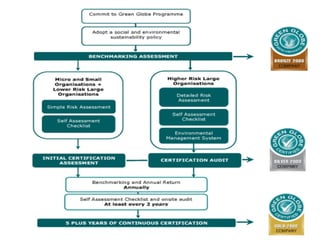
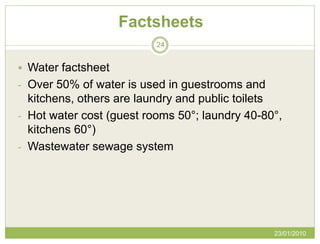
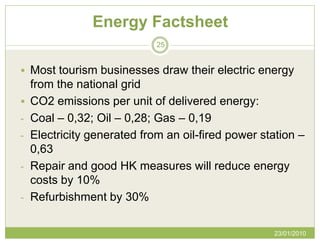
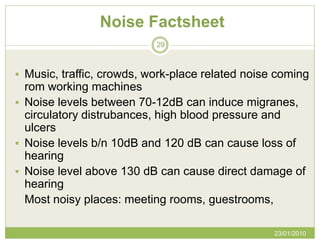
The document discusses Green Globe, a worldwide certification program for sustainable tourism and travel based on principles of sustainable development. Green Globe certification criteria focuses on benchmarking environmental performance in areas like energy, water, waste, and purchasing policies. Obtaining Green Globe certification involves implementing sustainability practices and an environmental management system to meet performance standards across key areas of assessment.