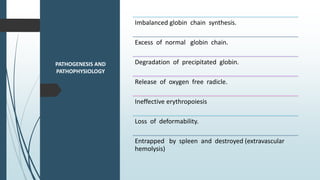
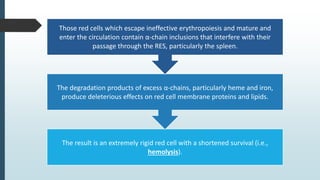
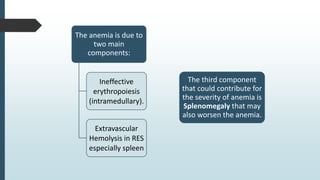
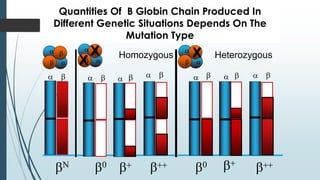
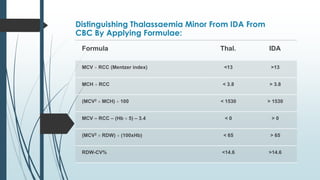
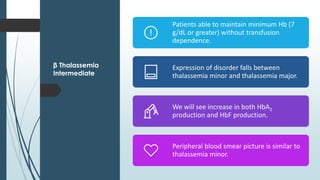
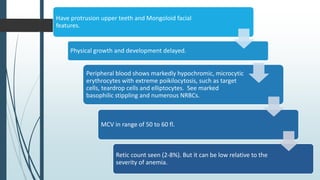
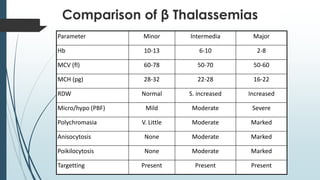
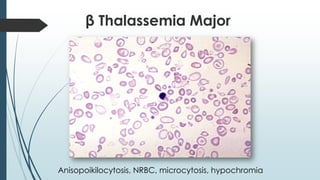
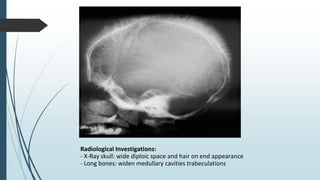
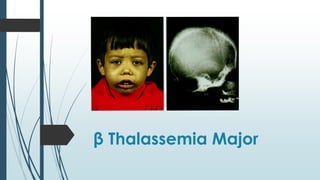
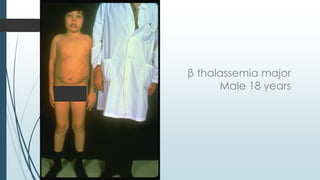
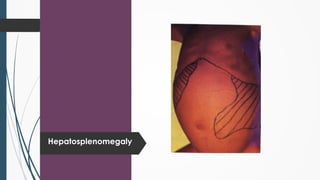
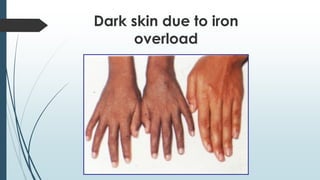
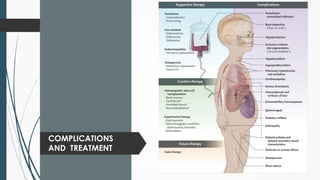
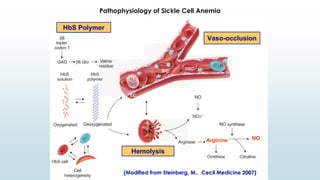
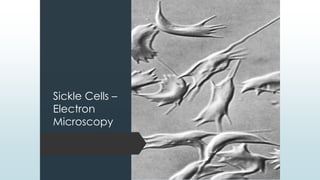
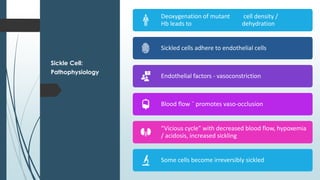
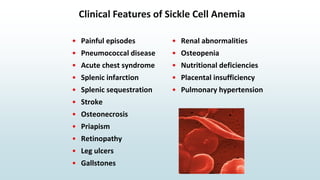
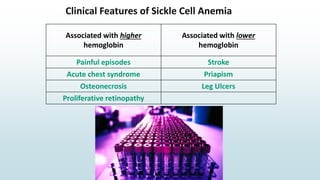
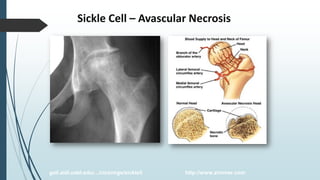
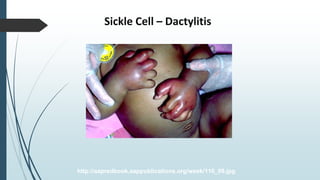
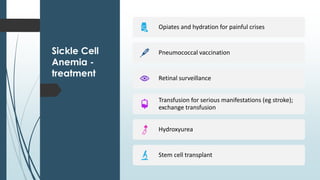
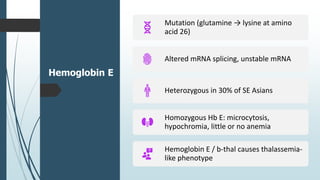
The document discusses β thalassemias, autosomal inherited disorders resulting in reduced β-globin synthesis, leading to severe anemia and various complications. It explains the pathophysiology, types of β thalassemia (minor, intermediate, major), and their clinical features, genetic mutations, laboratory investigations, and associated risks. Additionally, it addresses sickle cell anemia and hemoglobin variants, highlighting their prevalence, pathophysiology, and treatment options.