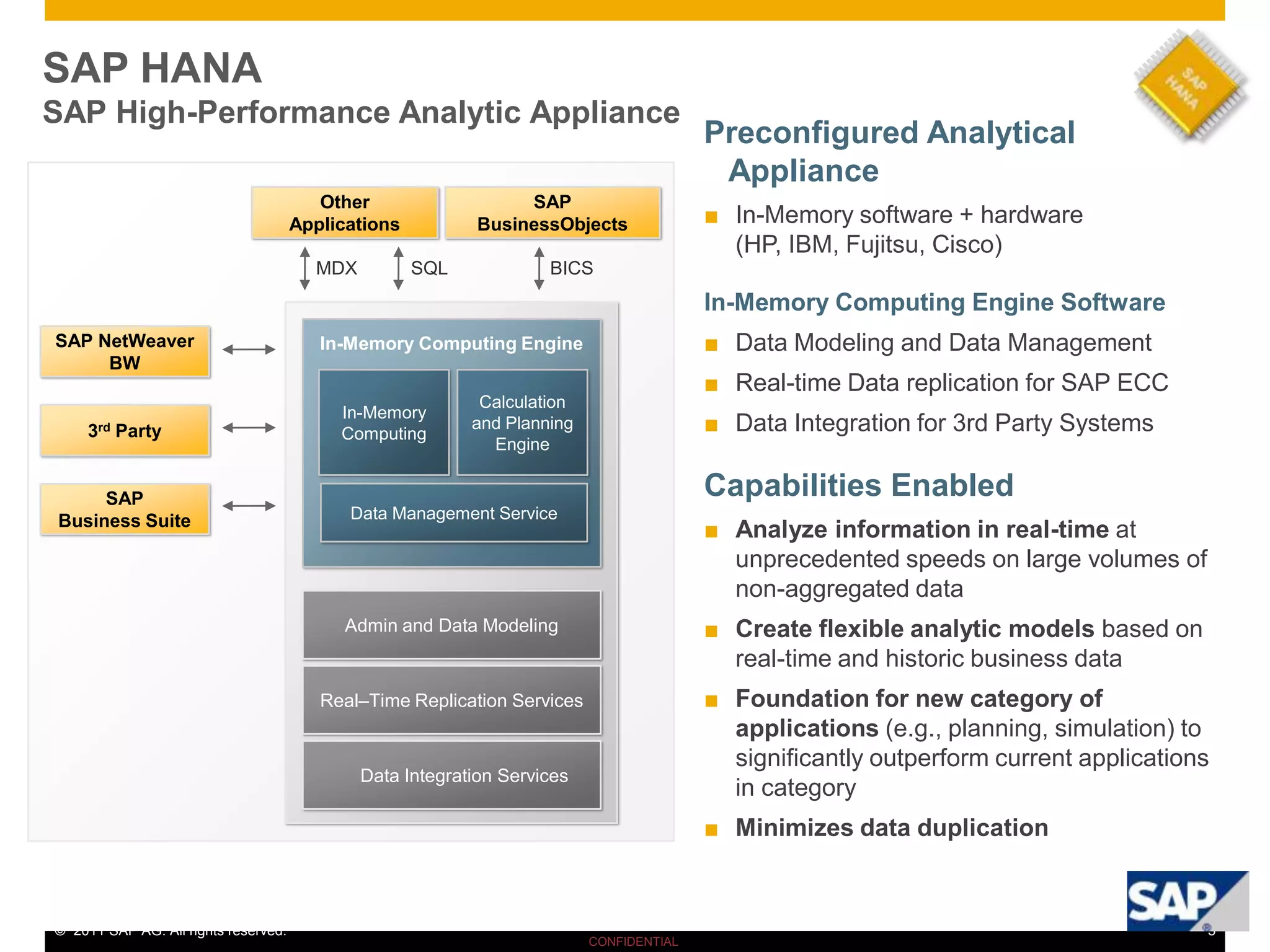
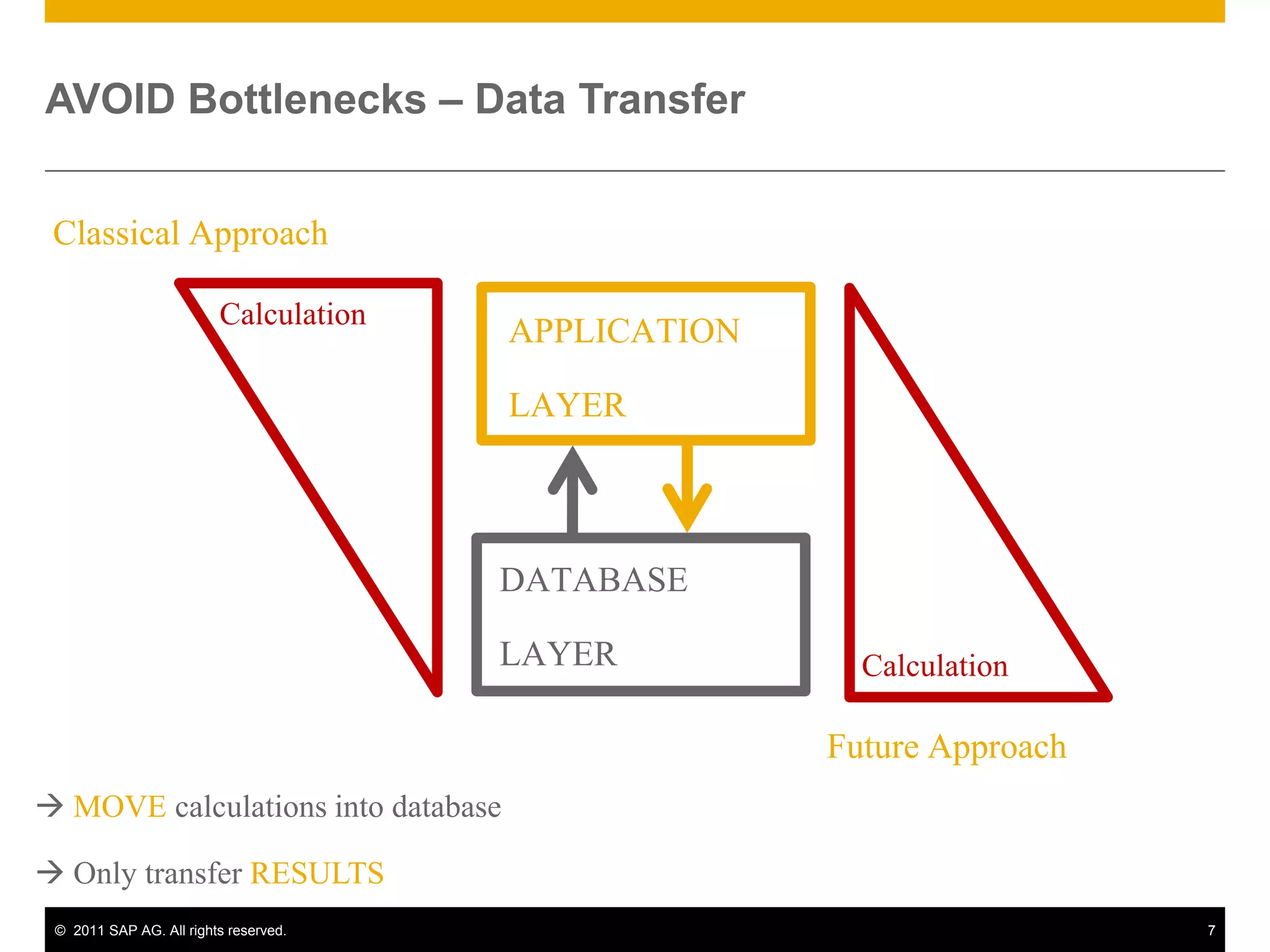
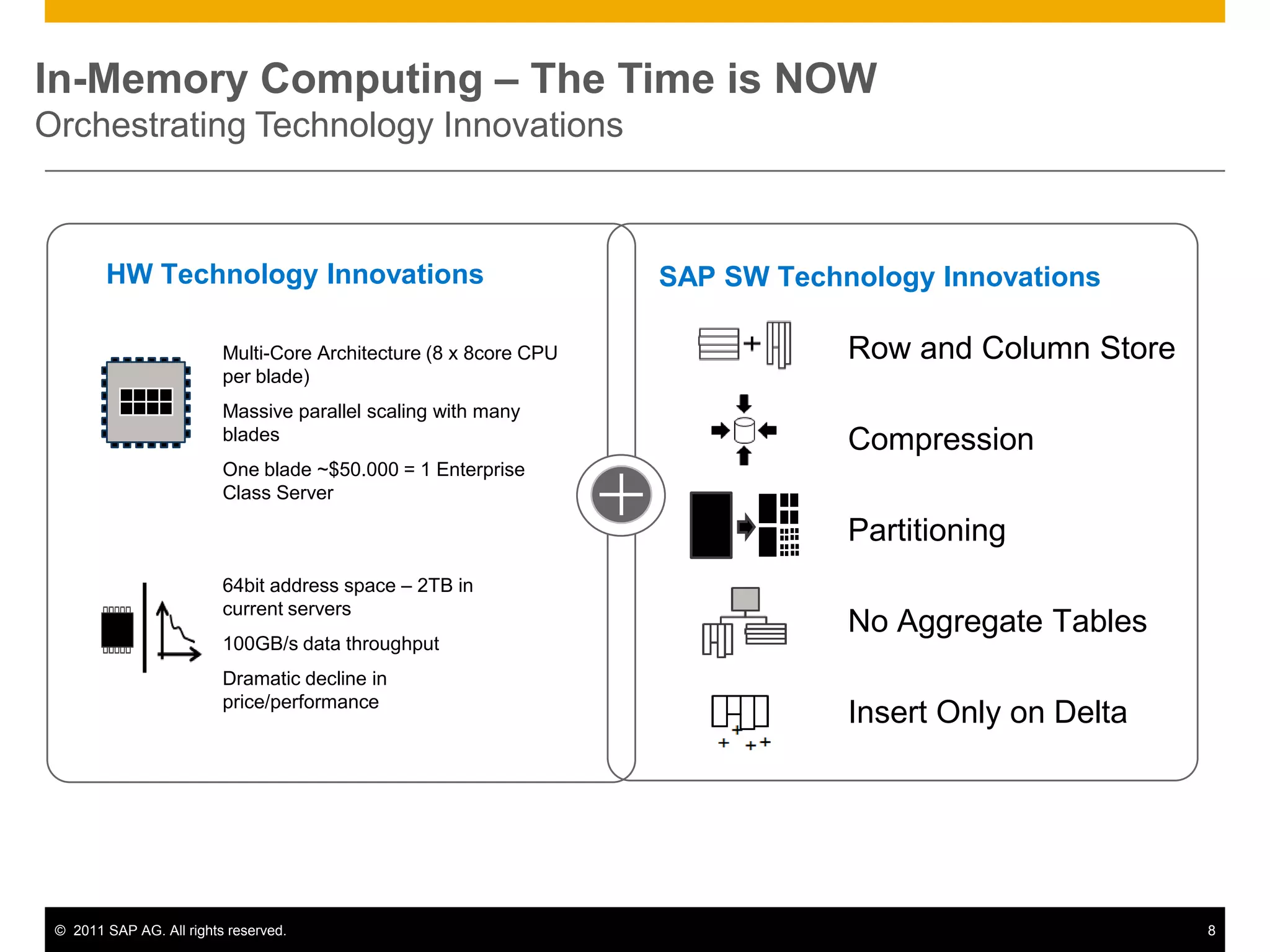
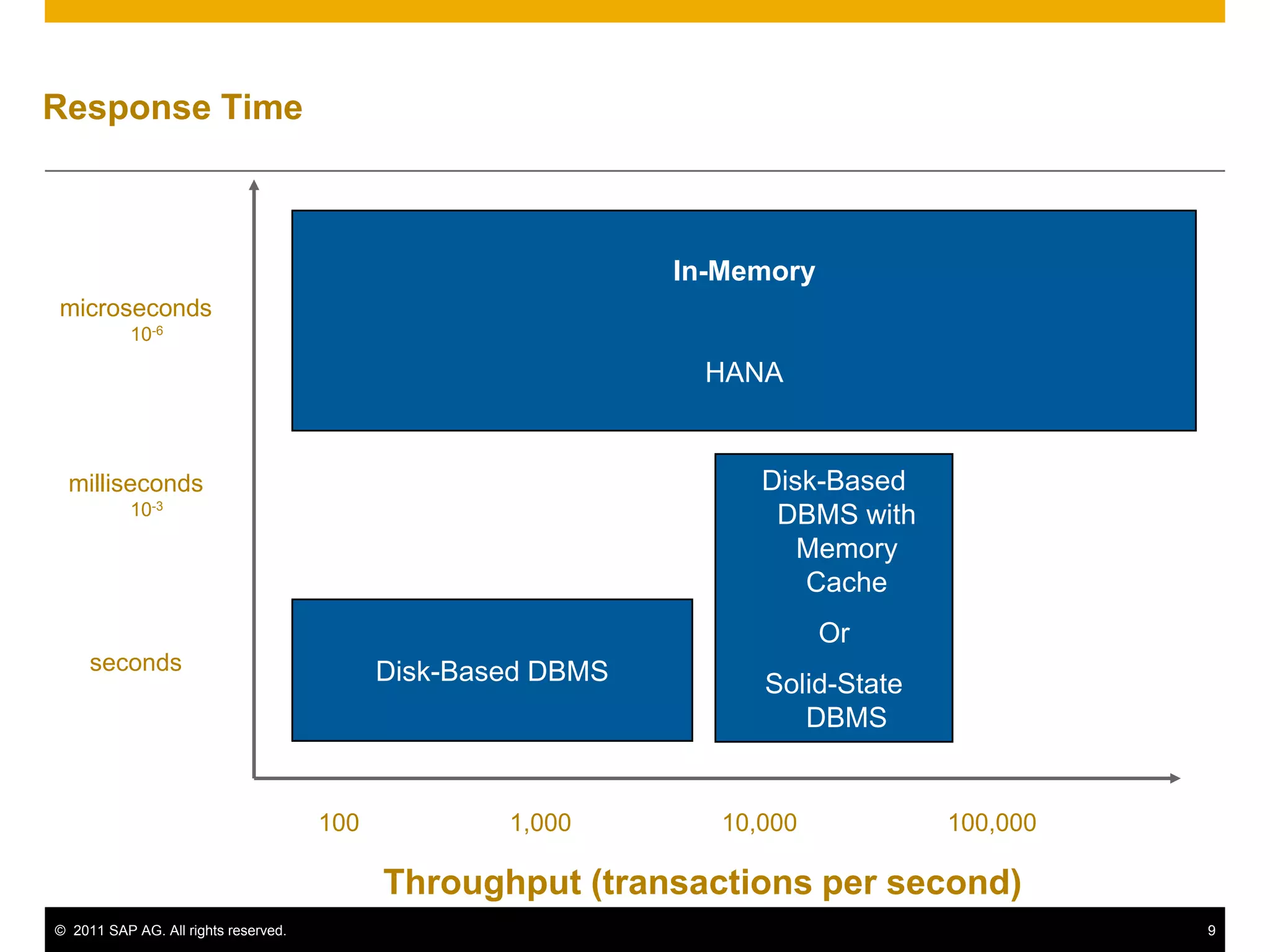
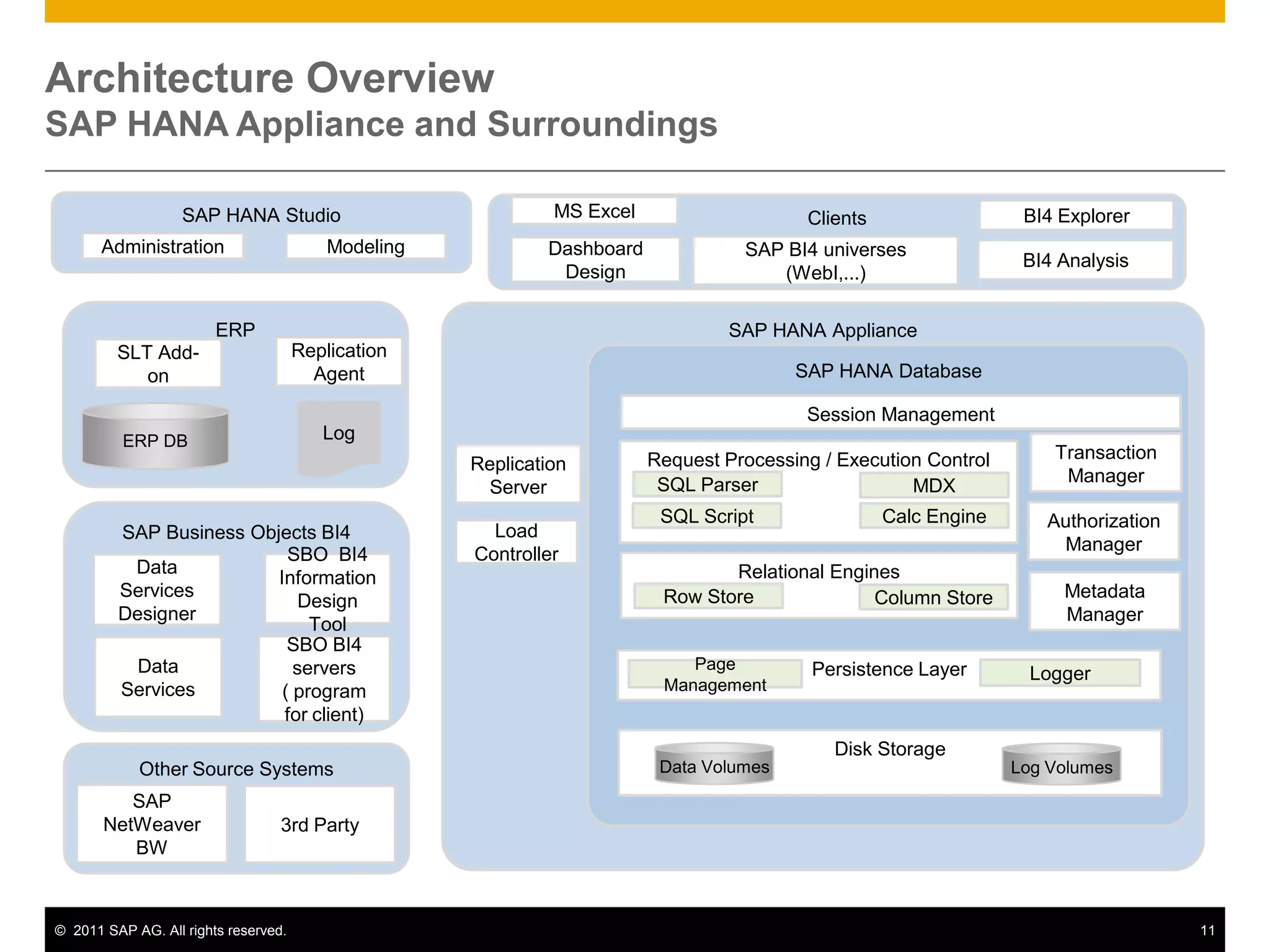
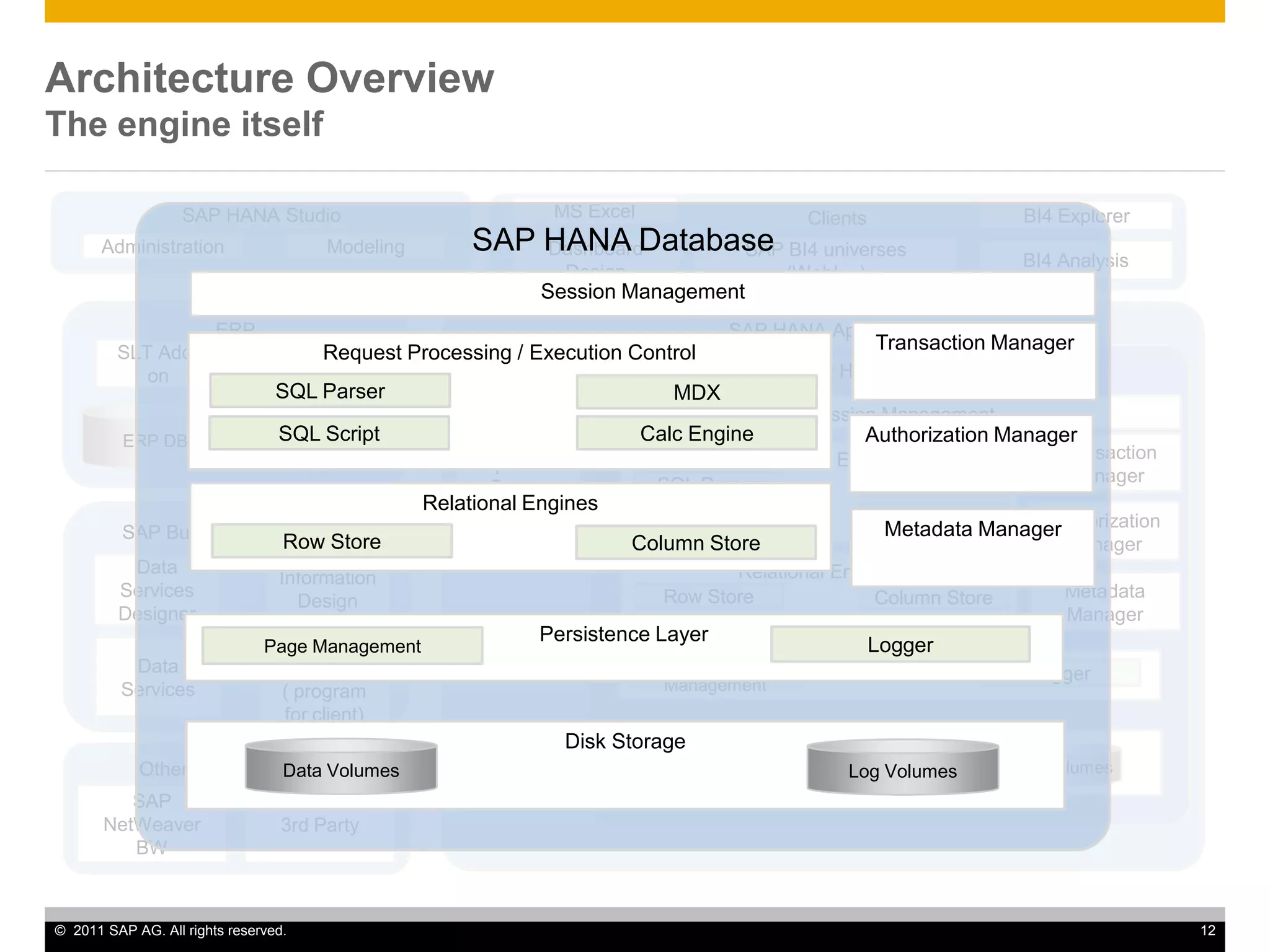
