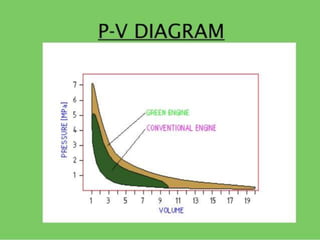
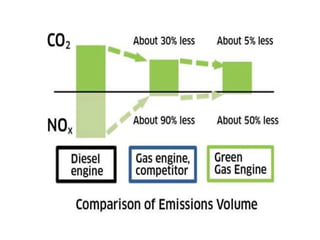
This document discusses green engine technology, which aims to modify internal combustion engines to increase efficiency and reduce emissions. It provides background on the need to develop green engines due to rising energy consumption and environmental issues. The key features of green engines are described, including direct fuel injection, variable compression ratios, and optimized combustion. The construction and 6-phase working principle of a prototype green engine are outlined, involving air intake, compression, mixing, combustion, power, and exhaust phases. Benefits over conventional engines cited are higher efficiency, lower emissions and fuel usage, and improved performance. Potential applications include automobiles, aircraft, generators, and more.