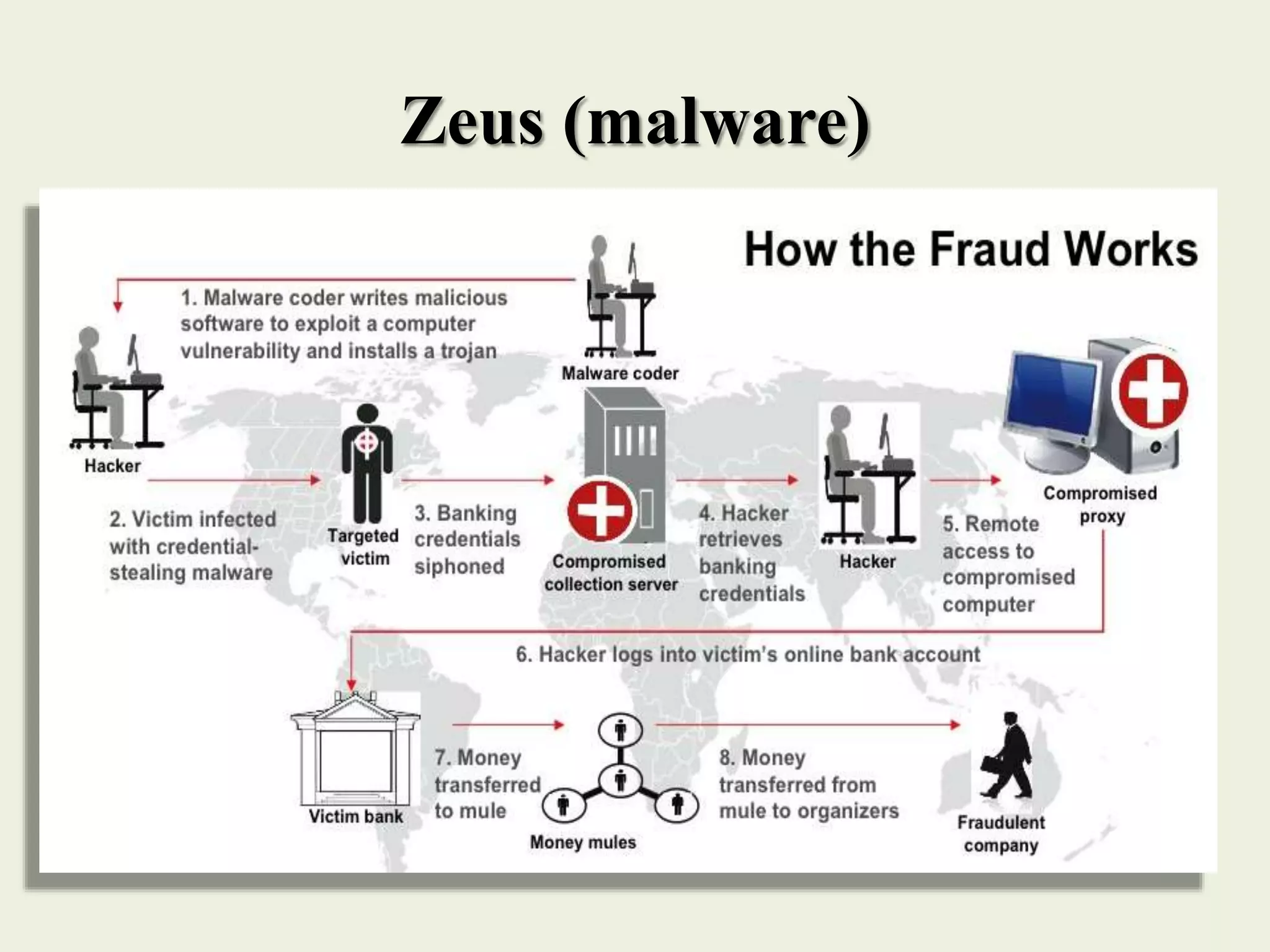
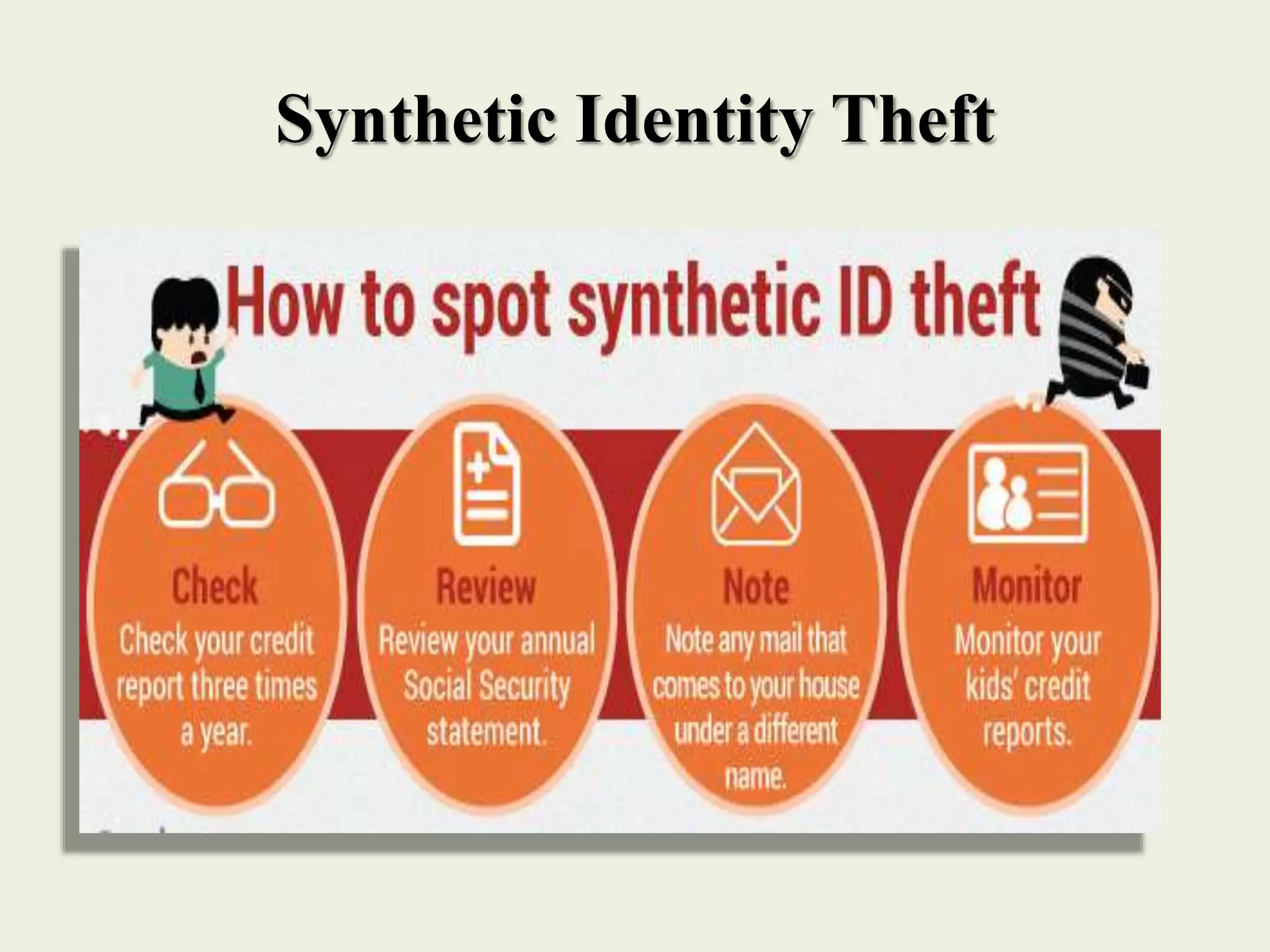
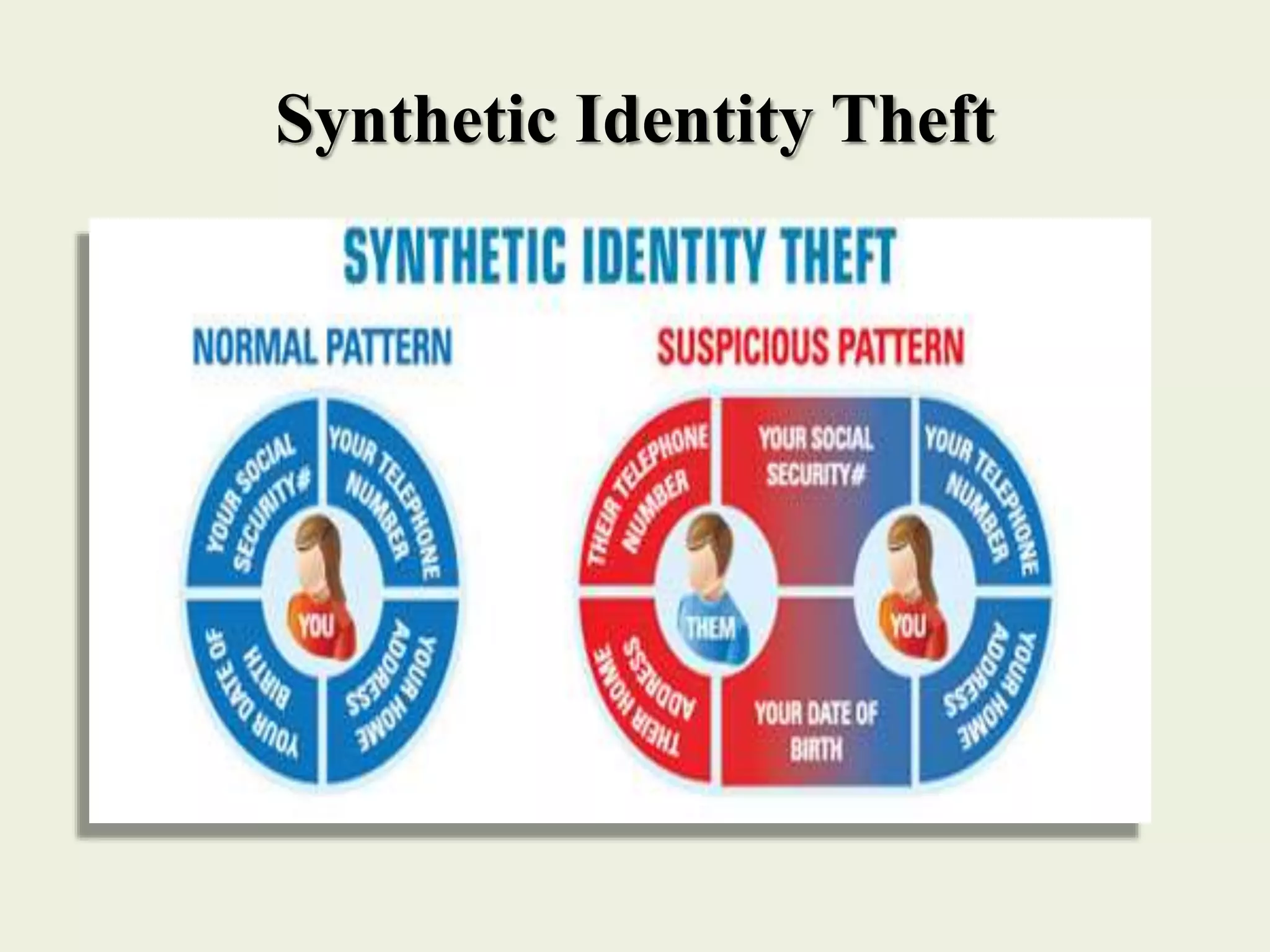
