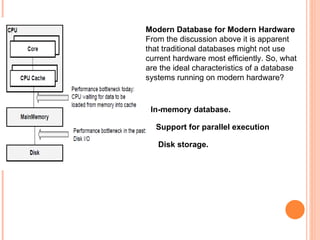
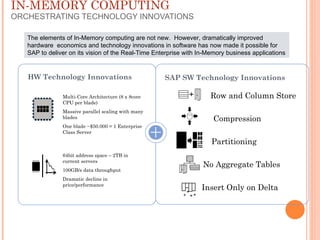
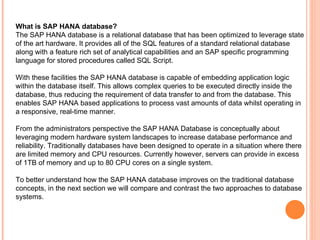
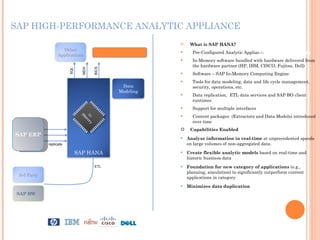
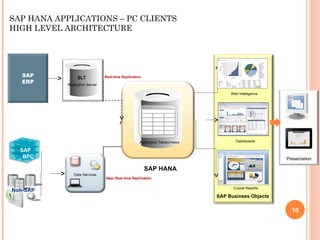
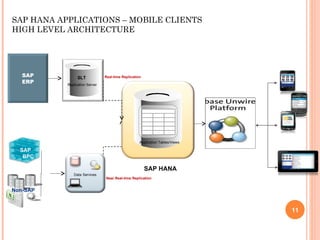
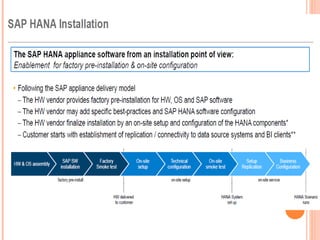
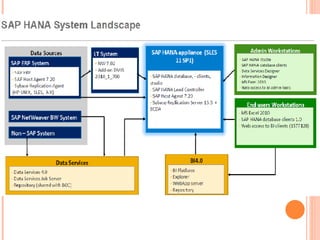
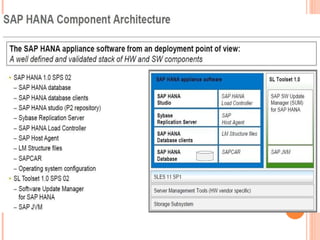
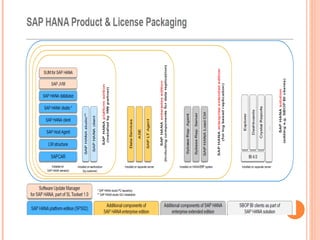
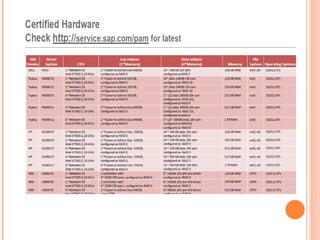
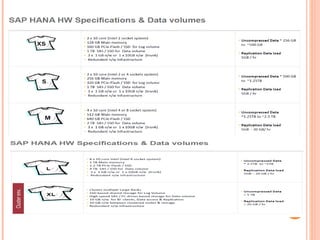
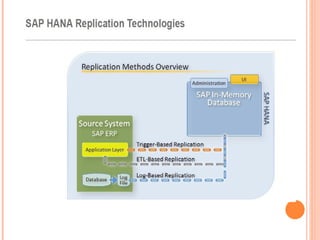
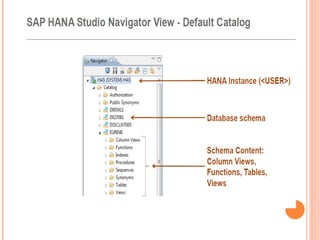
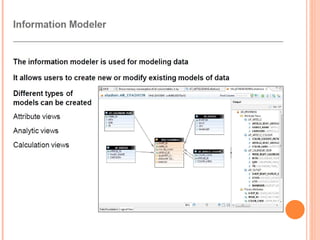
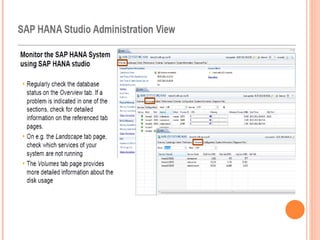
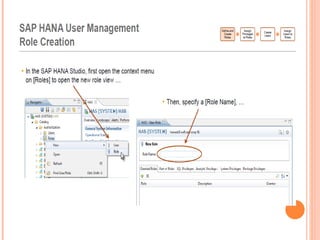
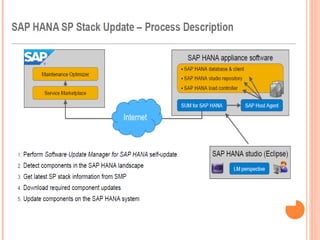
The document provides an overview of a 3-day training on SAP HANA for BW community. Day 1 covers what SAP HANA is, its architecture, and data acquisition methods. Day 2 focuses on modeling, reporting, and building apps in SAP HANA. Day 3 is about administration, monitoring, user management, and backup/recovery. The document also discusses how SAP HANA leverages in-memory computing on modern hardware for real-time analytics.
![SAP HANA AN INTRODUCTION FOR BW COMMUNITY Mishra SAP Practitioner Contact: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hanatrainingday1-13217227305192-phpapp01-111119111236-phpapp01/75/Hana-Training-Day-1-1-2048.jpg)