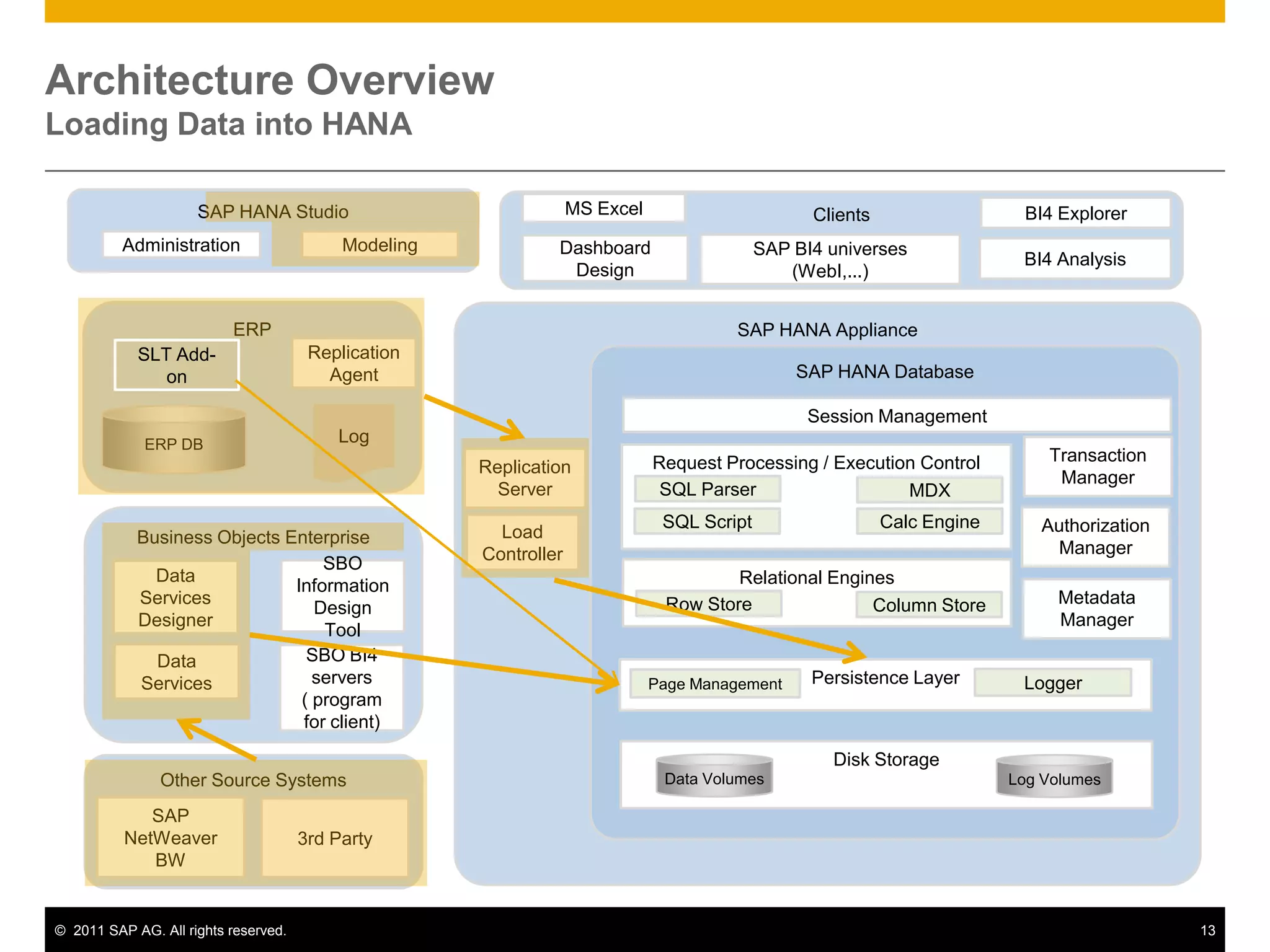
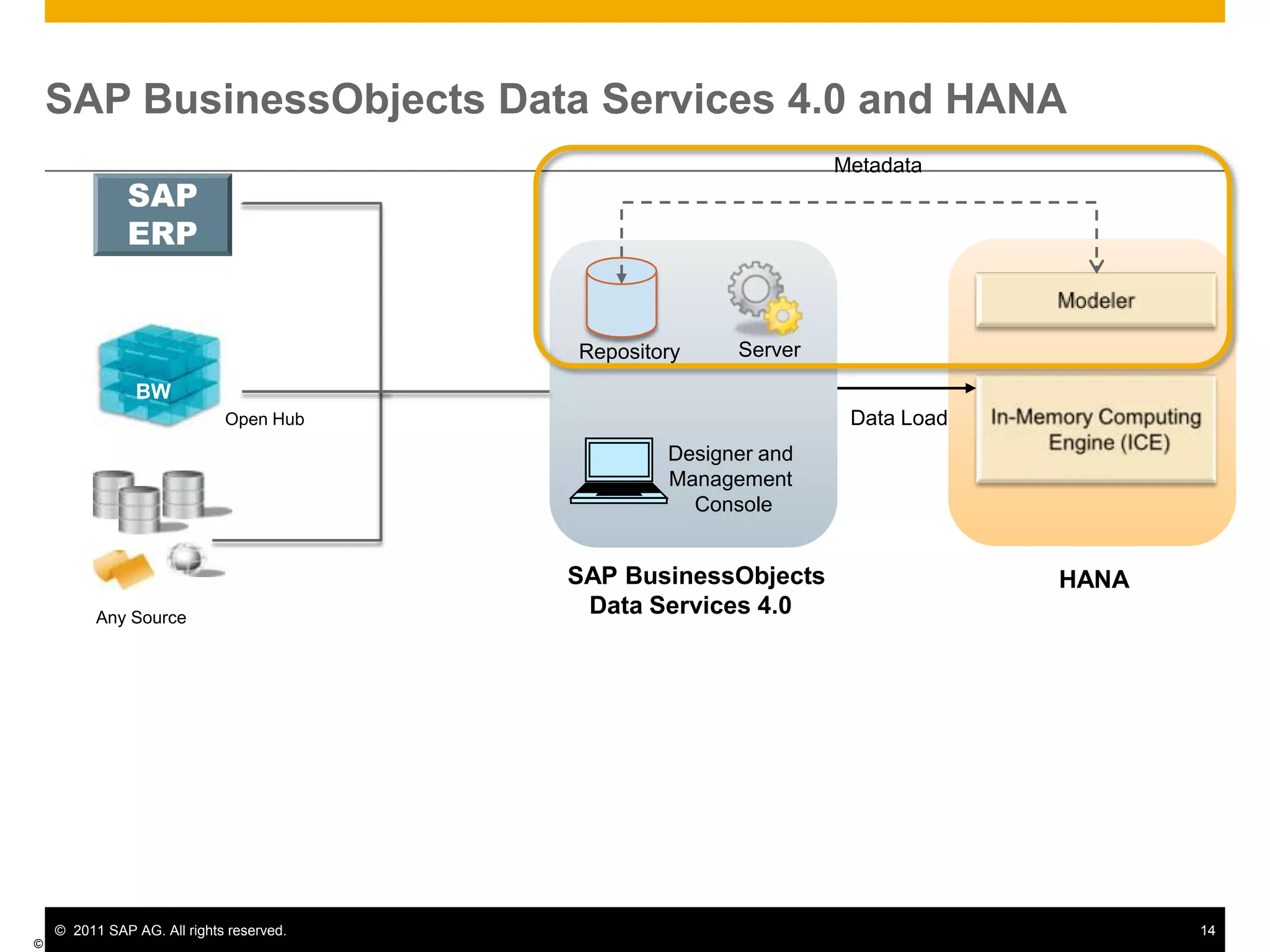
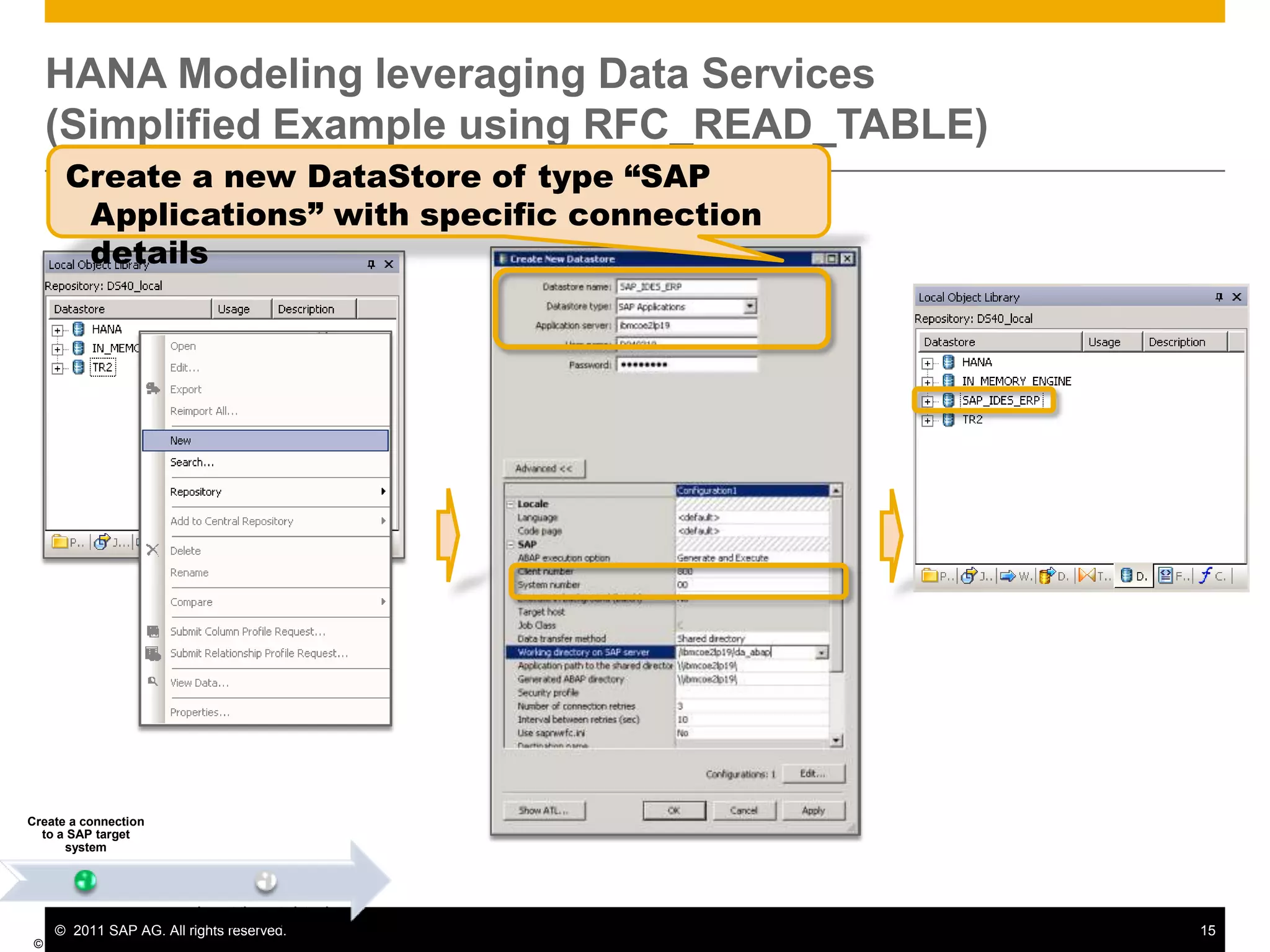
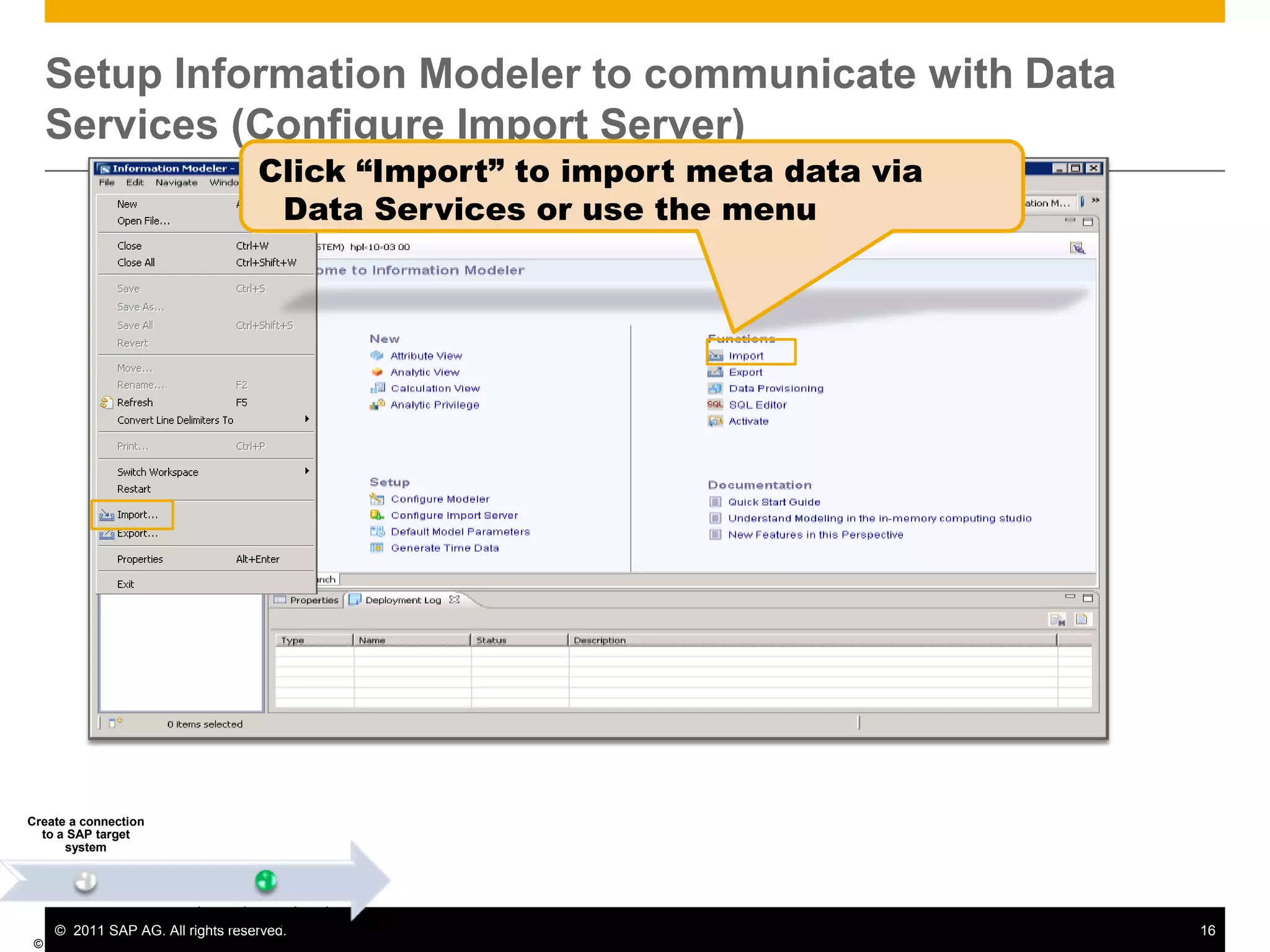
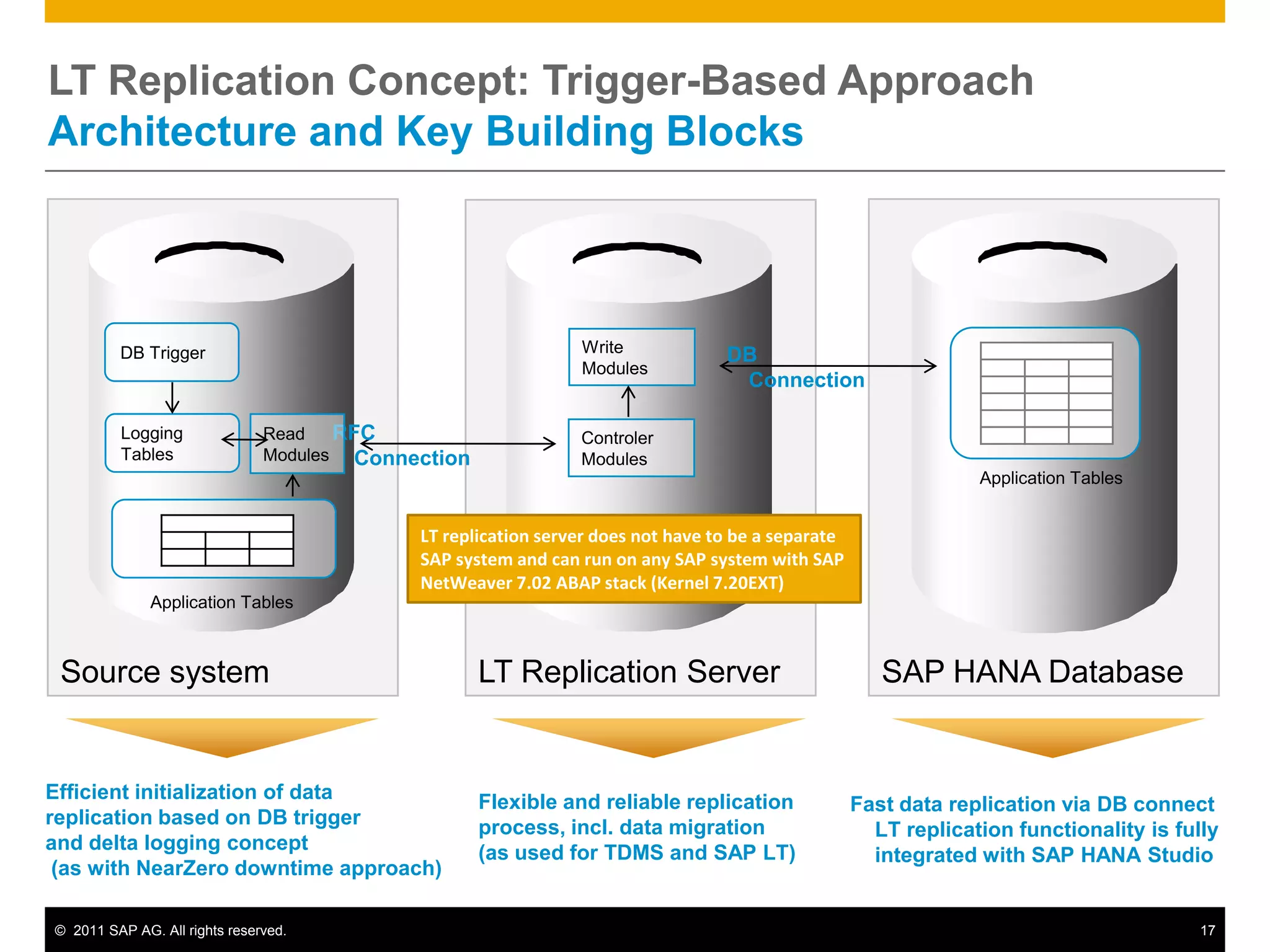
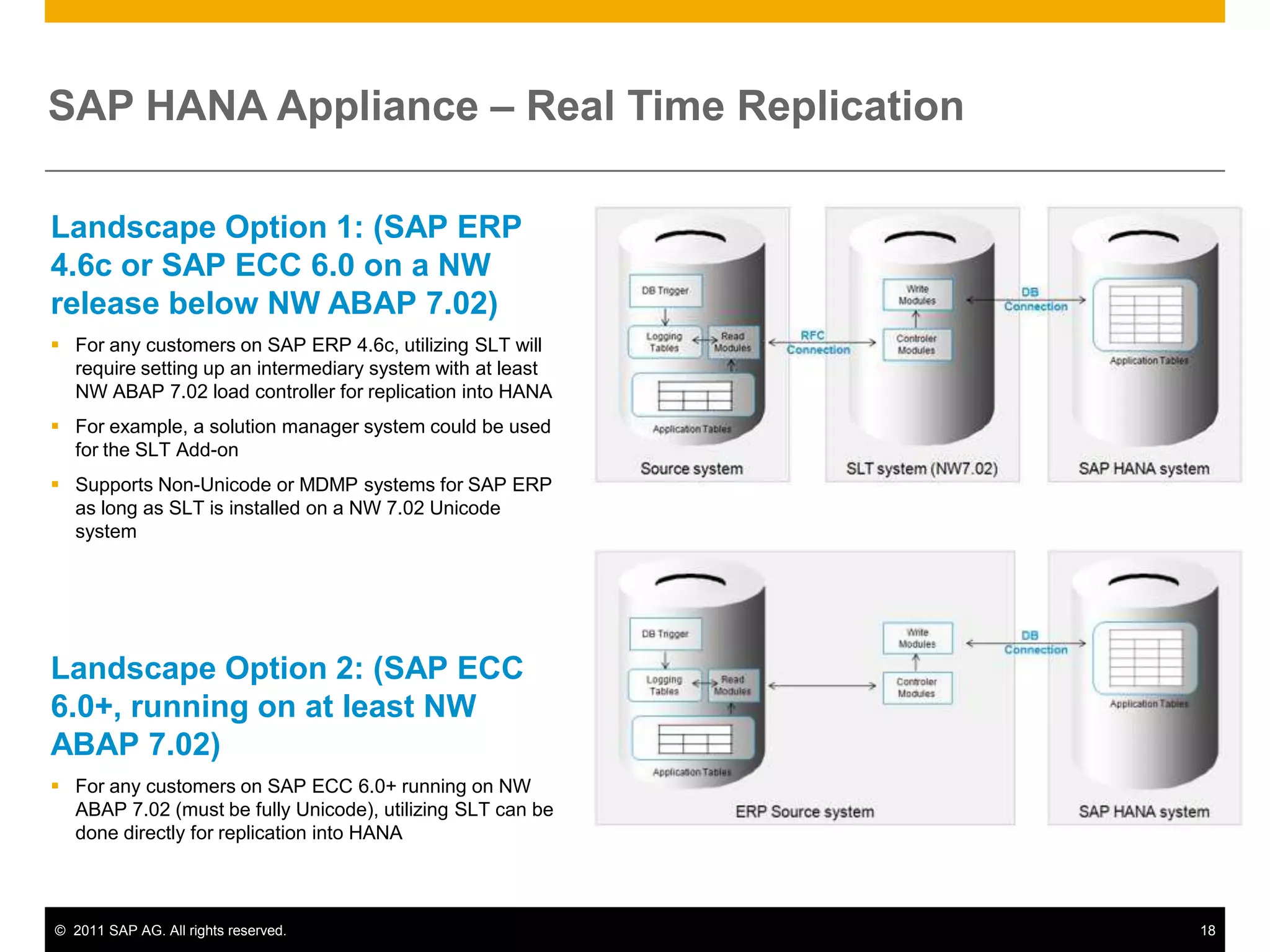
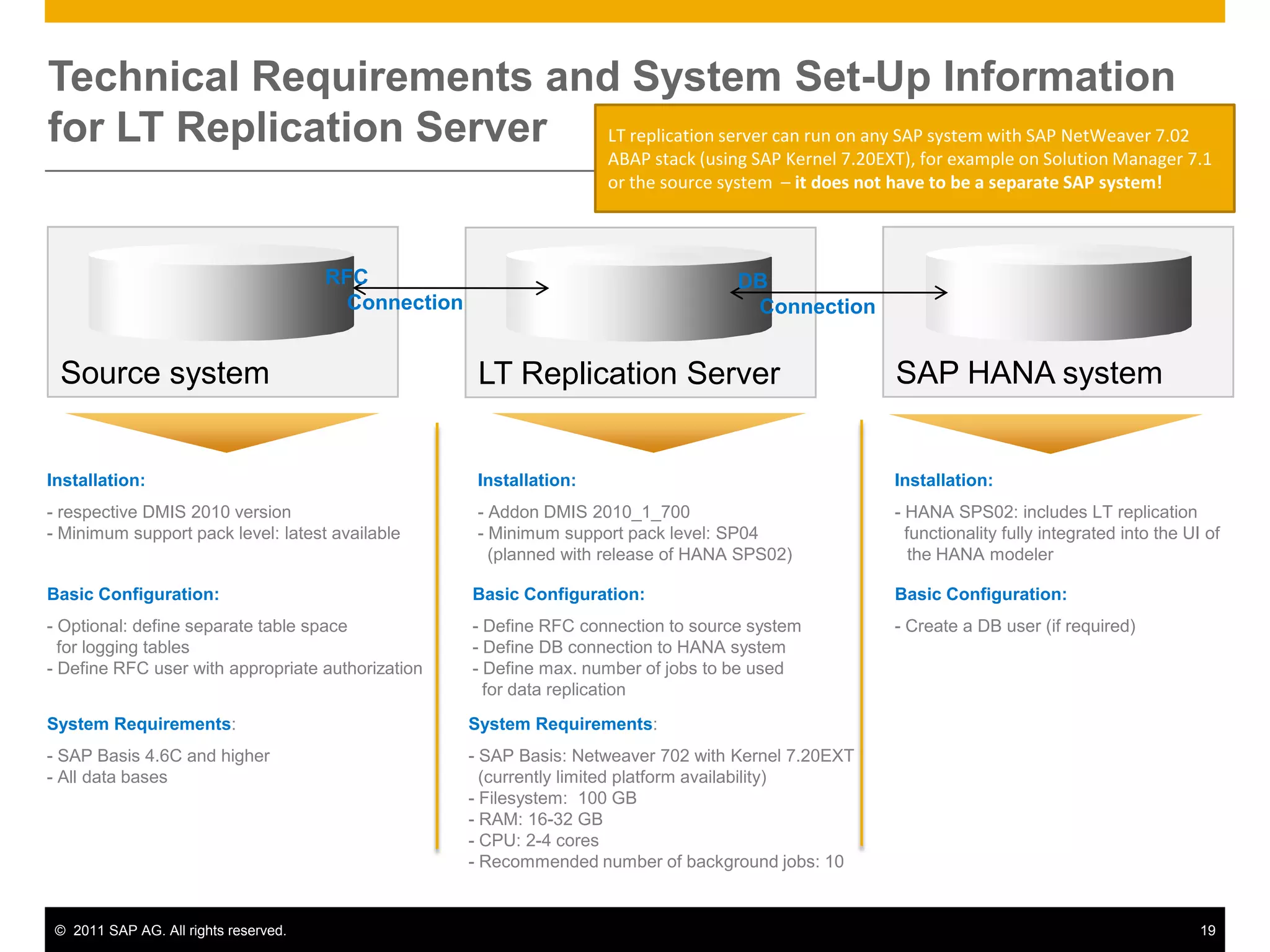
