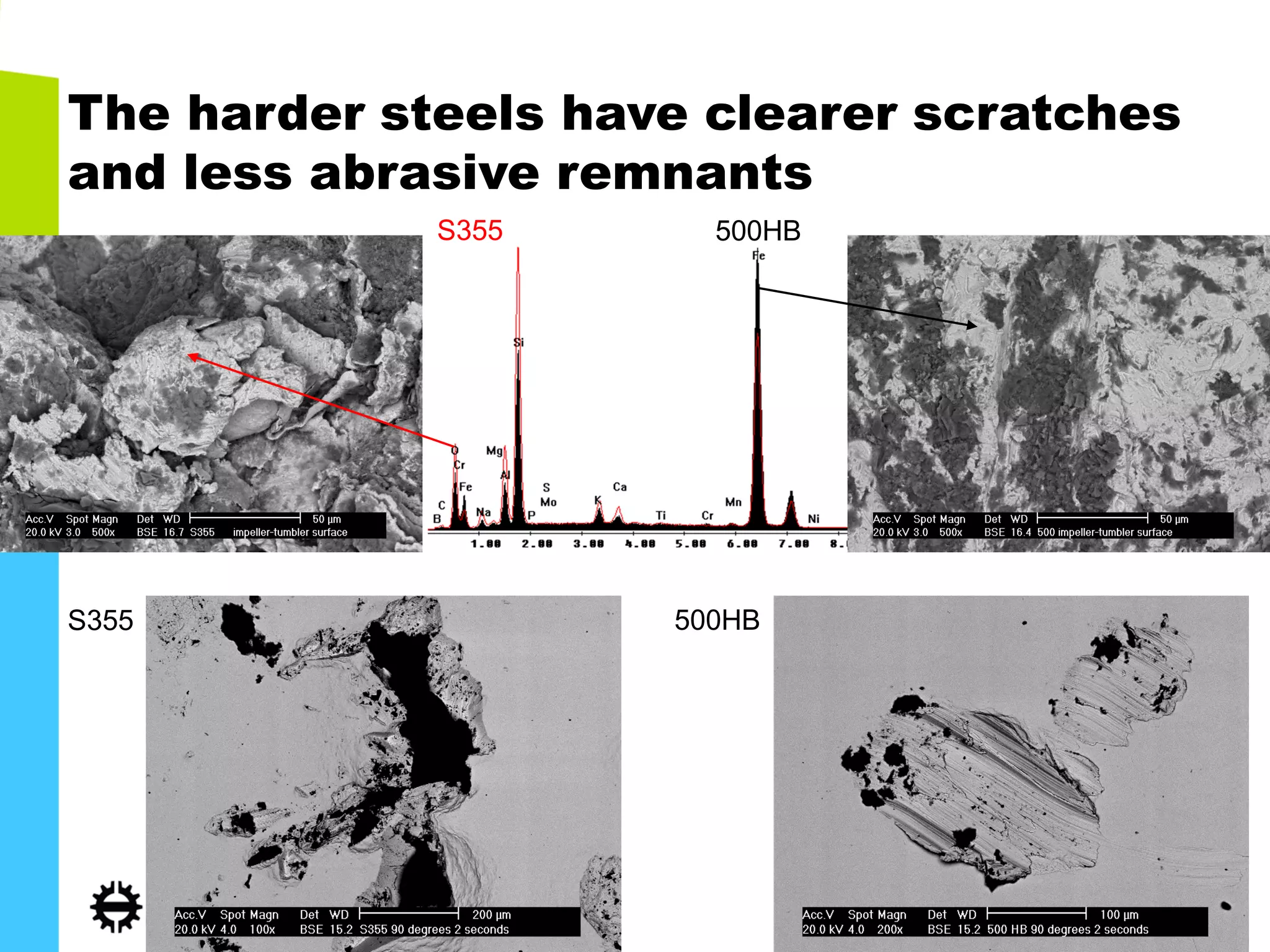
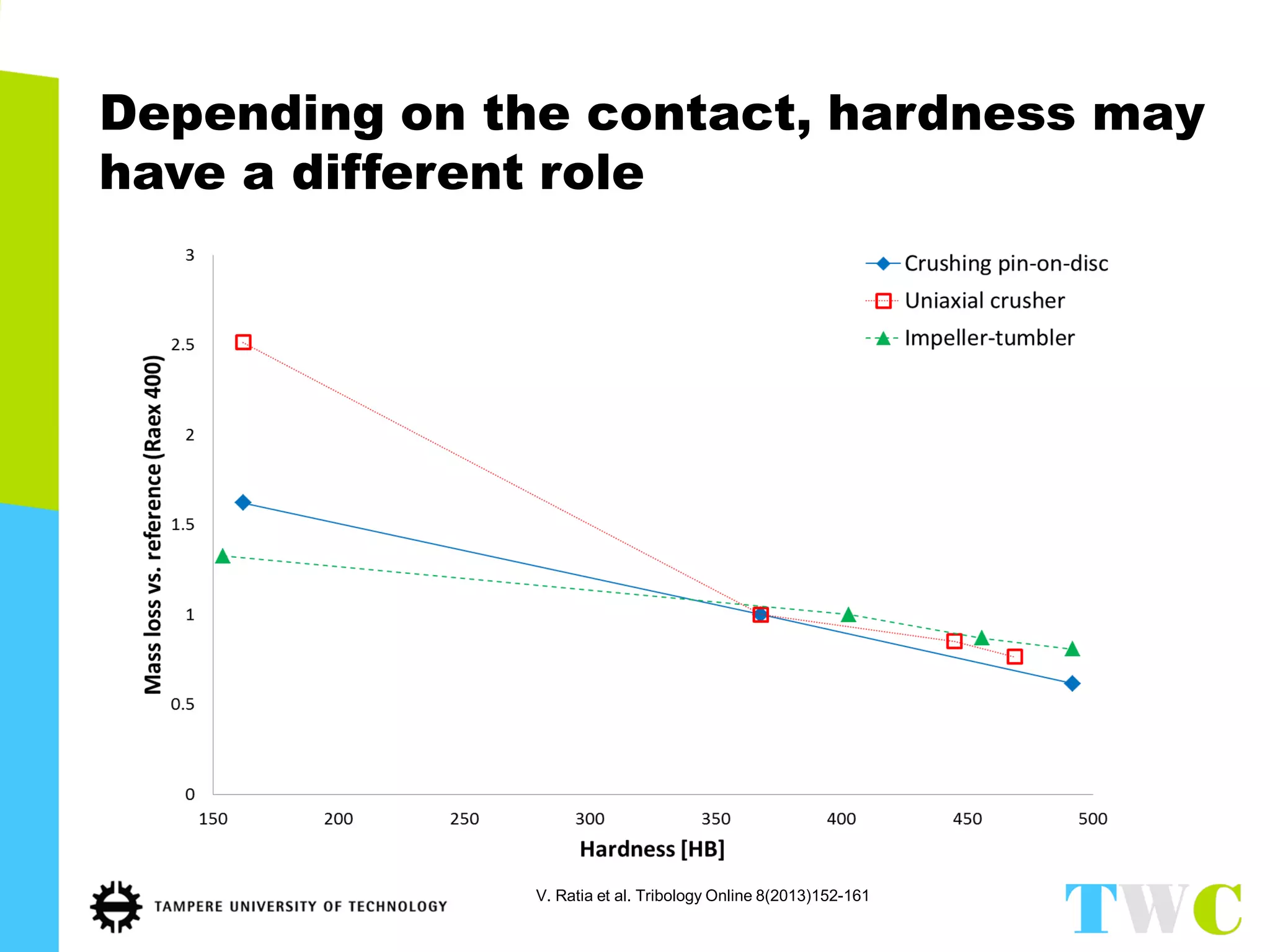
The document discusses abrasive and impact-abrasive wear testing of wear-resistant steels used in mining and mineral processing. It details the properties of these steels, such as higher strength and hardness compared to conventional steels, and highlights various applications in industries like agriculture and forestry. The wear testing methodologies described include an impeller-tumbler and uniaxial crusher to evaluate material performance under controlled conditions.


![0.142
0.158
0.163
0.165
0.172
0.173
0.176
0.180
0.186
0.189
0.192
0.199
0.202
0.208
0.216
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
0.000
0.050
0.100
0.150
0.200
0.250
0 2 15 4 14 3 10 11 5 24 18 17 6 16 1
Surface hardness [HV5]
Mass loss [g]
Wear resistant steels have higher
strength and hardness than
conventional structural steels
• Commonly graded
according to hardness
in Brinell scale:
400HB, 500HB, 600HB
• Tensile strength
typically 1200-1600
MPa
• Notch impact energy at
-40C typically 30 J/cm2
• Microstructure often
martensitic, but bainite,
ferrite, pearlite and
austenite are also
possible
ruukki.com
N. Ojala et al. WTC 2013 & Wear 317(2014)225-232](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardrocktribpresentationslideshare-141126083059-conversion-gate01/75/Abrasive-and-impact-abrasive-wear-testing-of-steels-for-mining-transporting-and-minerals-processing-4-2048.jpg)