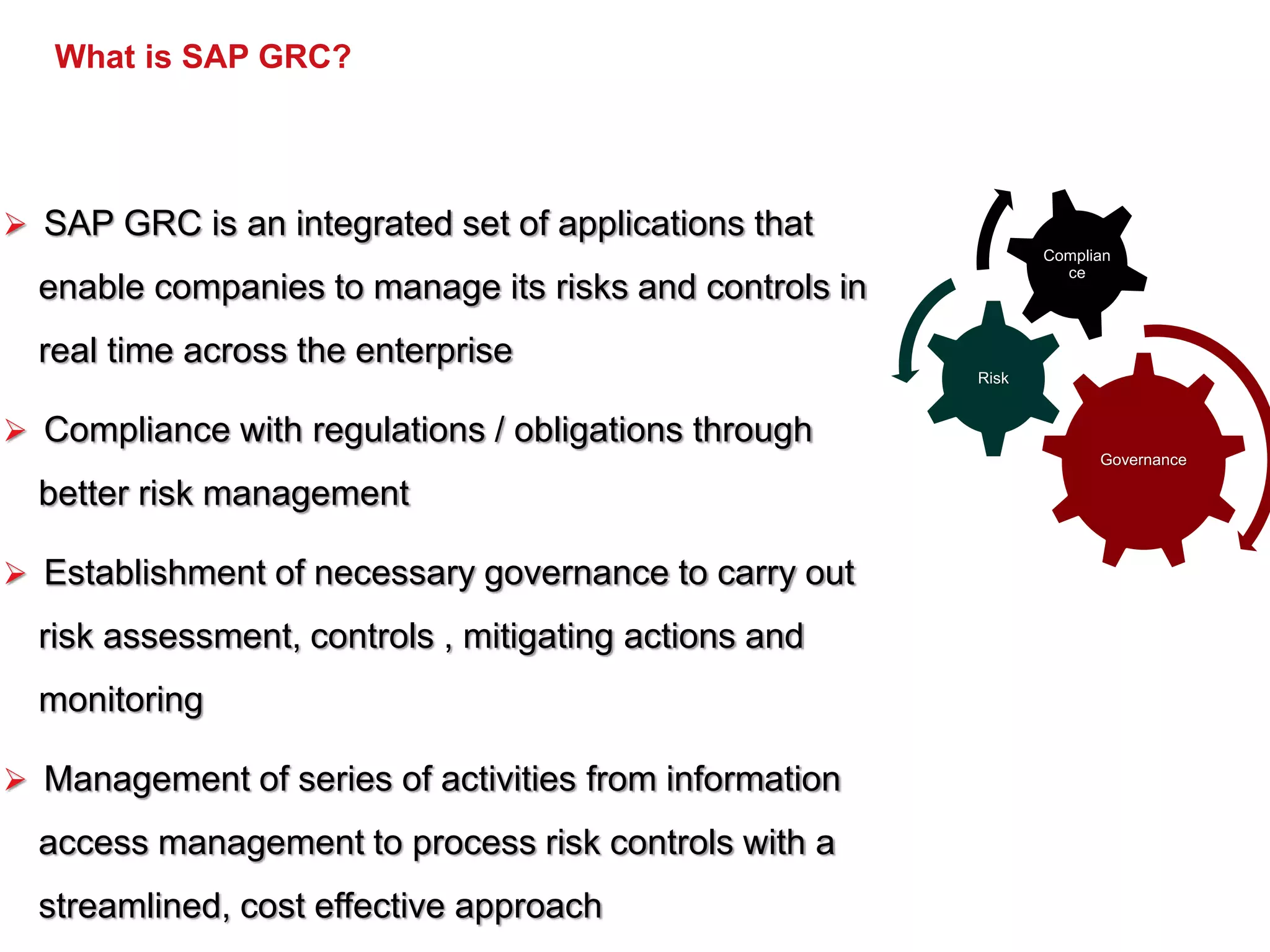
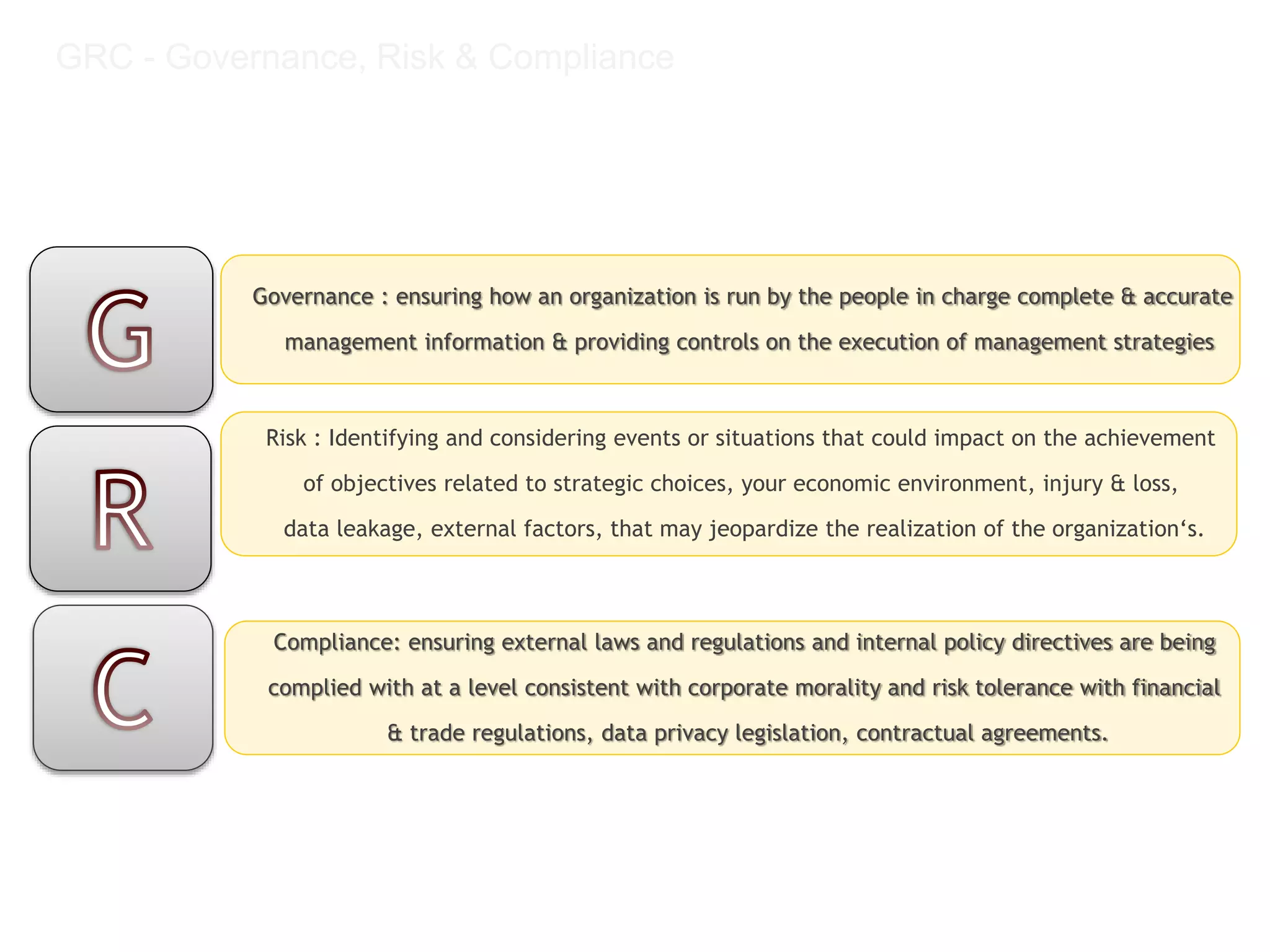
The document provides an overview of SAP GRC training which includes:
- An introduction to the components of GRC including governance, risk, and compliance.
- A discussion of the key access control components in GRC - access risk management, access request management, business role management, and emergency access management.
- Descriptions of the configuration and customization steps for access risk analysis, access request management, business role management, and emergency access management in GRC.
- Terminology related to emergency access management such as firefighter, firefighter ID, owner, and controller.
- The process for configuring a firefighter ID.