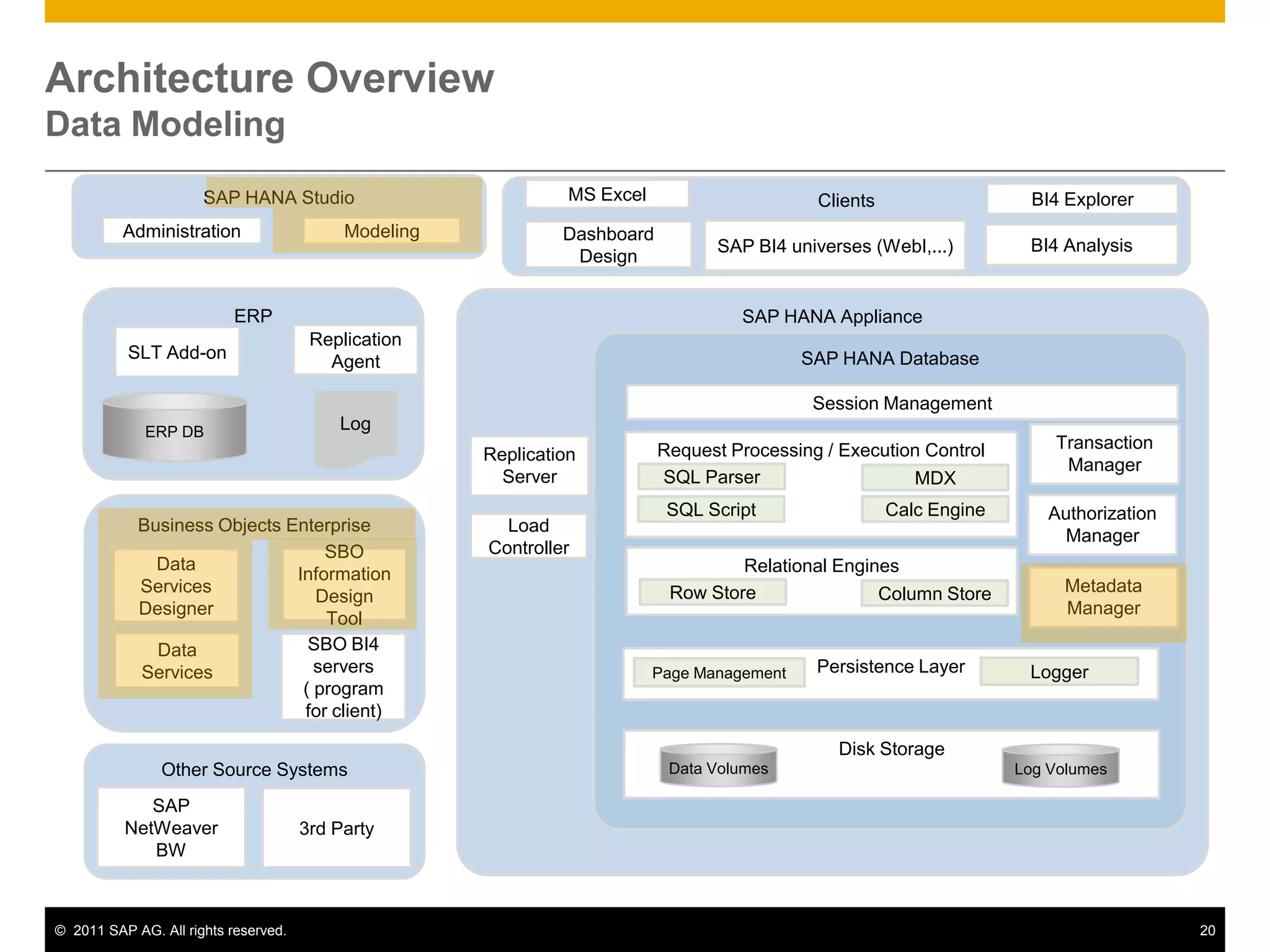
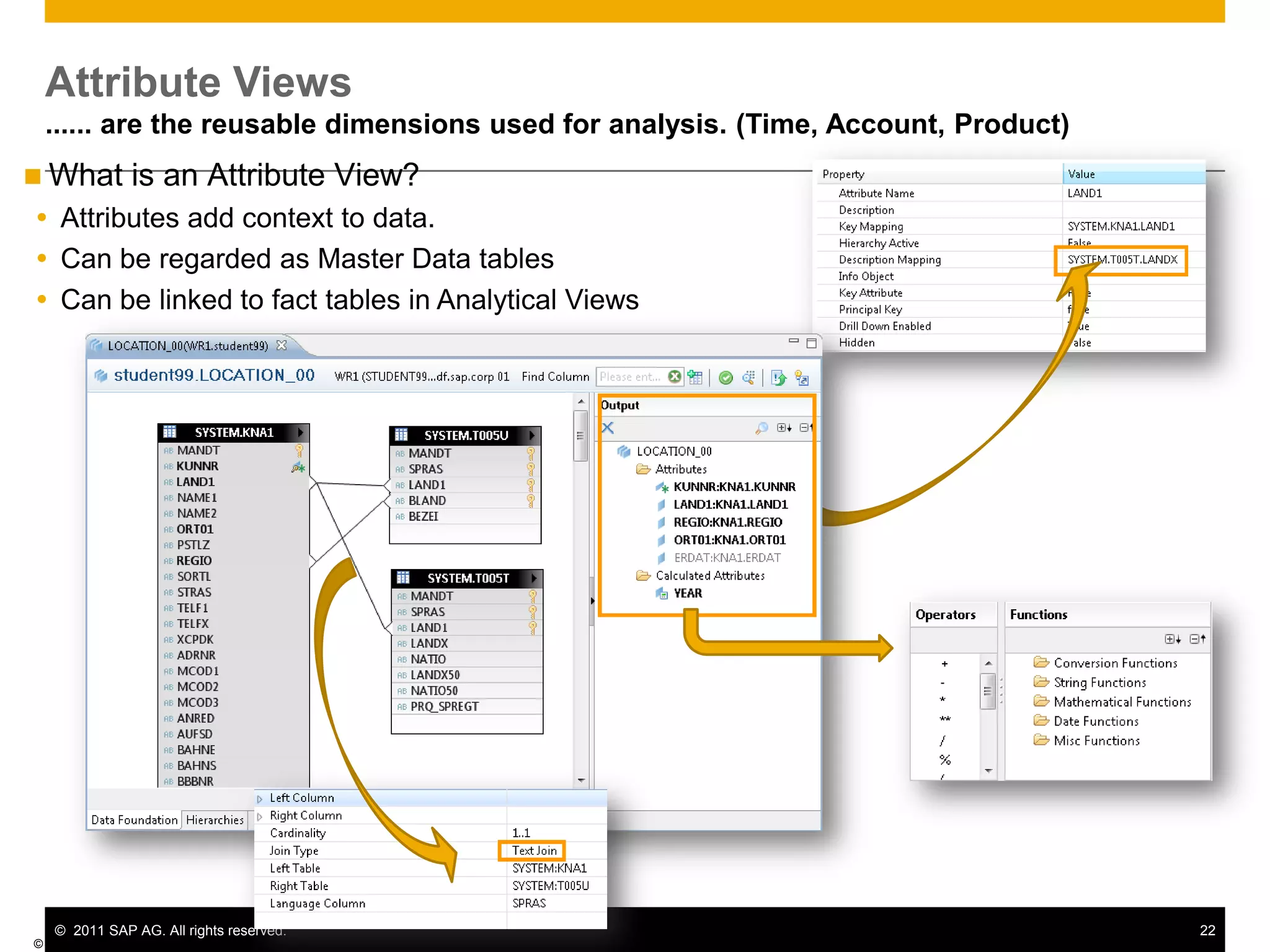
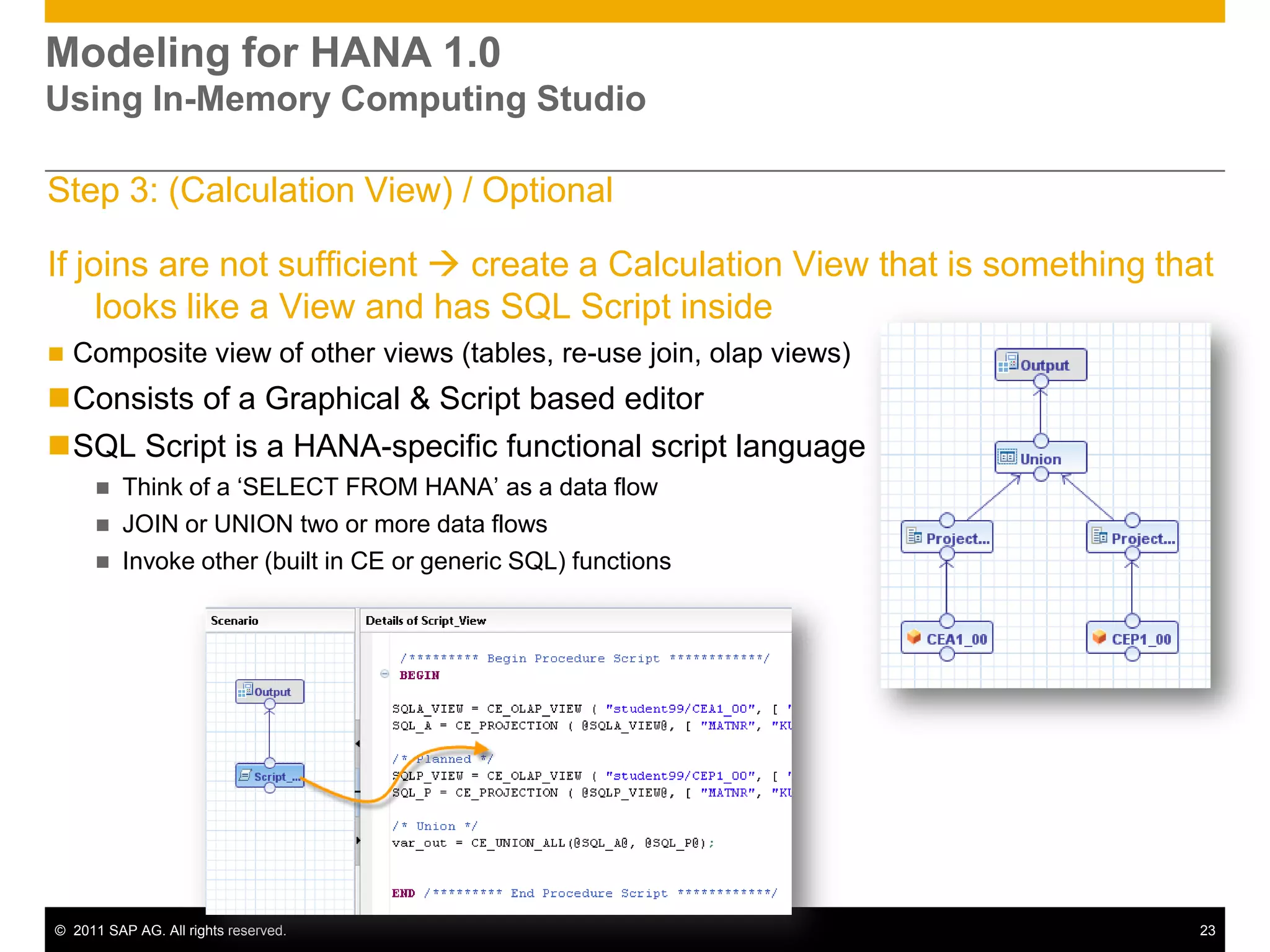
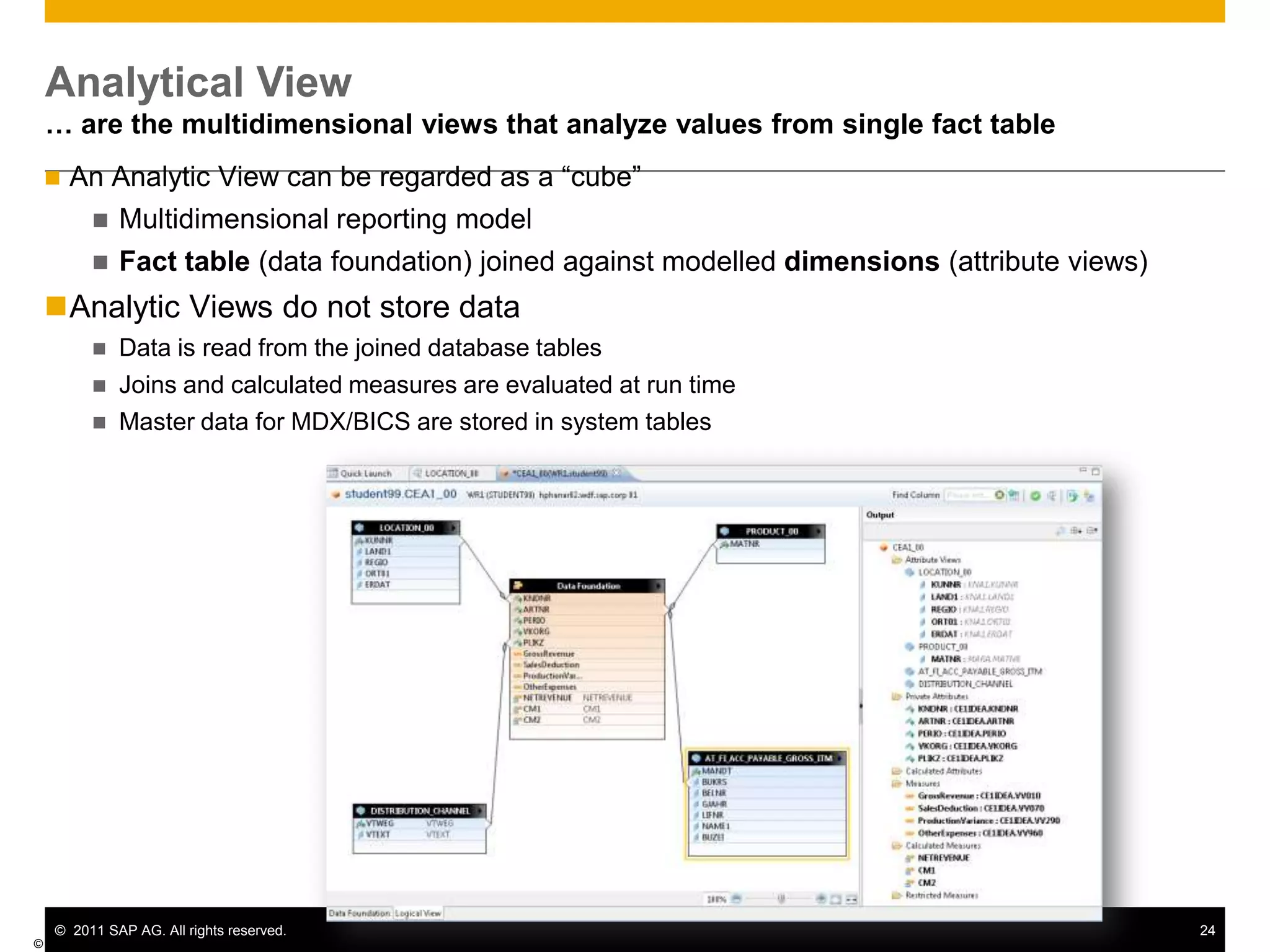
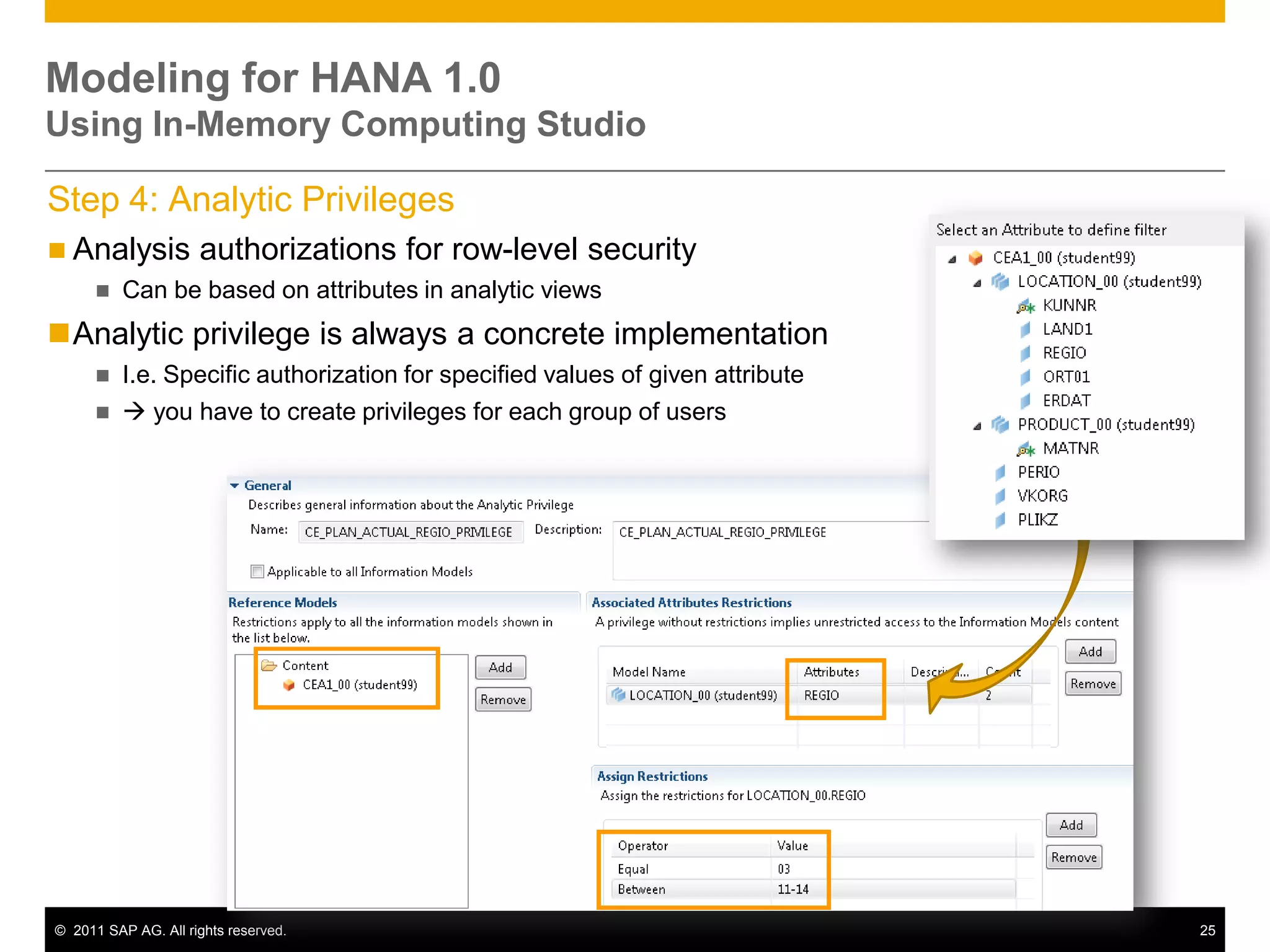
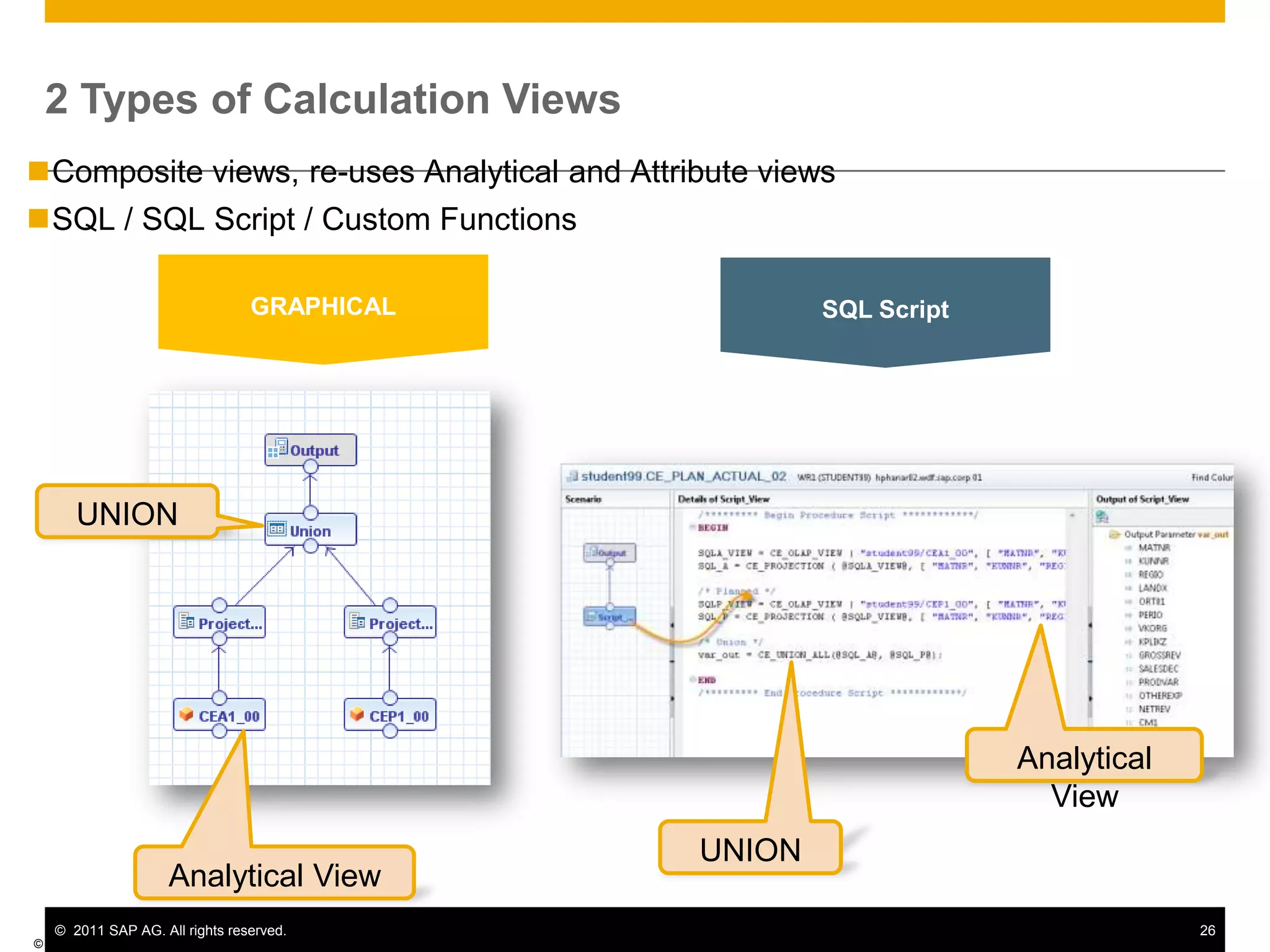