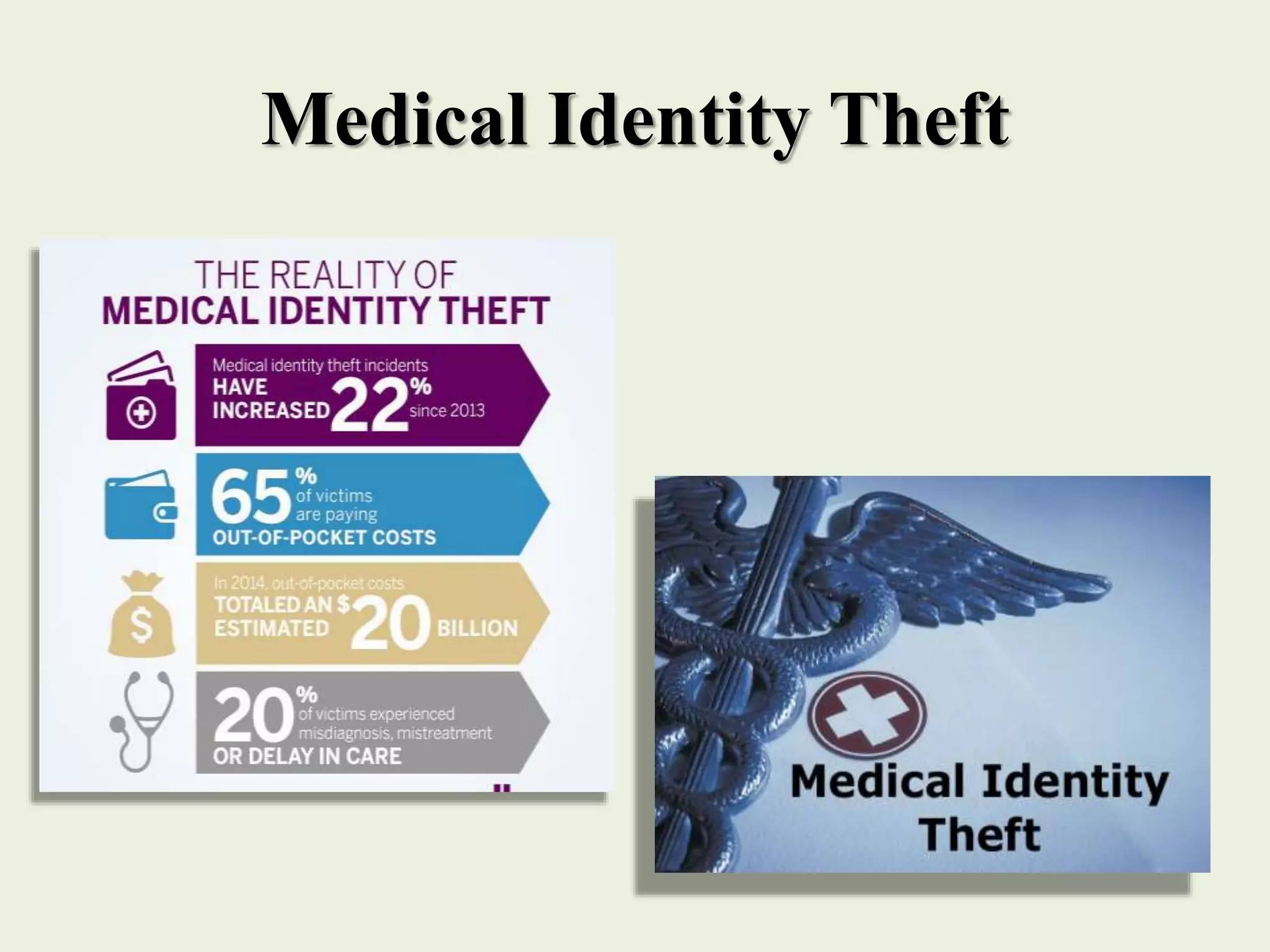
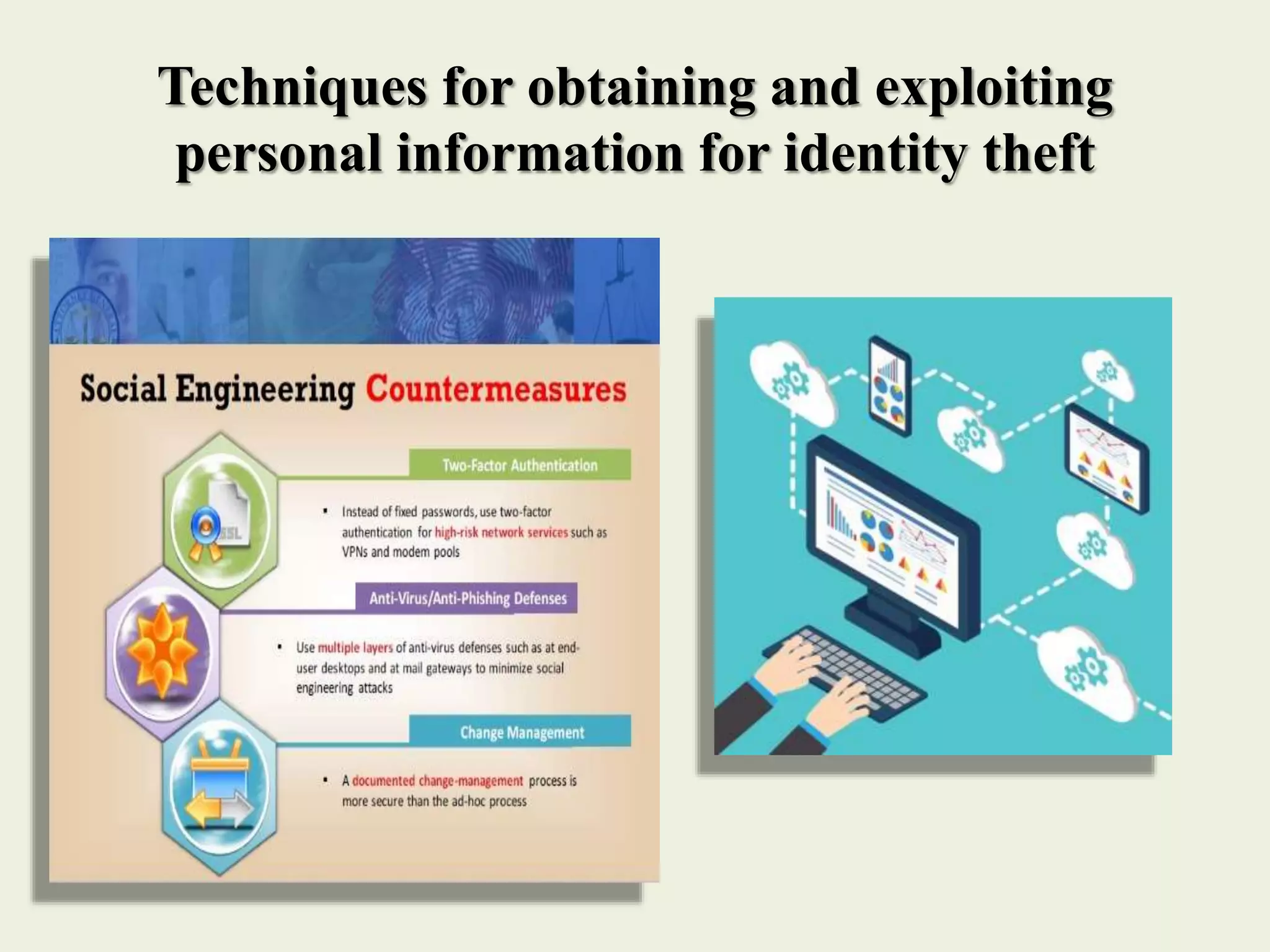
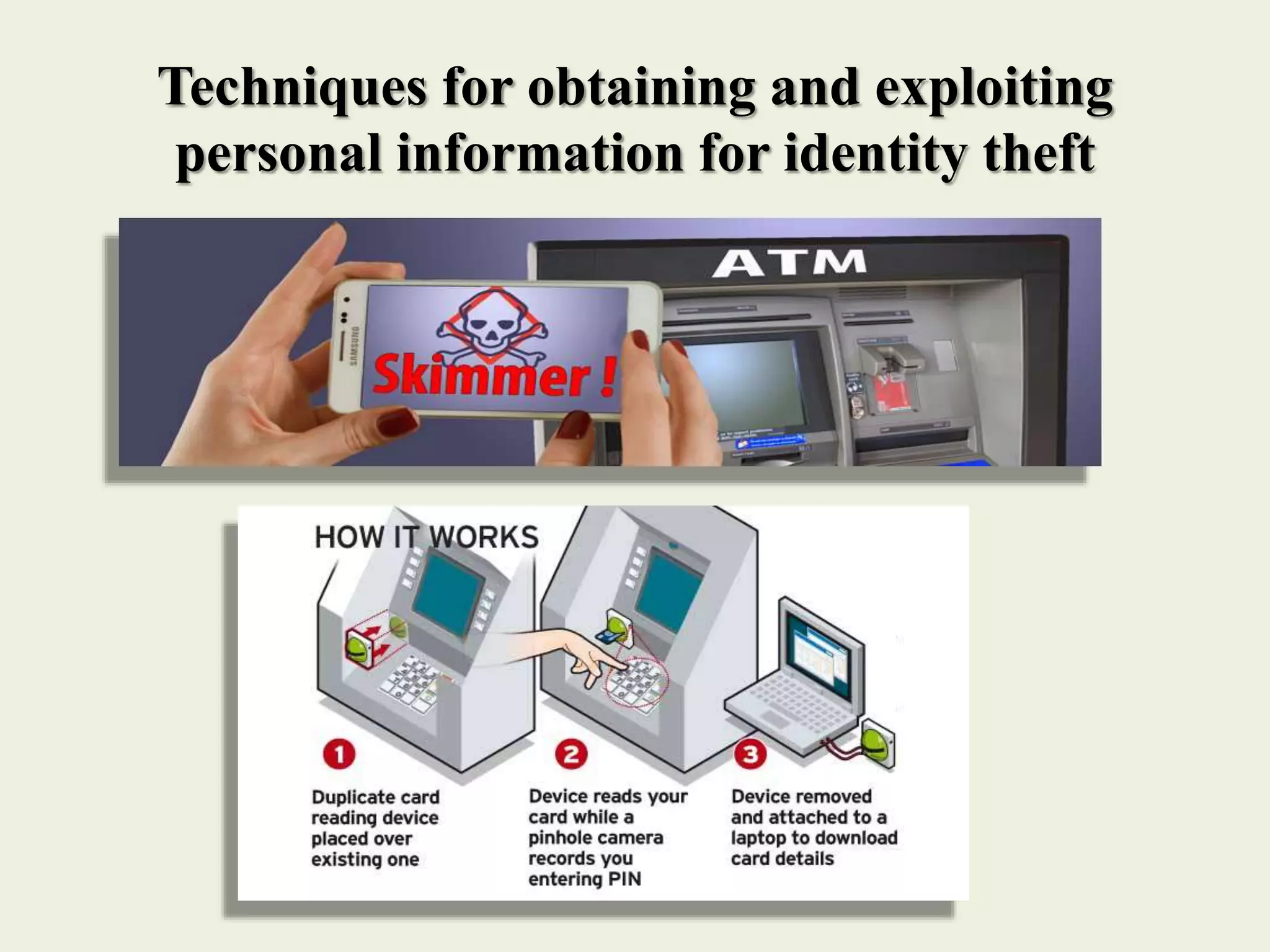
