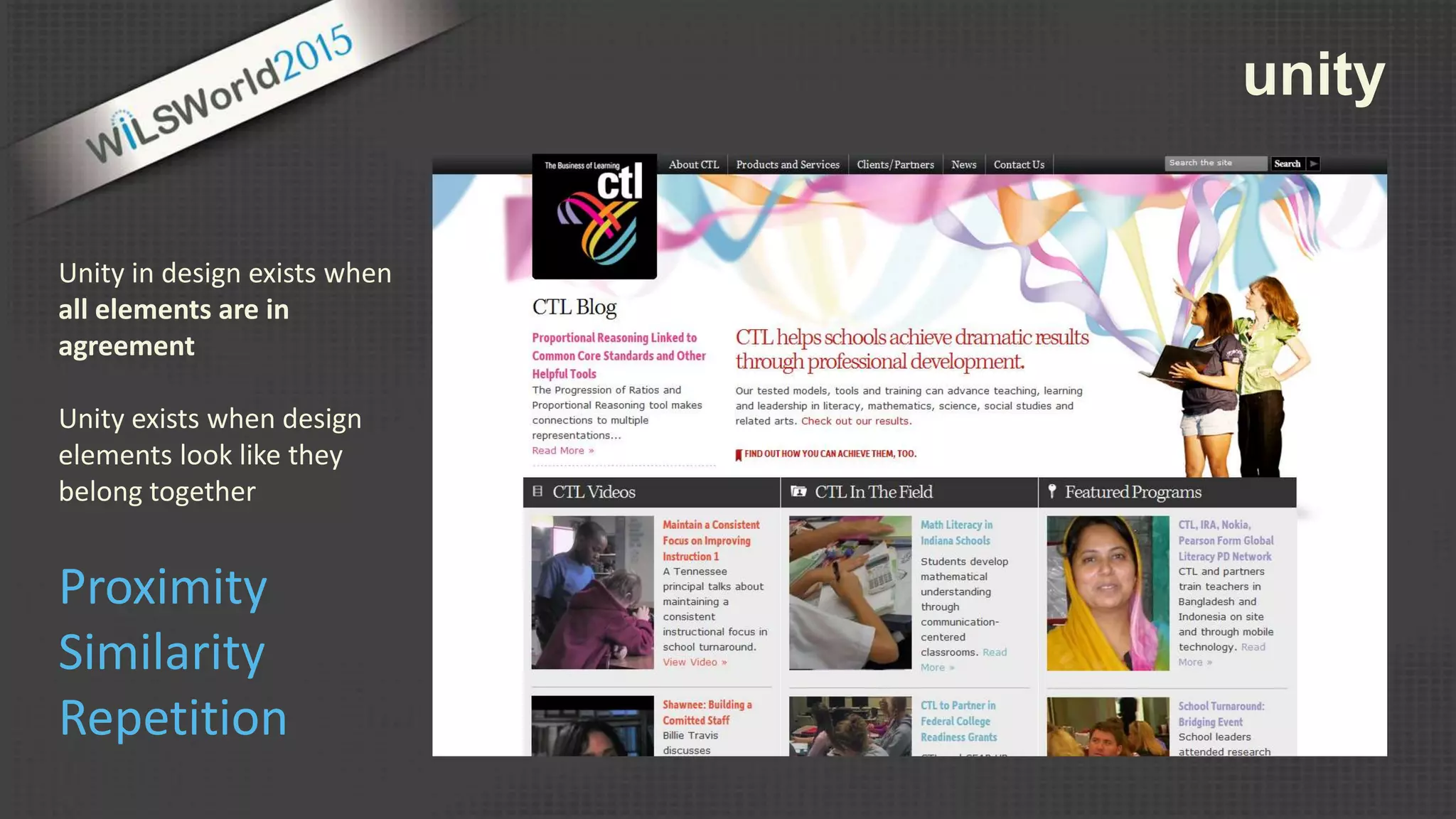