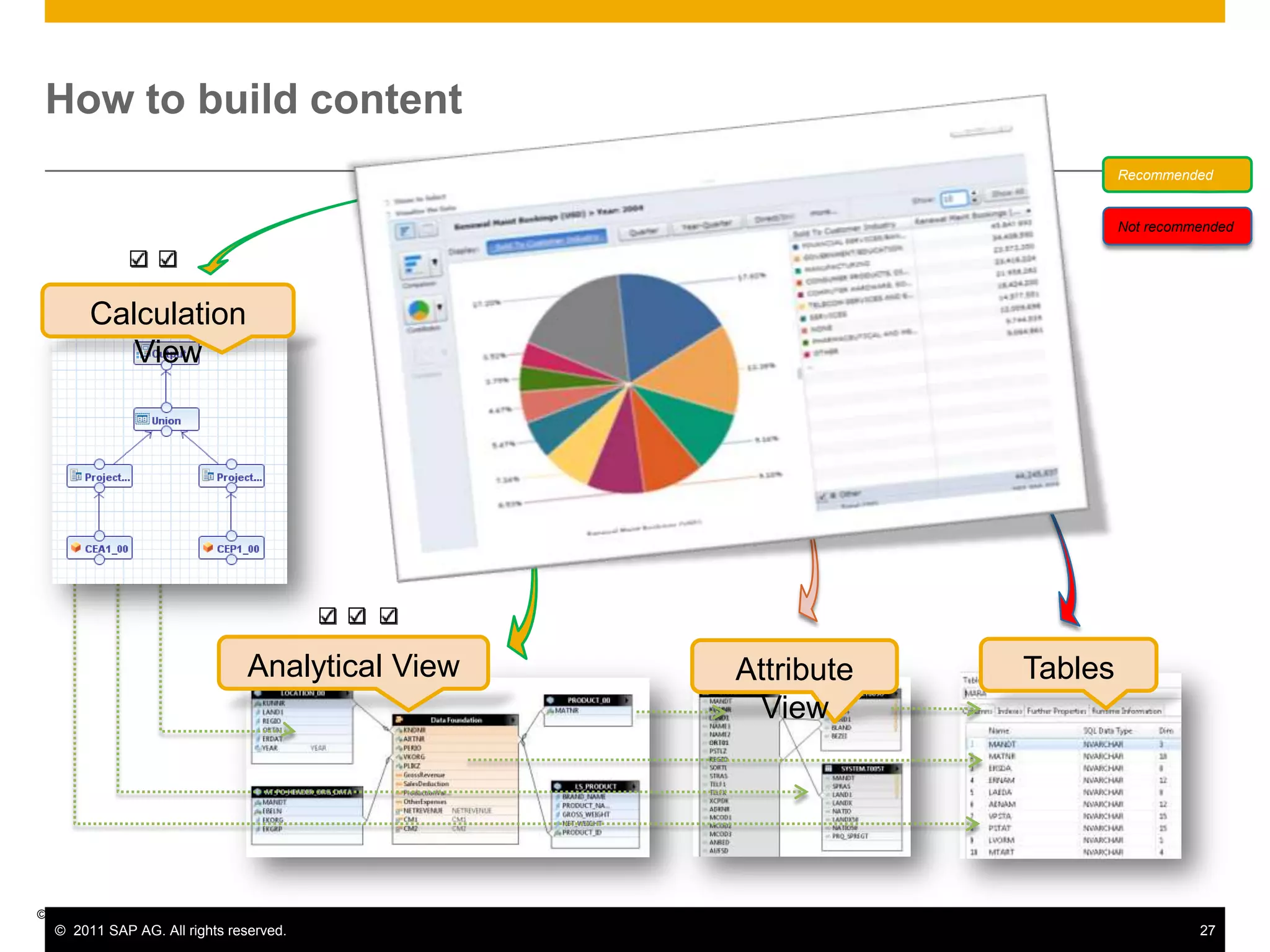
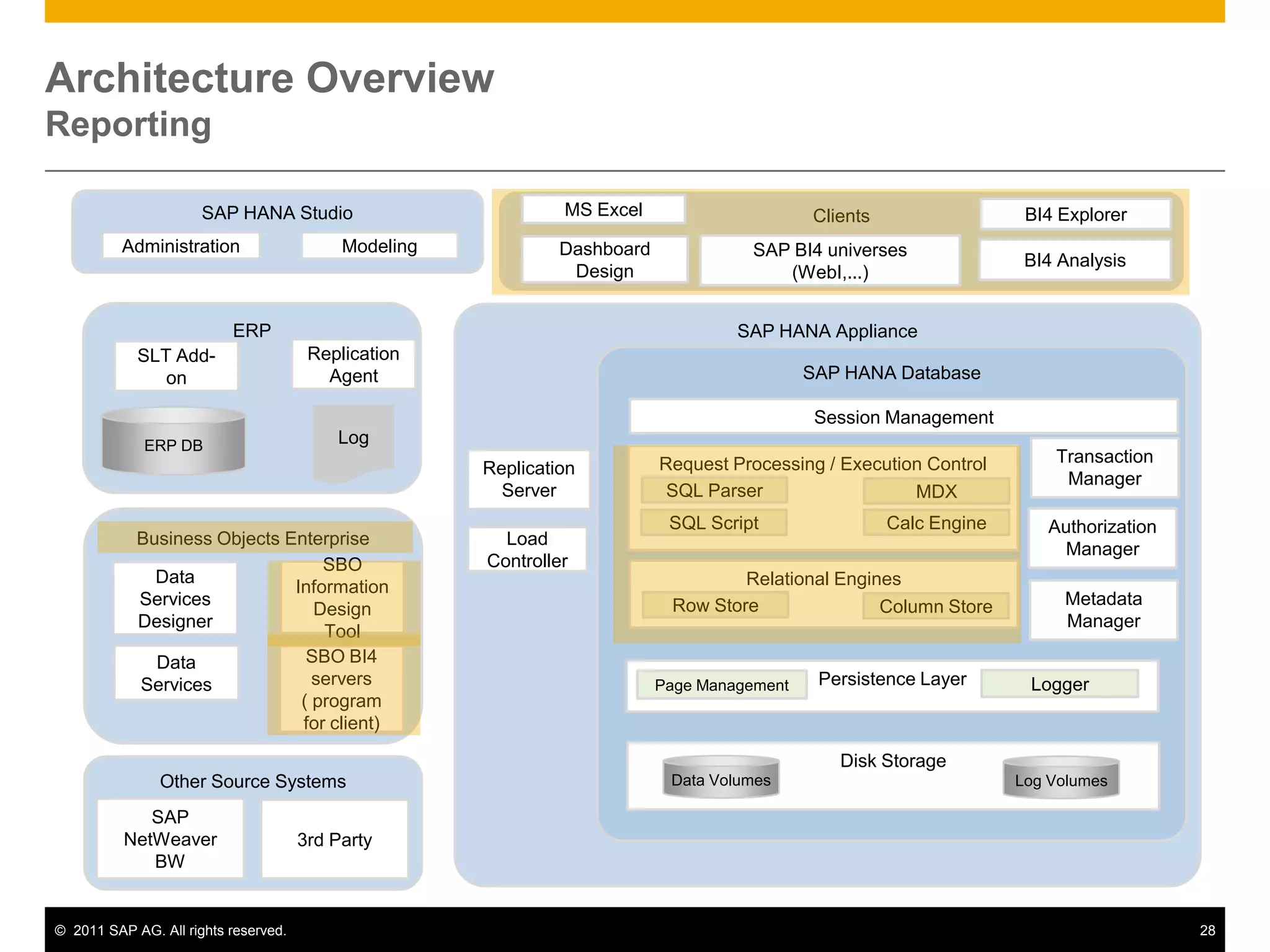
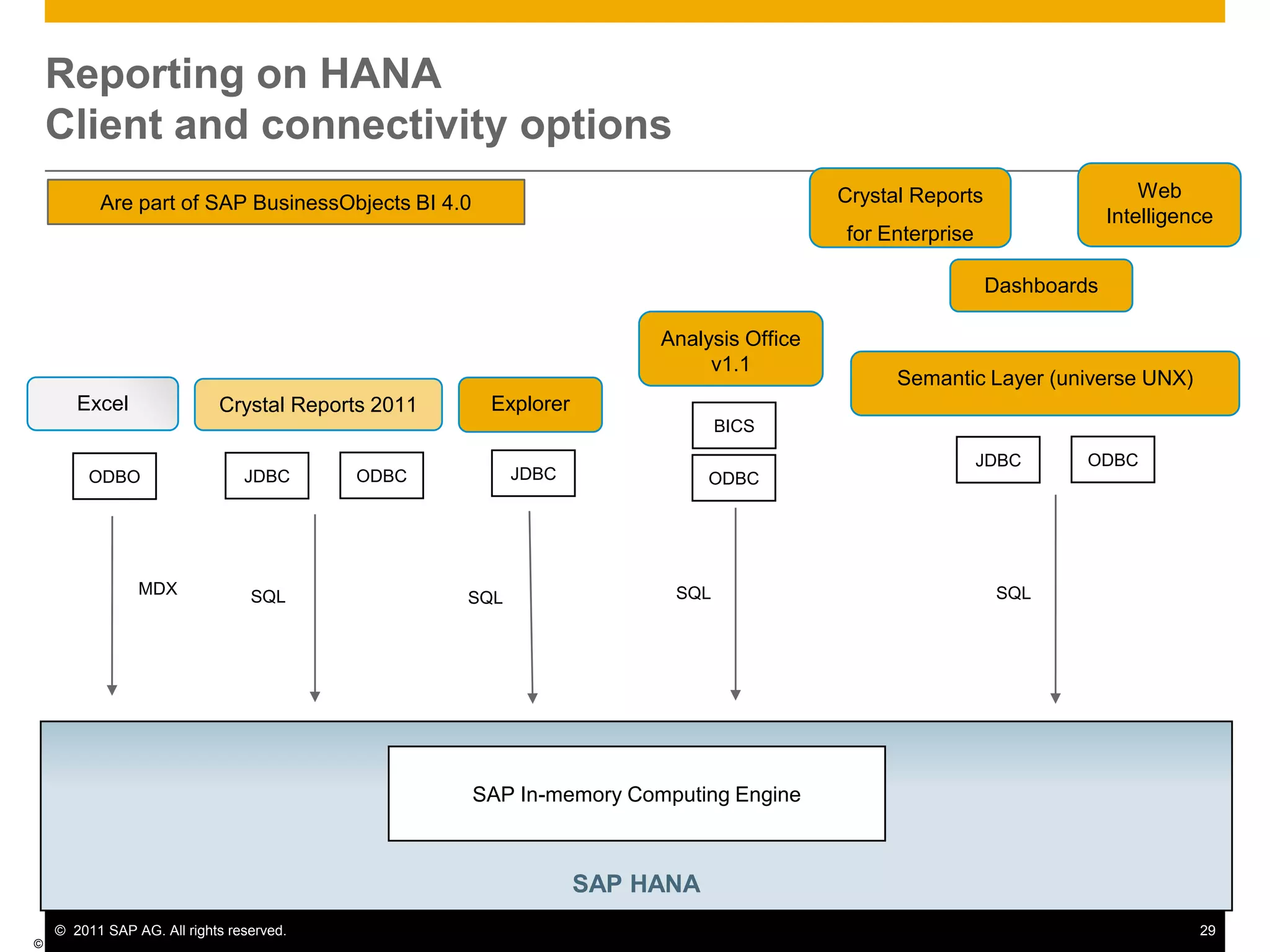
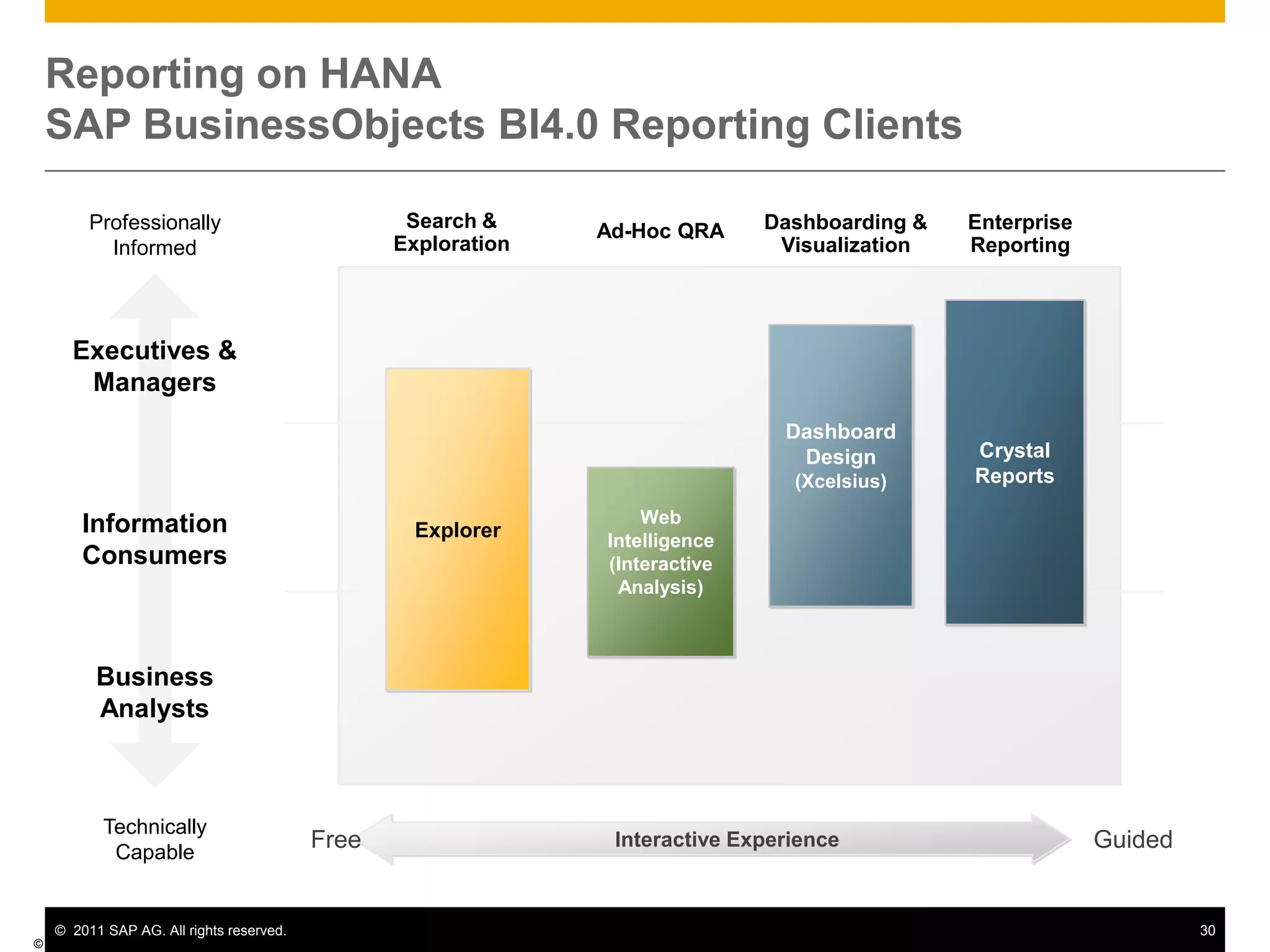
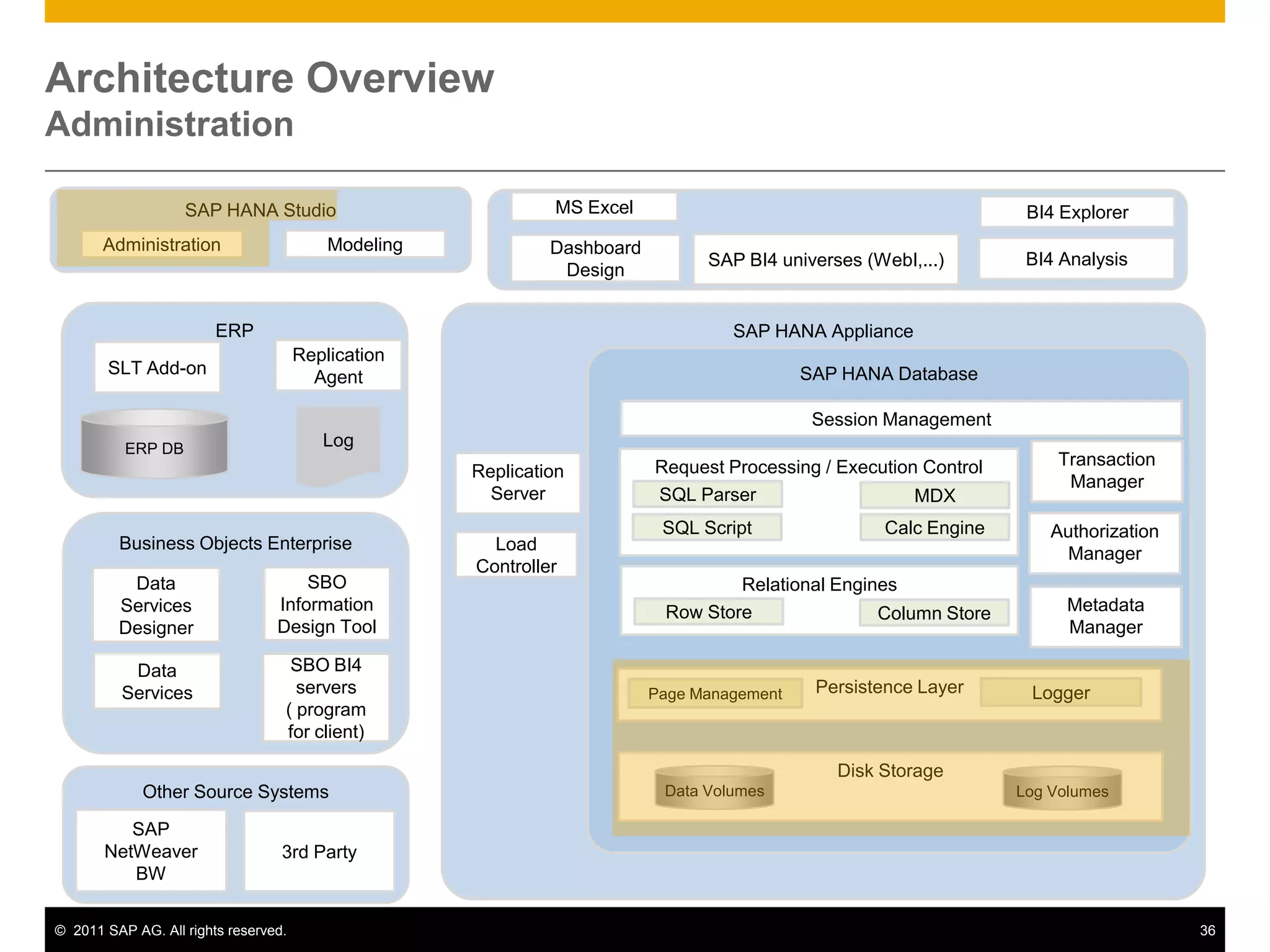
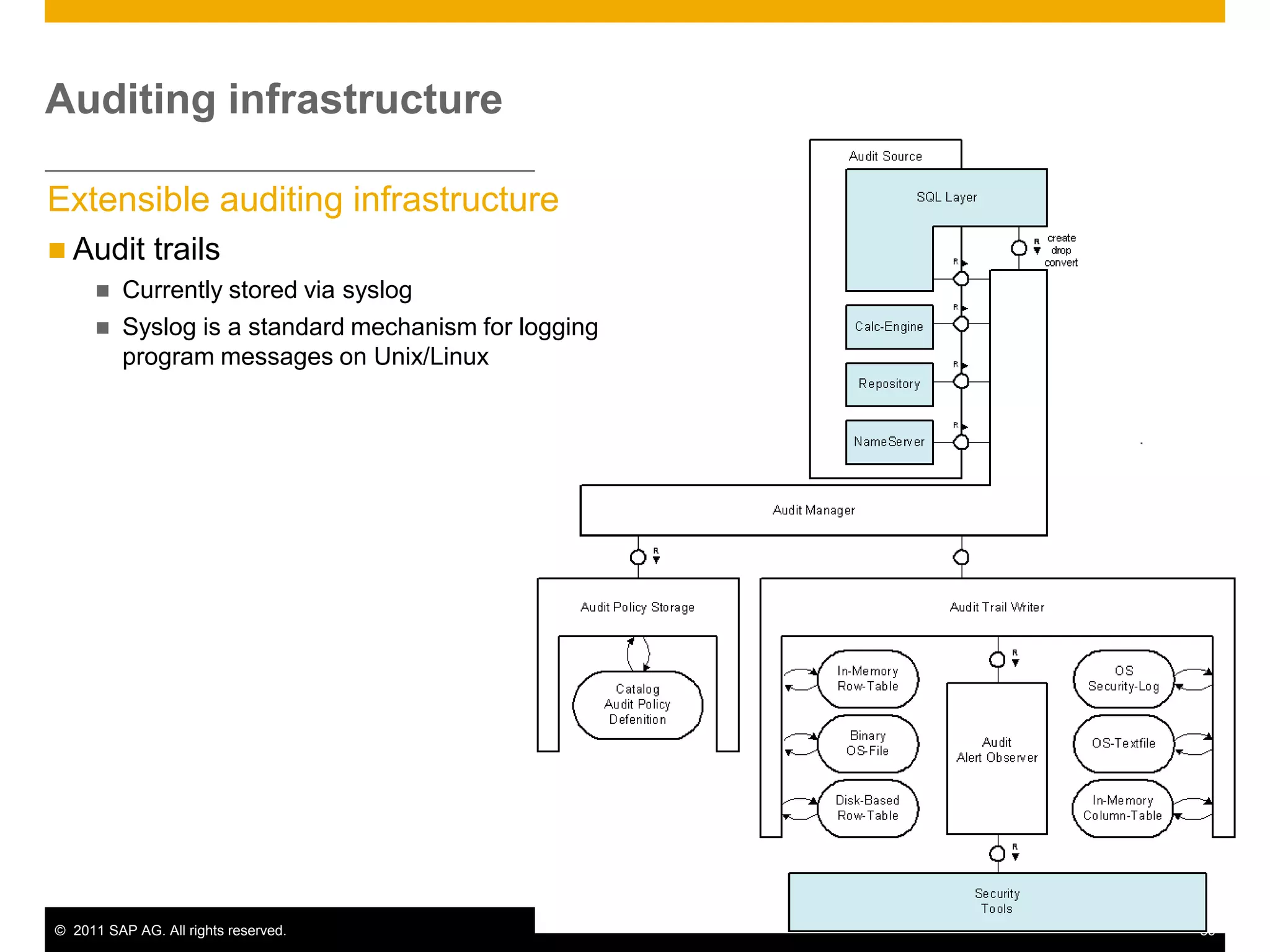
