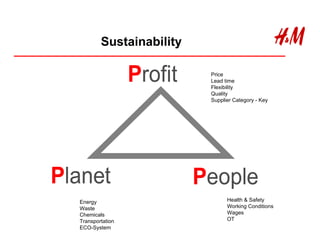
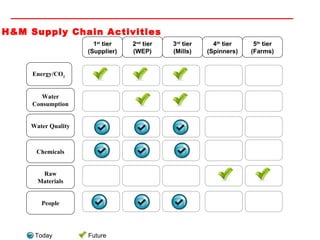
The document discusses the importance of energy efficiency and carbon responsibility in the global textile industry. It notes that energy has become a crucial but depleting resource that also contributes to global warming. For the textile industry, becoming more energy efficient presents both an opportunity to reduce costs and compete globally, as well as a threat if other countries improve their environmental and social standards before India does. Some facts about energy usage in the Indian textile industry are provided, and it is estimated that small and medium enterprises could save 15-20% of their energy consumption through factors like high capacity utilization, equipment tuning, and technology upgrades. The document concludes by emphasizing the importance of saving energy.