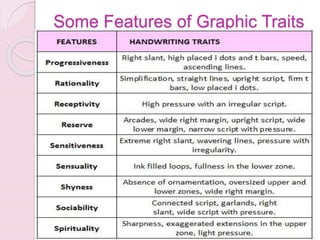
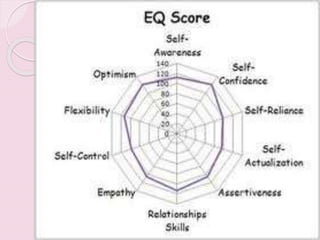
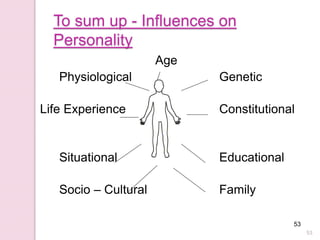
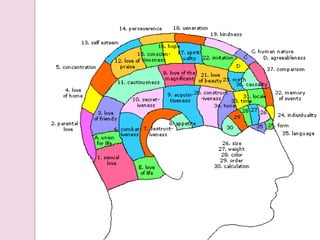
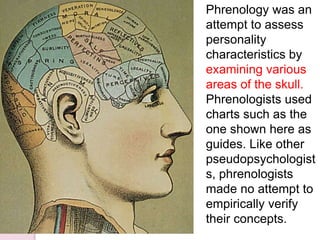
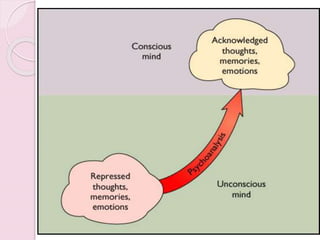
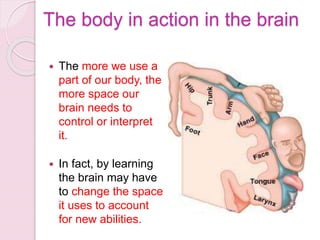
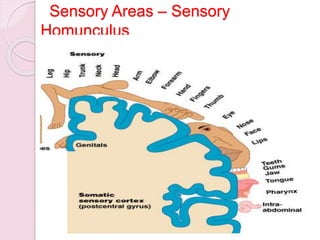
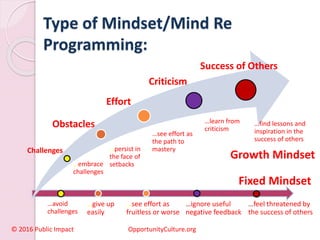
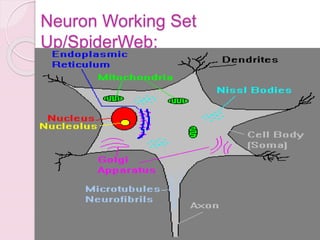
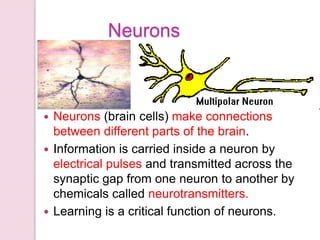
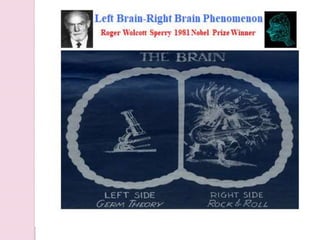
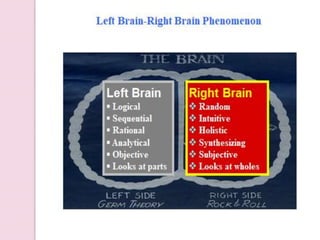
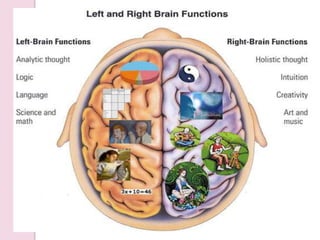
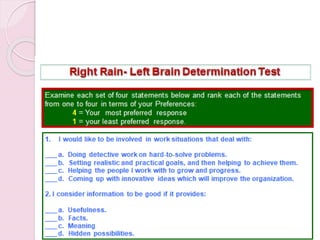
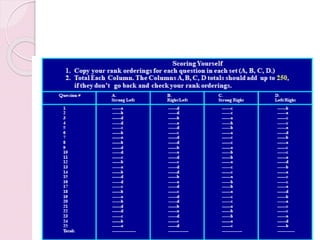
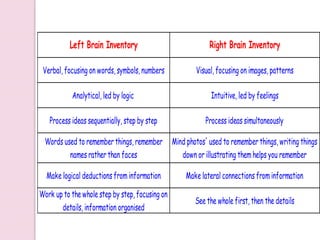
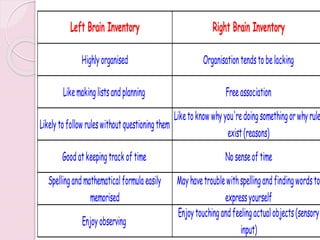
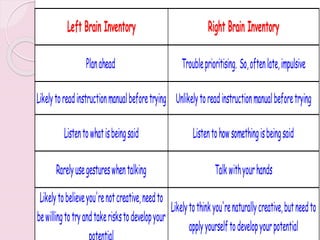
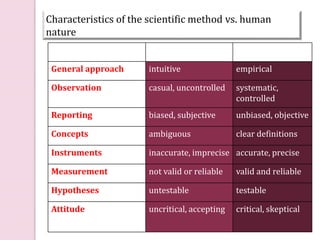
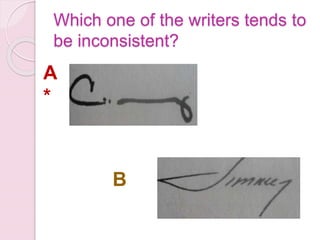
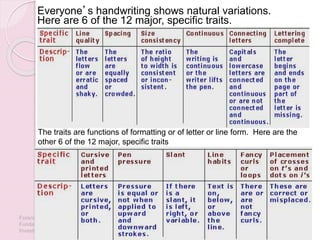
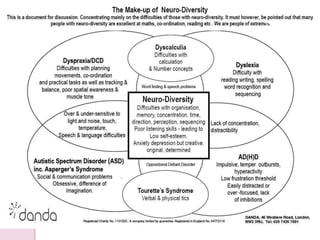
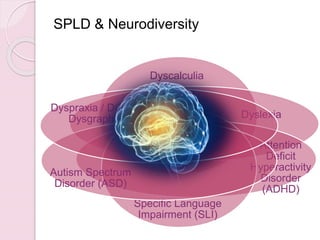
Graphology is the analysis of handwriting to assess personality traits. It has been used for hundreds of years to evaluate people for jobs, marriages, and more. While some view it as pseudoscience, proponents believe handwriting reveals unconscious clues about an individual since no two people write exactly the same way. Graphology can provide insight into communication skills, independence, enthusiasm, and other characteristics through an analysis of writing style, size, slant, and other graphological factors.