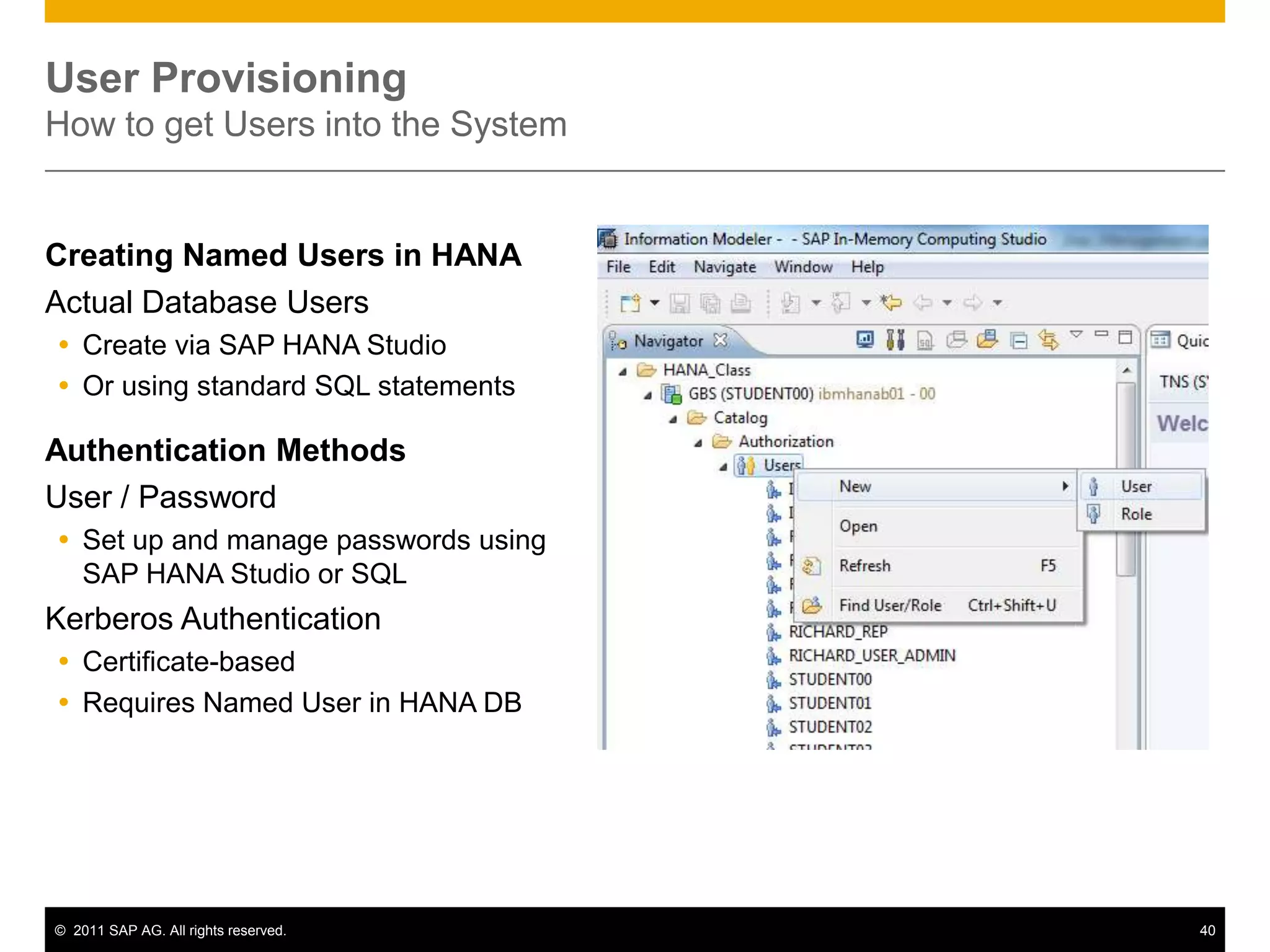
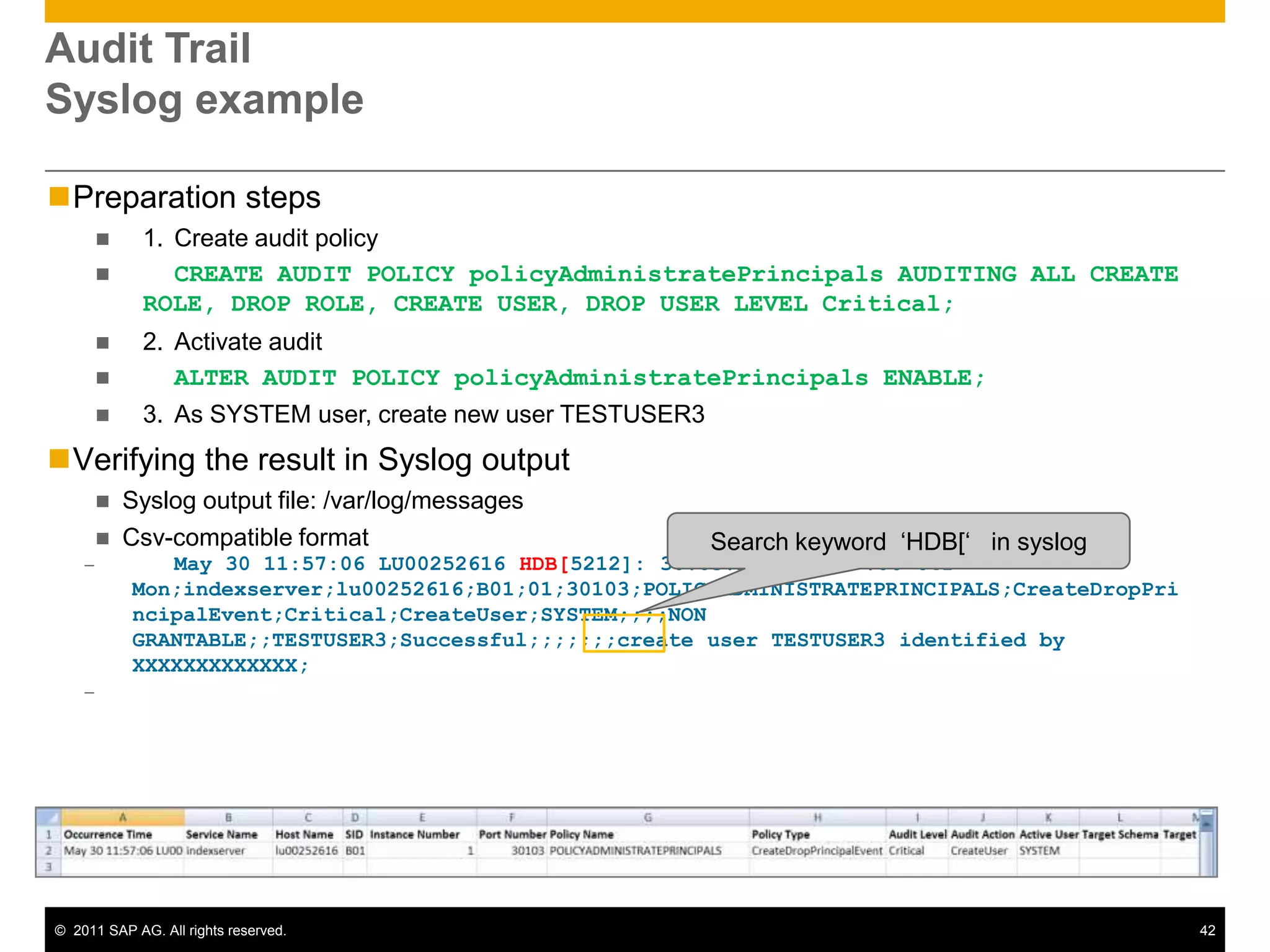
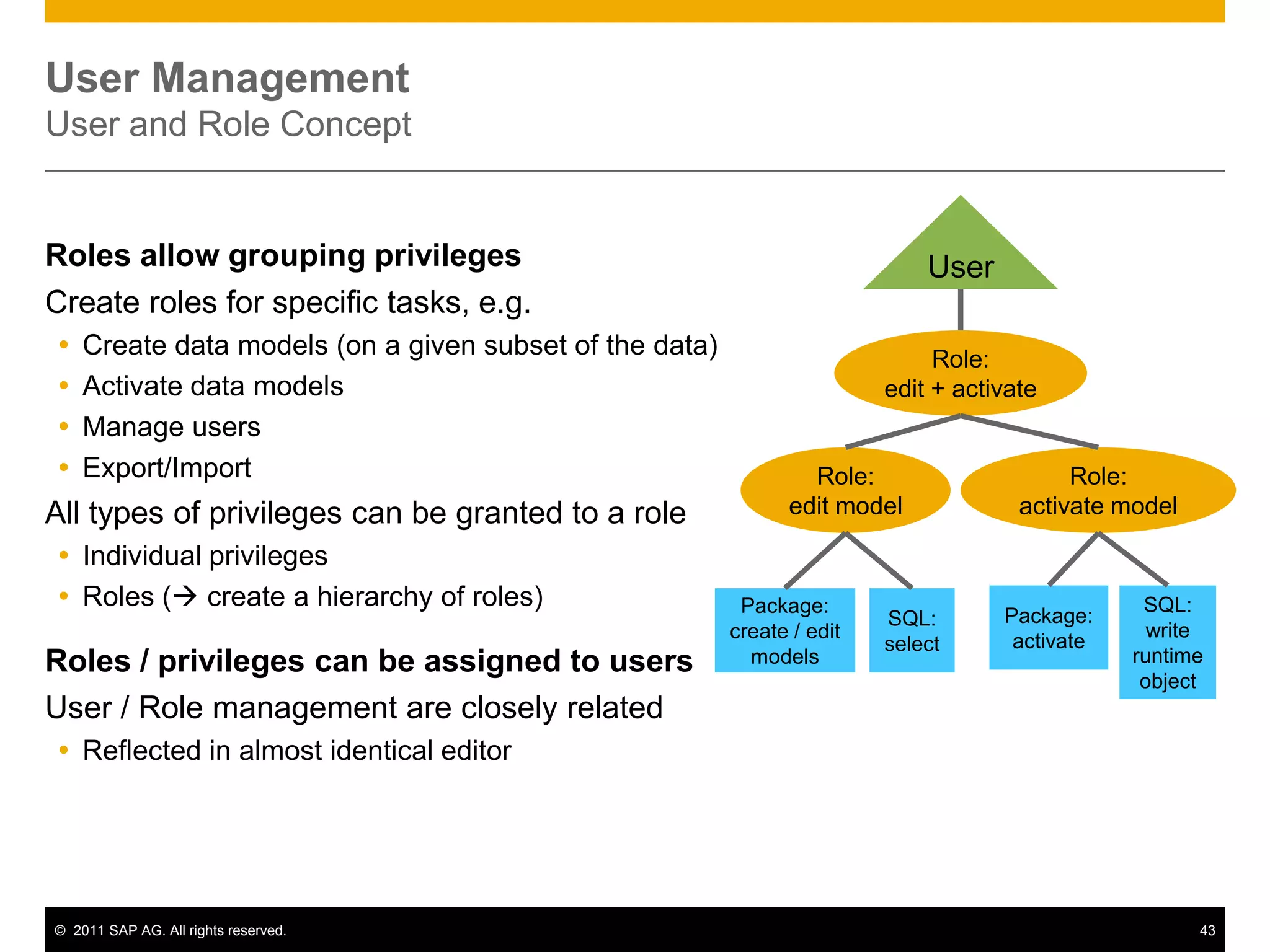
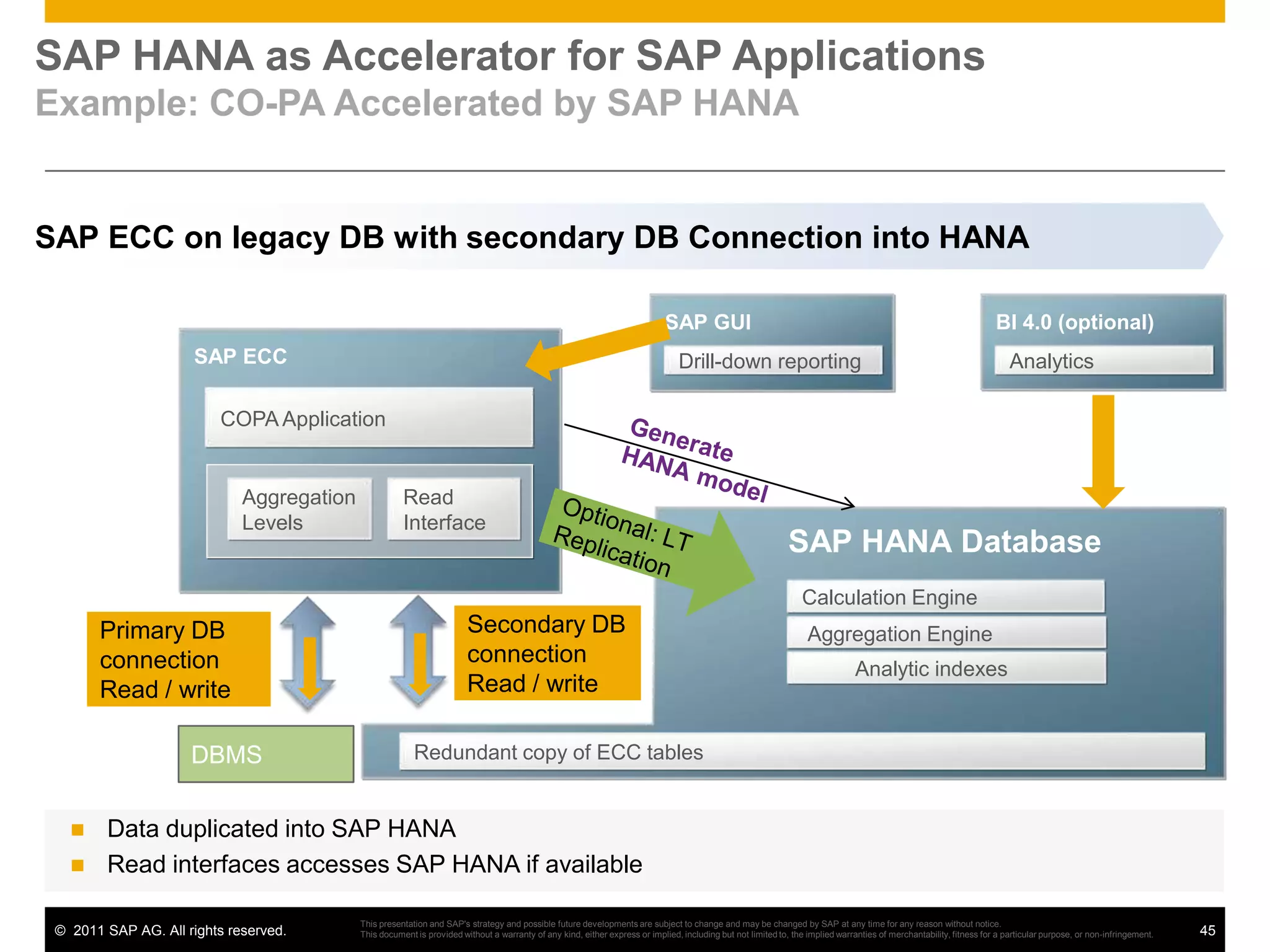
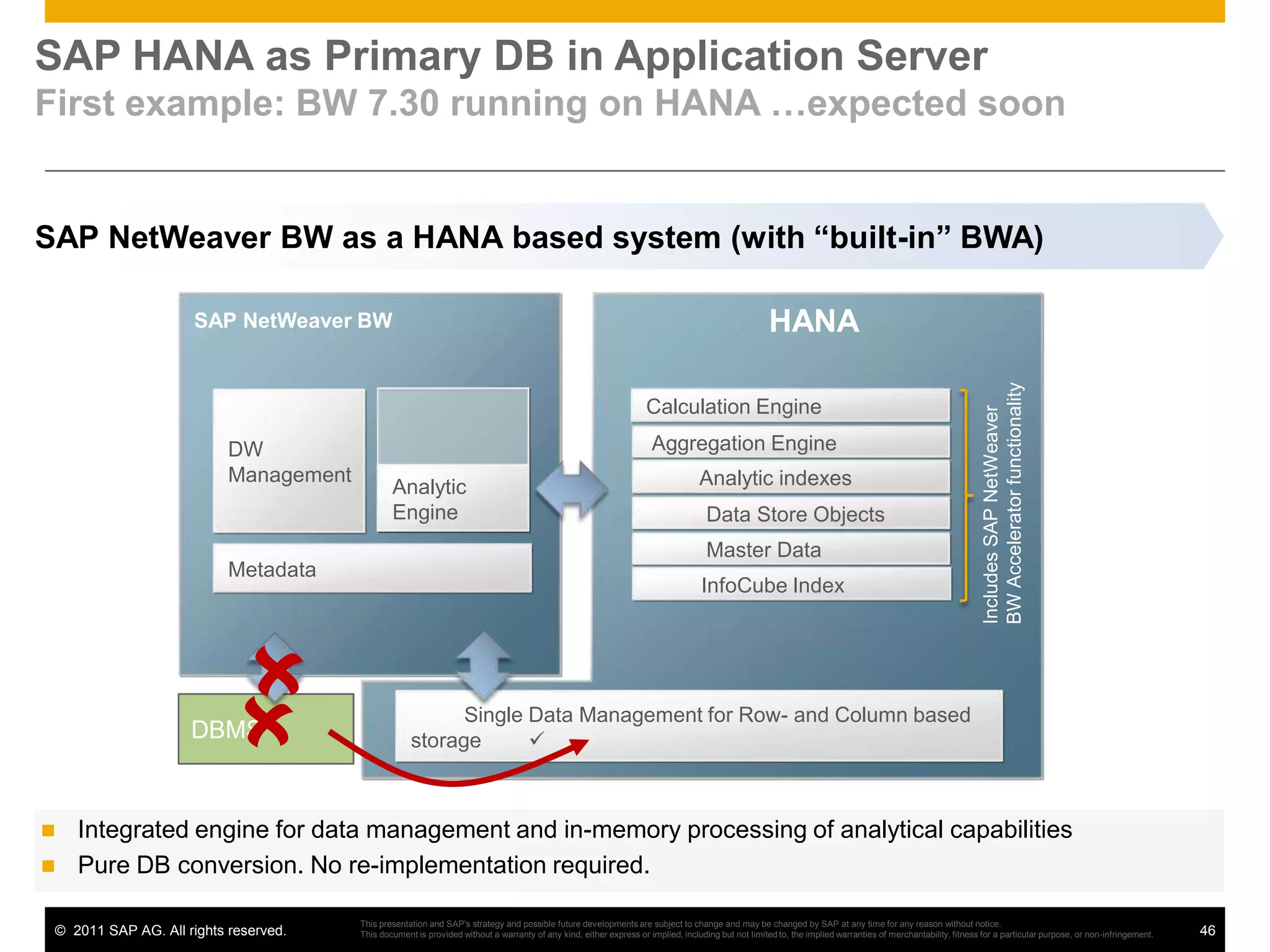
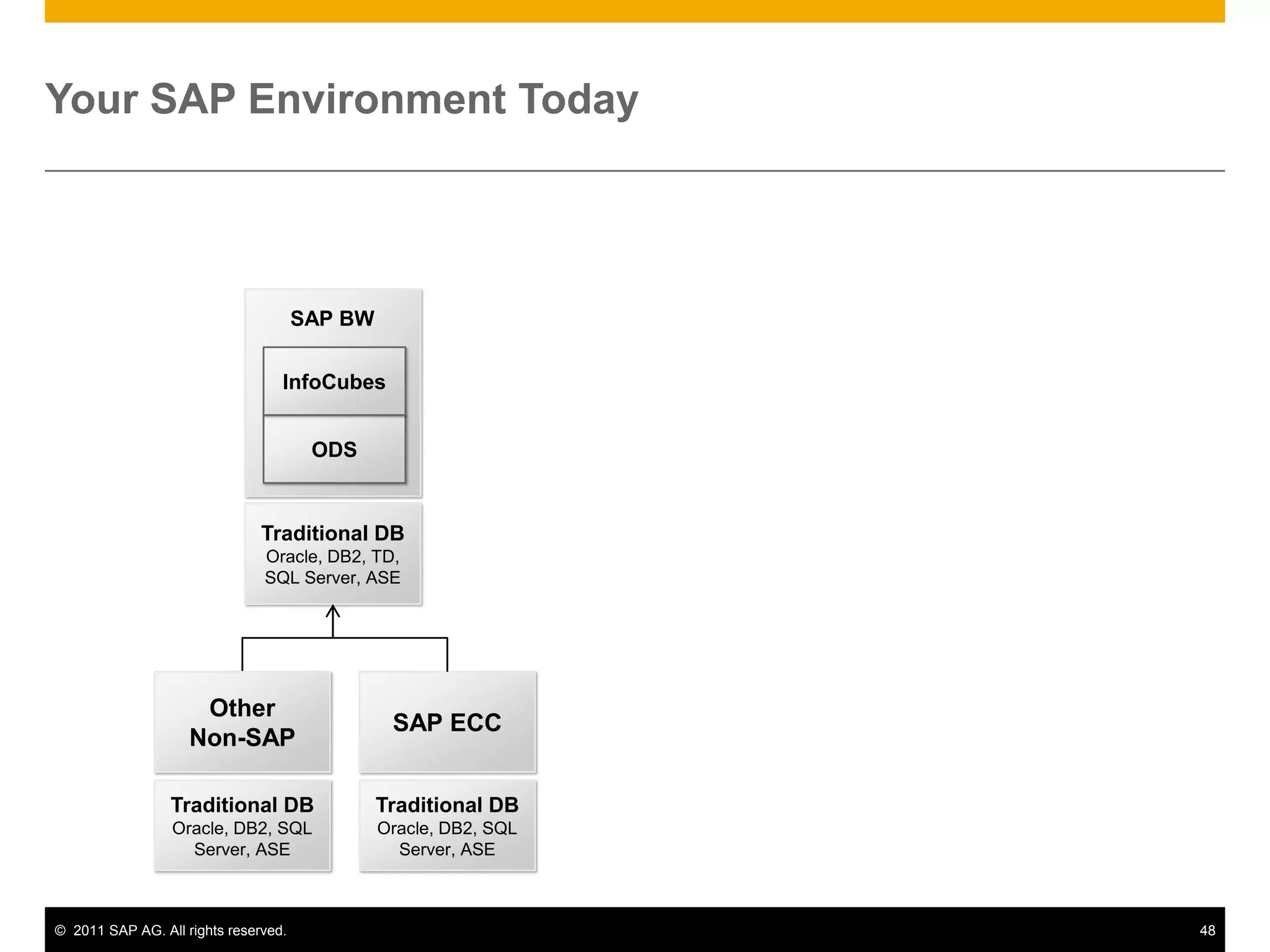