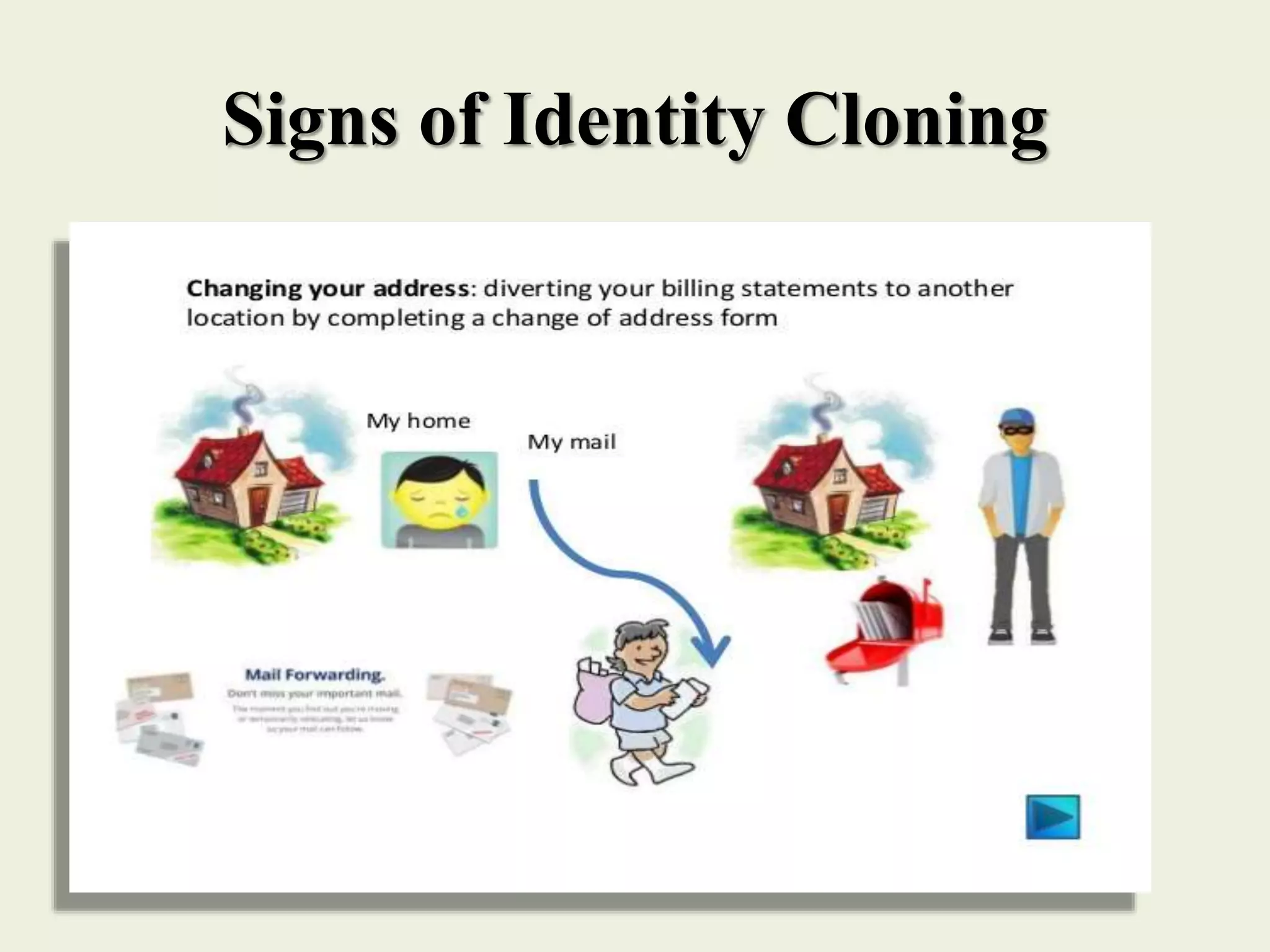
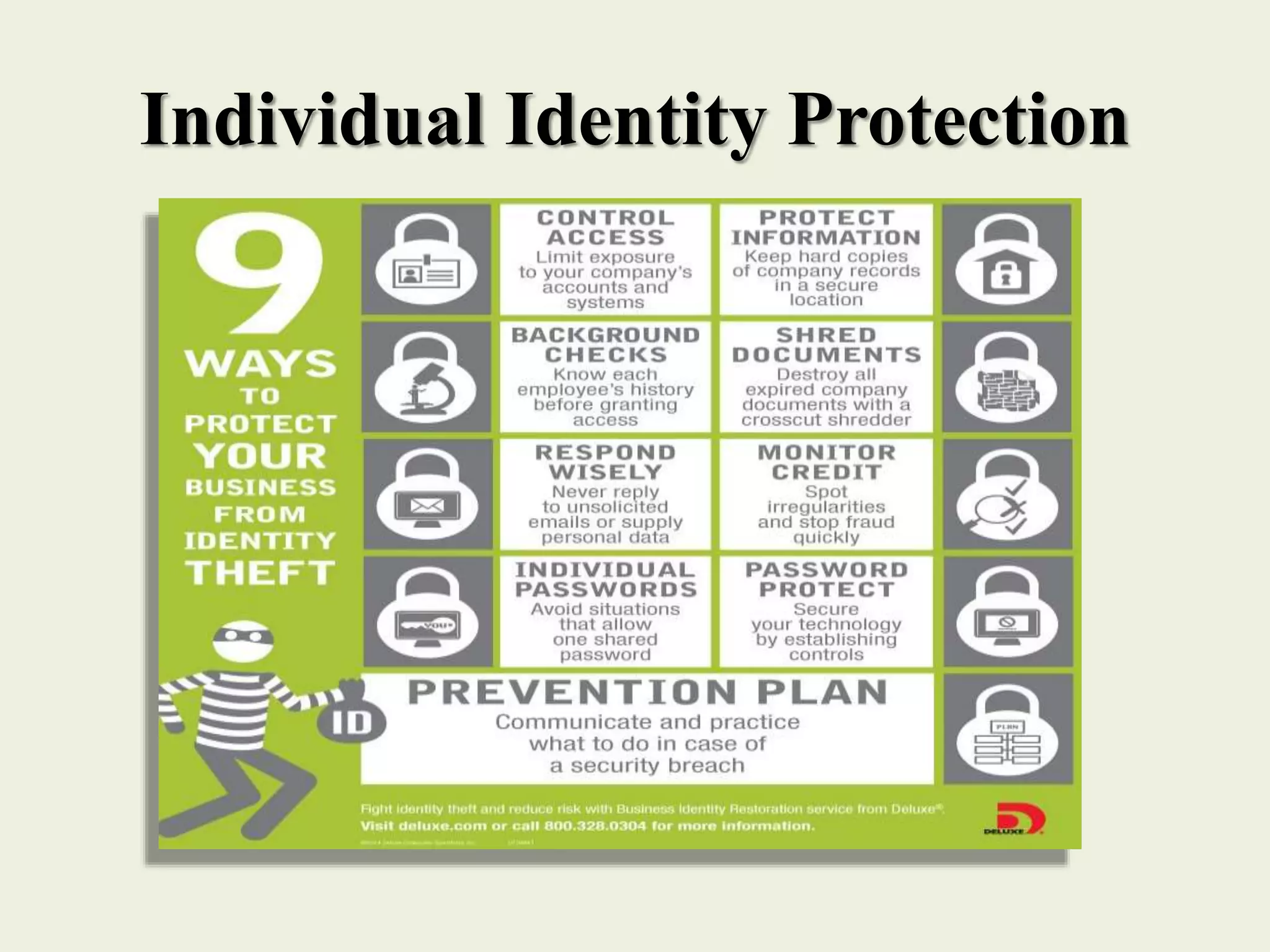
The document outlines various forms of identity theft, including financial identity theft, medical identity theft, and identity cloning, explaining how these crimes target individuals for financial gain or to assume another's identity. It also discusses the techniques used by identity thieves to obtain personal information, the indicators of becoming a victim, and the substantial consequences victims face, particularly in cases of identity cloning. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of being vigilant and protective of personal information to prevent falling victim to these crimes.