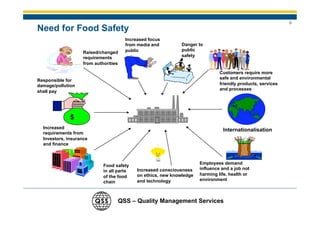
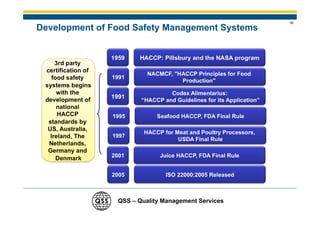
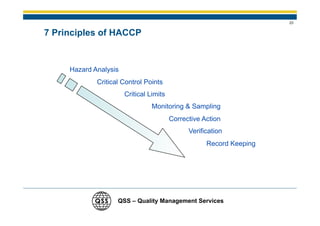
1) There is a need for HACCP certification in the food industry due to large outbreaks of foodborne illness globally that cause human suffering and economic costs.
2) Major outbreaks like the 2011 E. coli outbreak in Germany and the 2008 milk contamination incident in China sickened and killed many people, costing countries hundreds of millions.
3) Factors like increased public awareness, regulatory requirements, and international trade are driving the need for stronger food safety systems like HACCP certification in the food industry to protect public health.