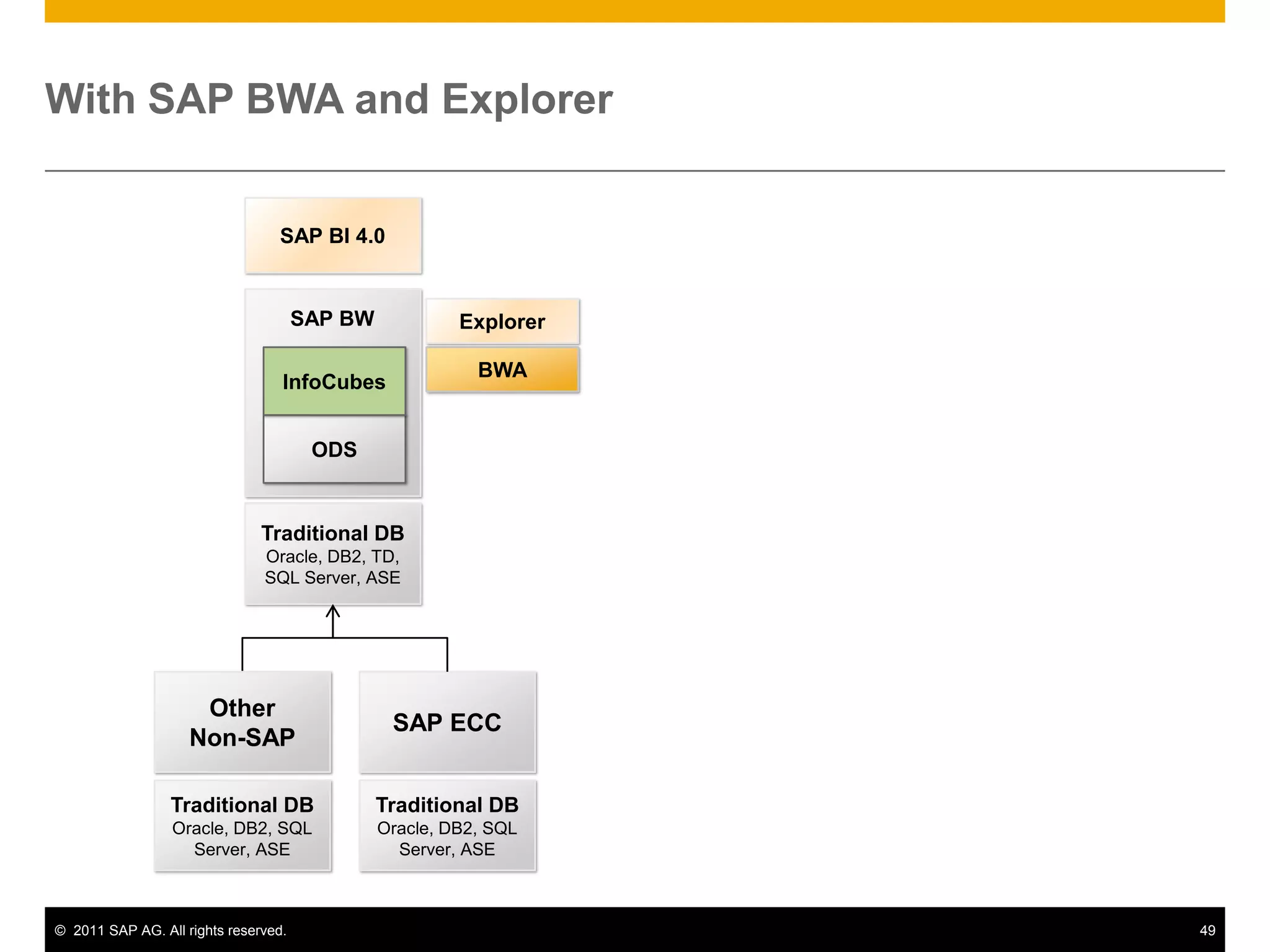
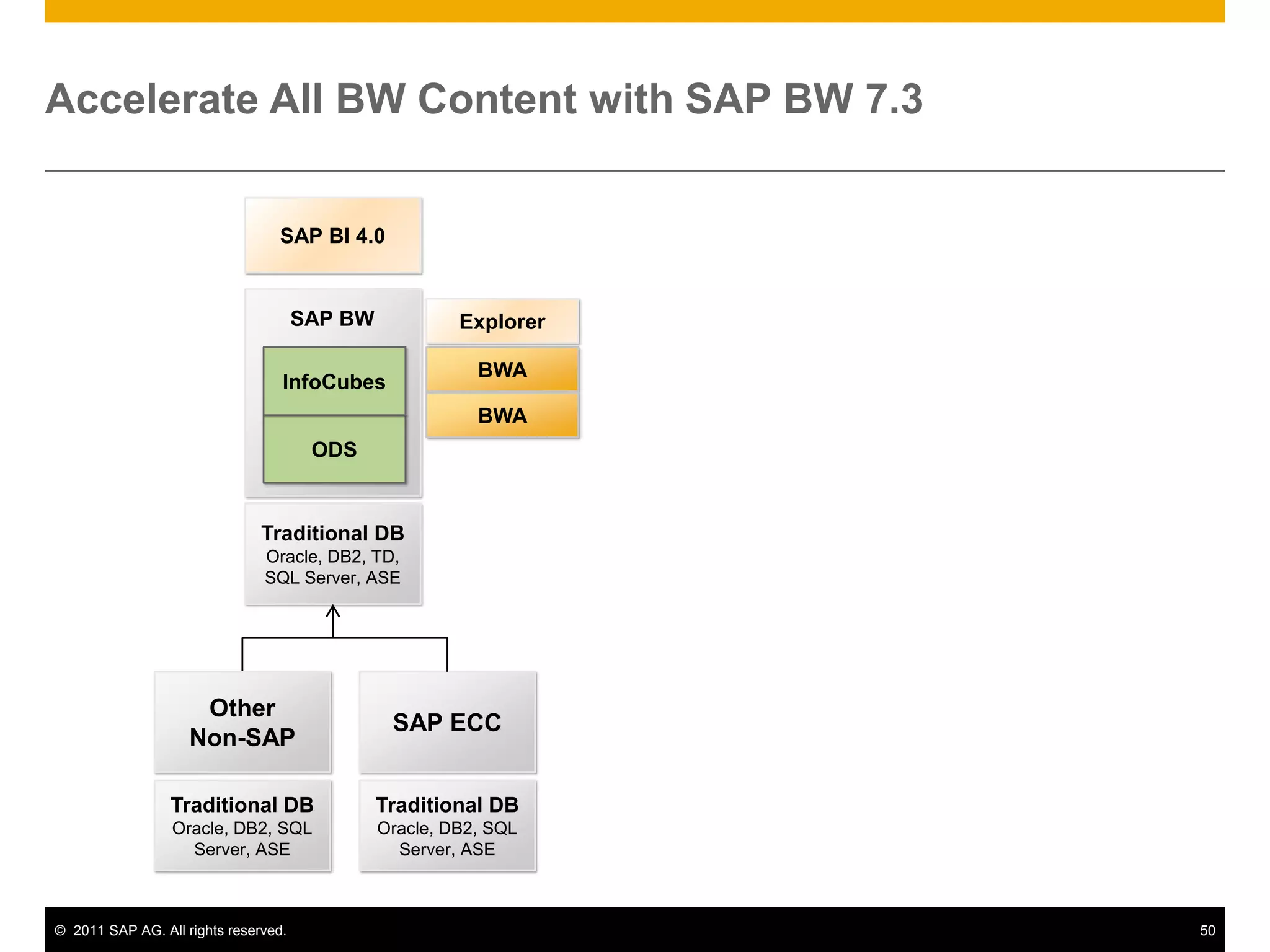
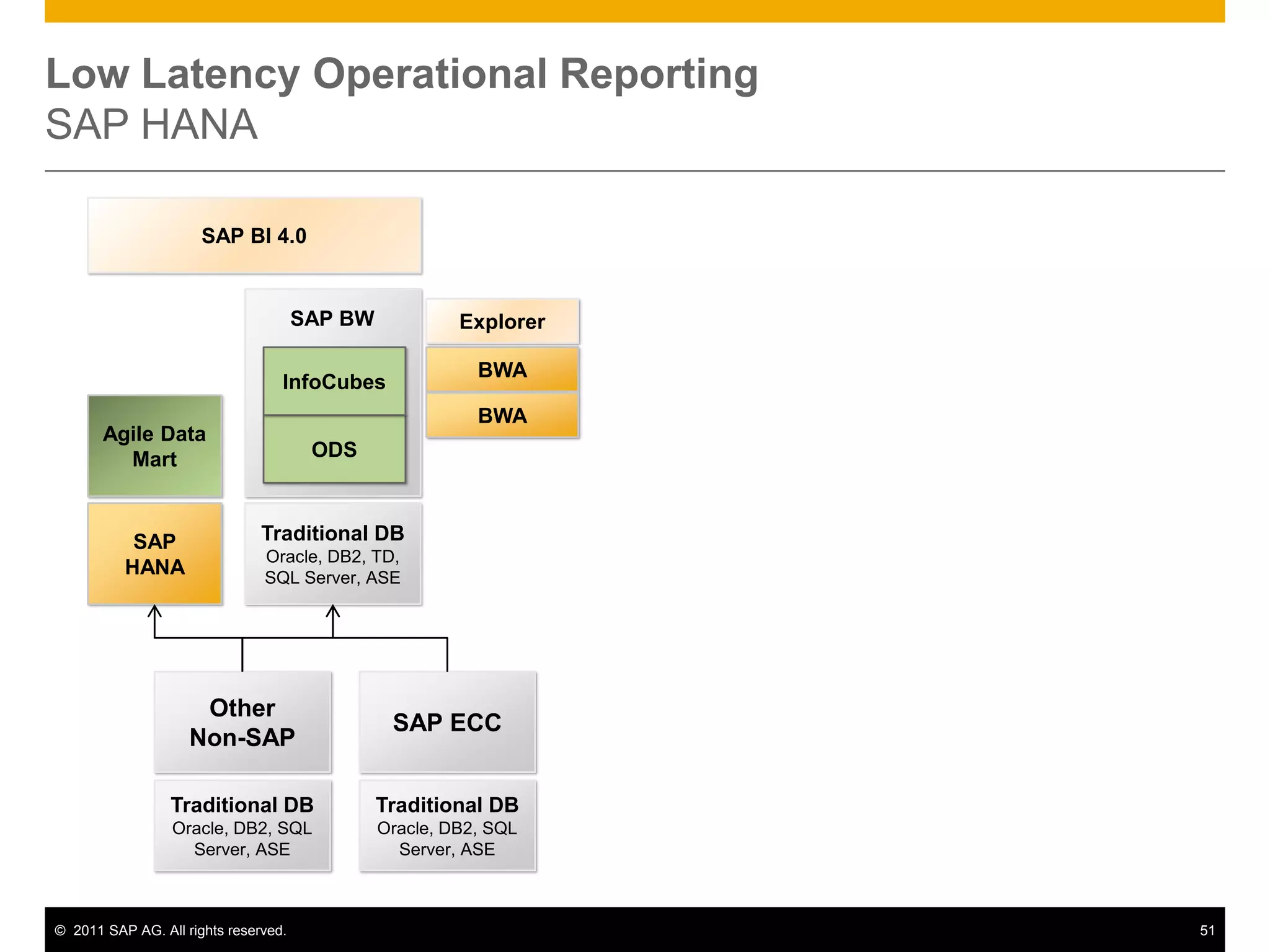
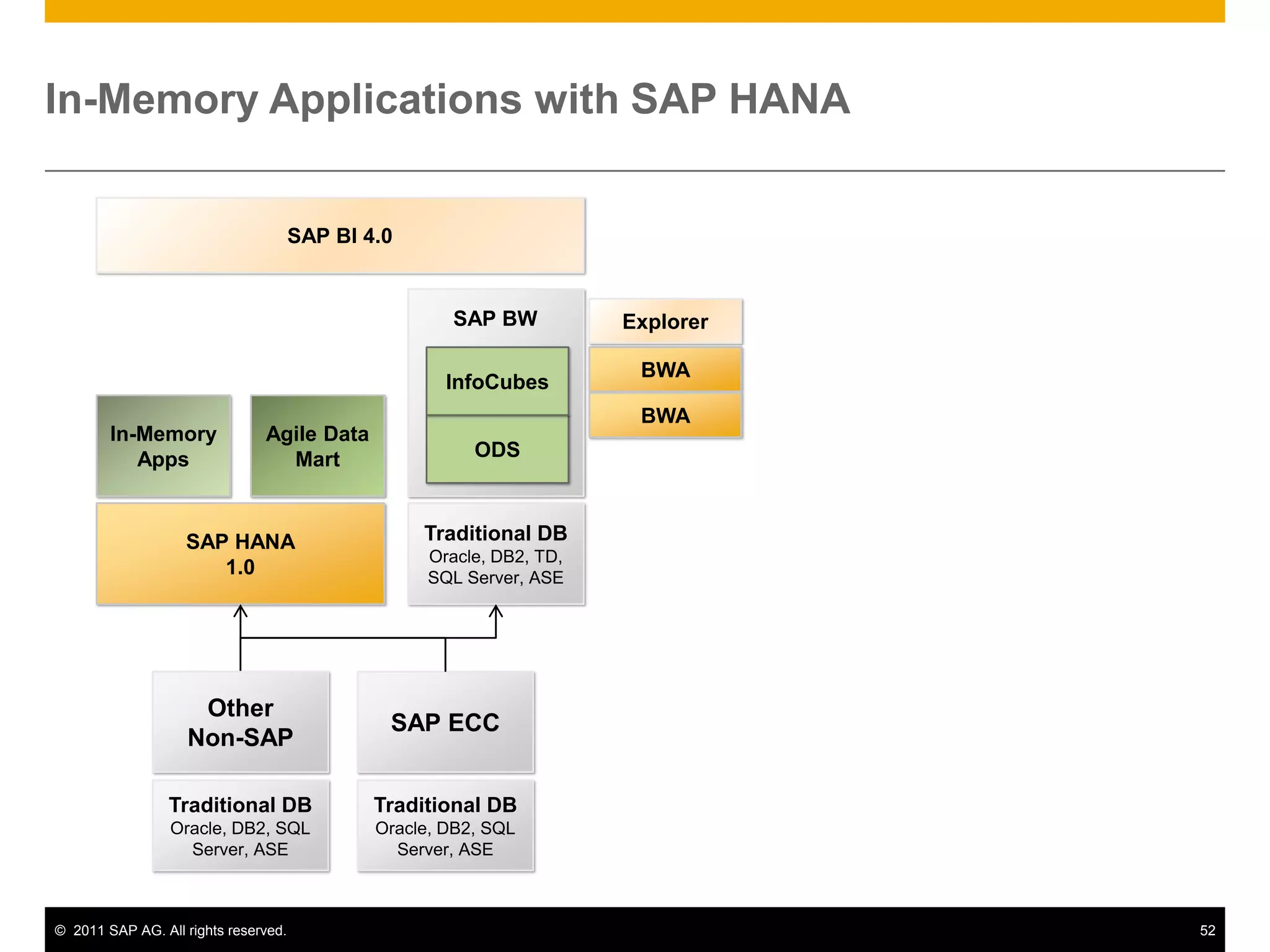
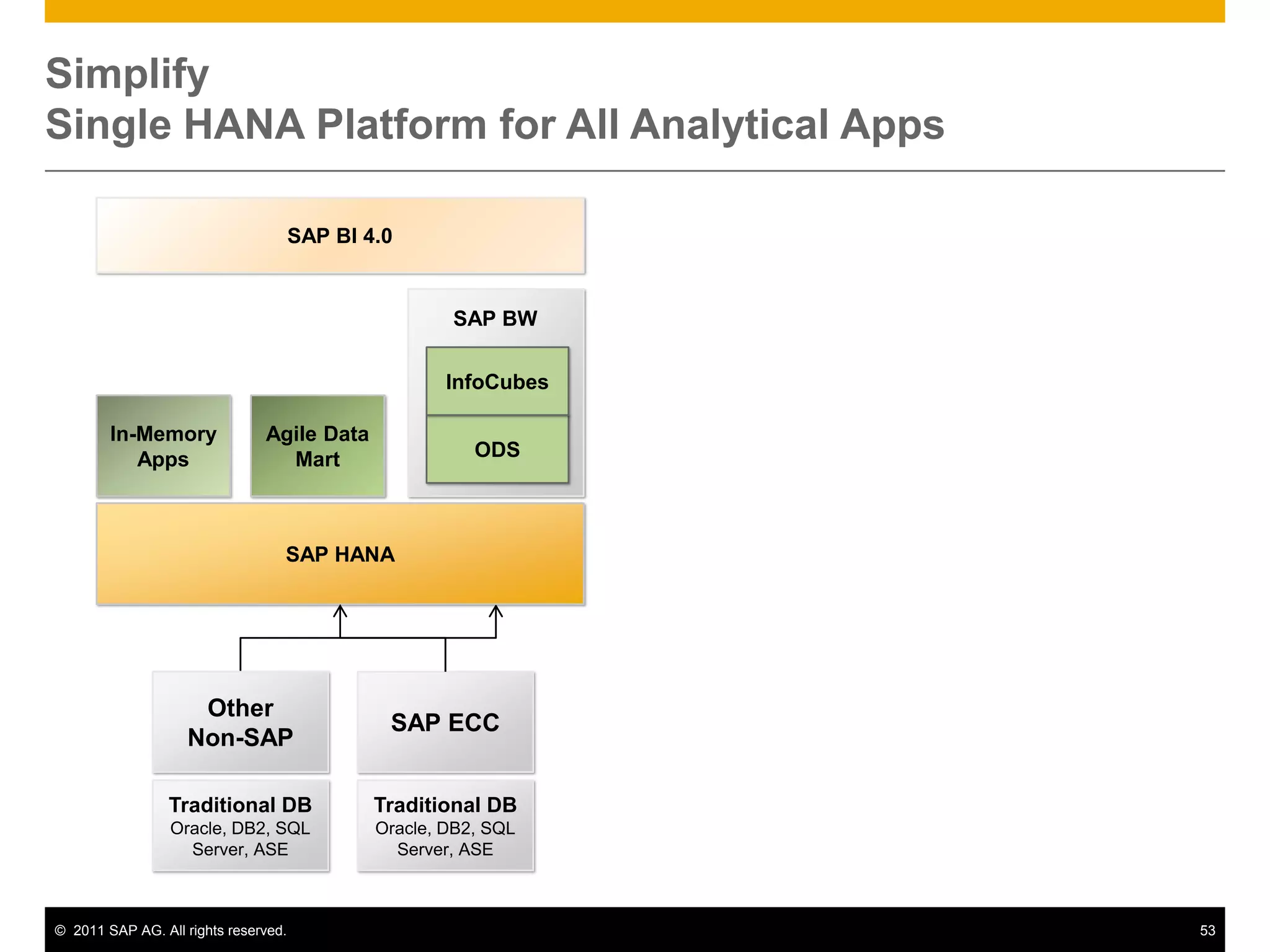
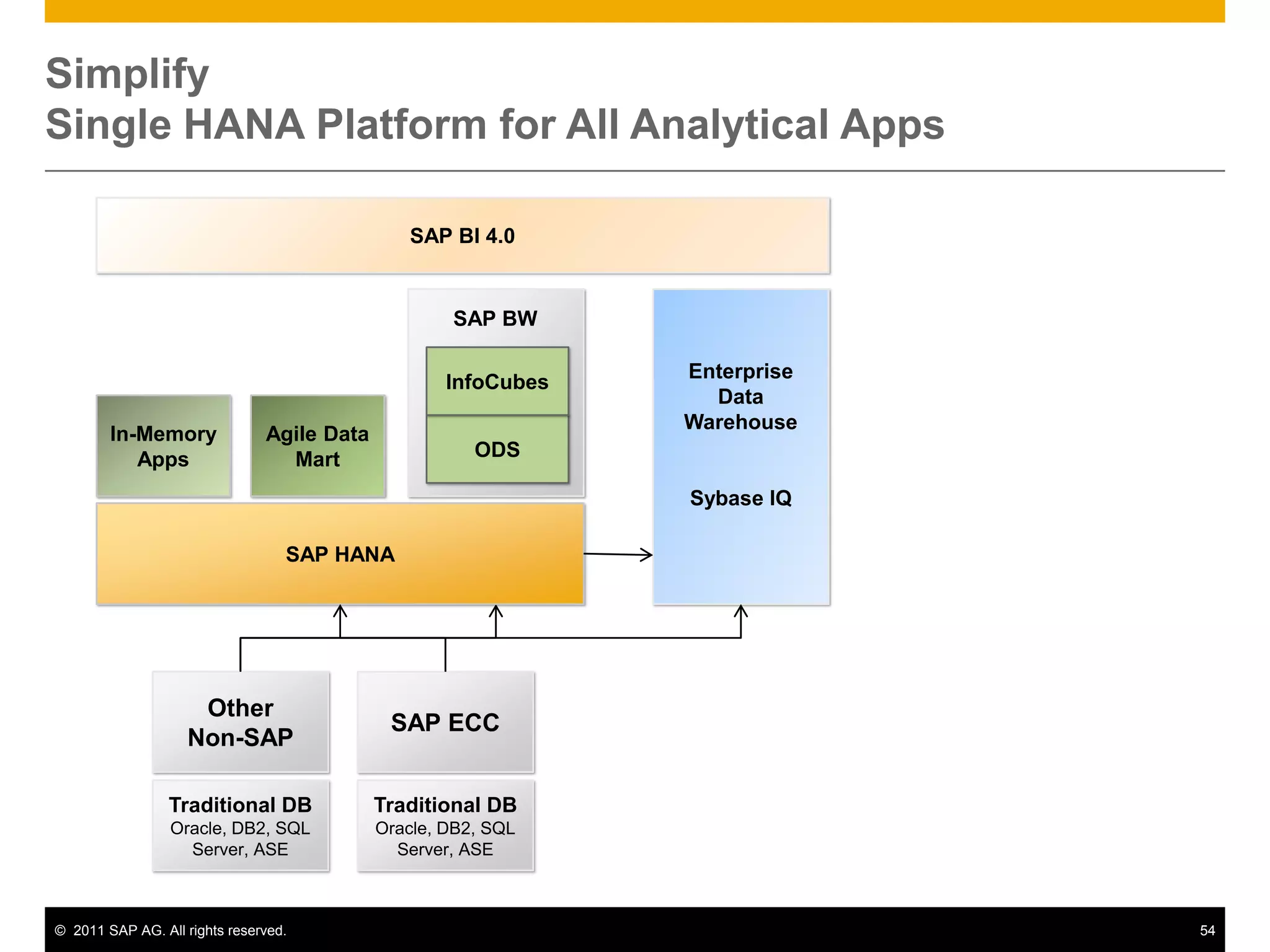
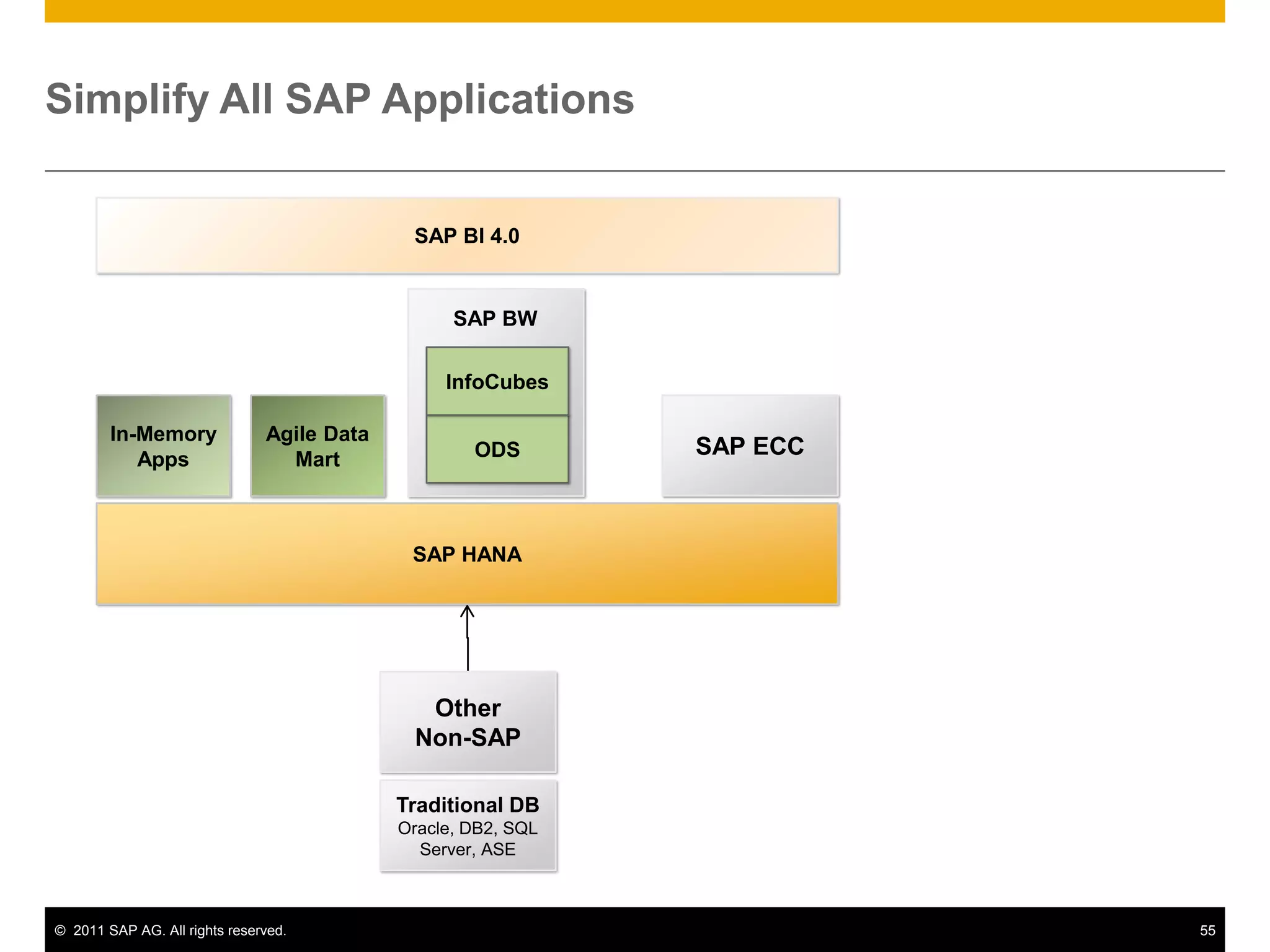
