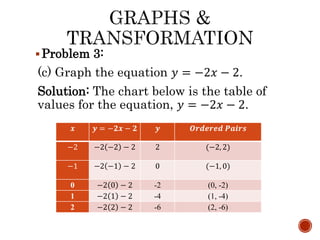
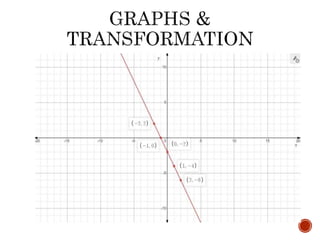
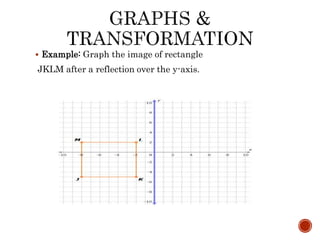
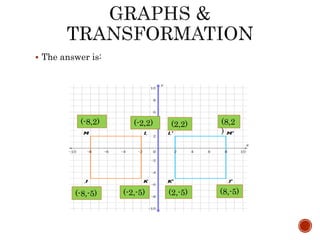
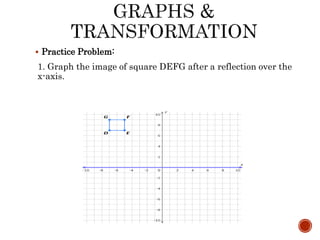
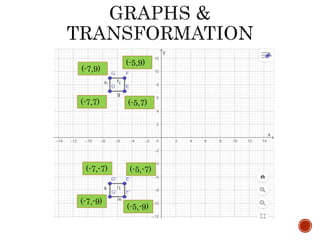
The document outlines a lesson on the concept of reflection across an axis, including explanations, rules for reflecting points across the x-axis and y-axis, and provides practice problems with solutions. Specific examples, such as graphing the reflection of a rectangle and a square, illustrate these principles. Students are instructed to complete classwork from handouts, including specific problems related to reflecting equations and figures.