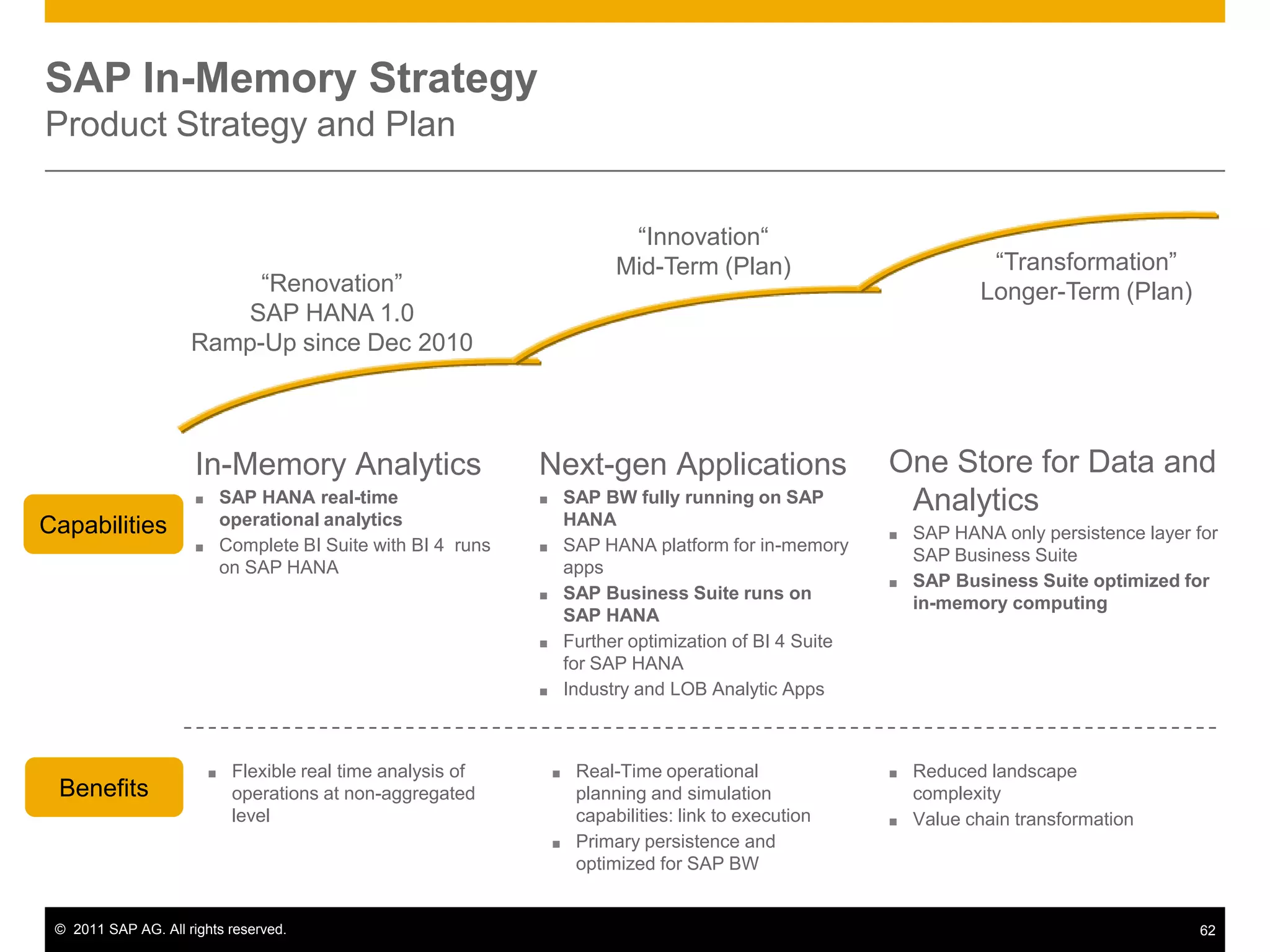
HANA is an in-memory database appliance that allows organizations to analyze large volumes of operational data in real-time. It provides a high-performance foundation for business analytics. Data is loaded into HANA using tools like SAP Data Services. Real-time replication of transactional data from SAP systems can be done using the SAP LT replication functionality. Data is modeled in HANA using attribute and analytical views, separating master and fact data.