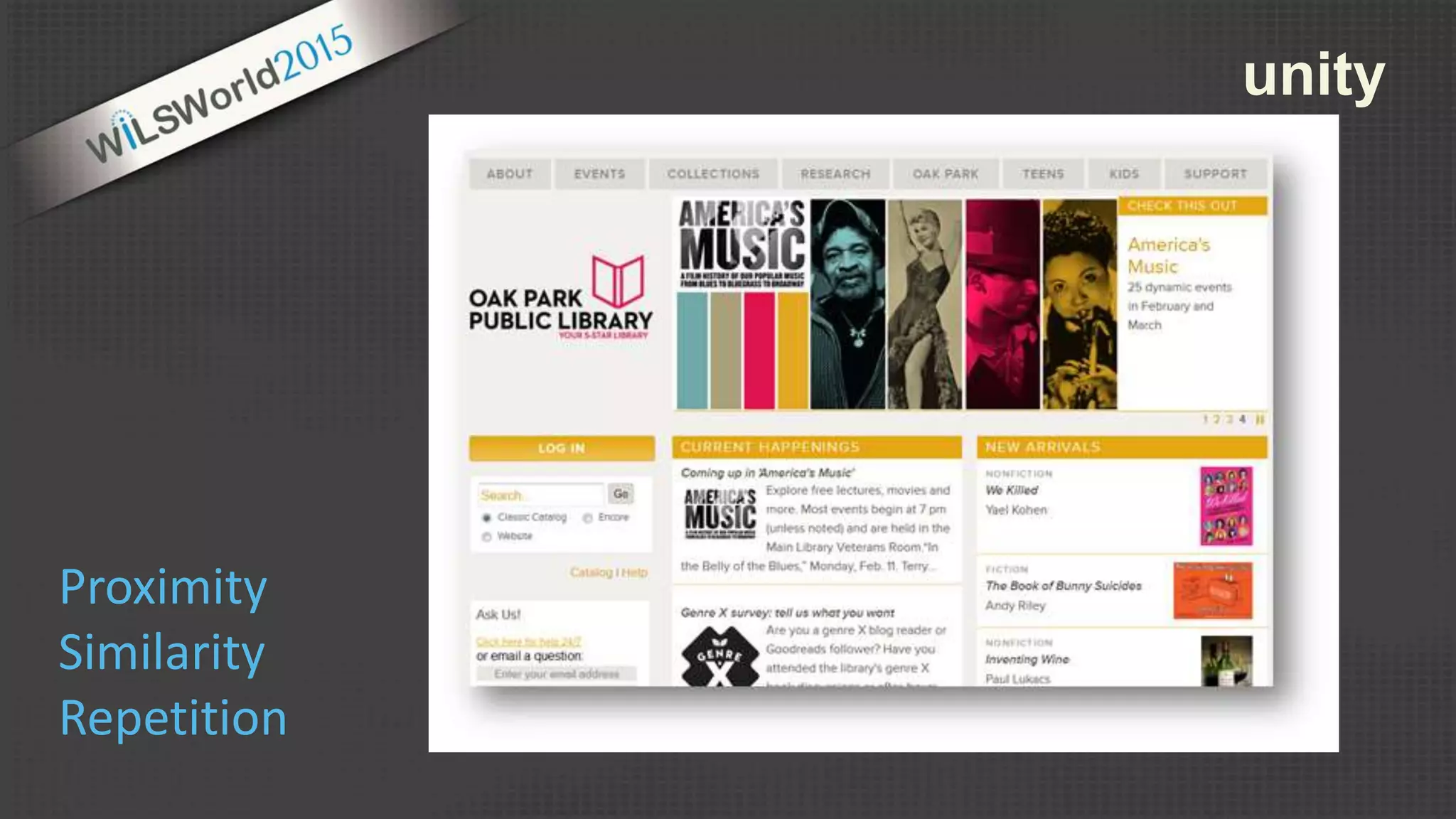
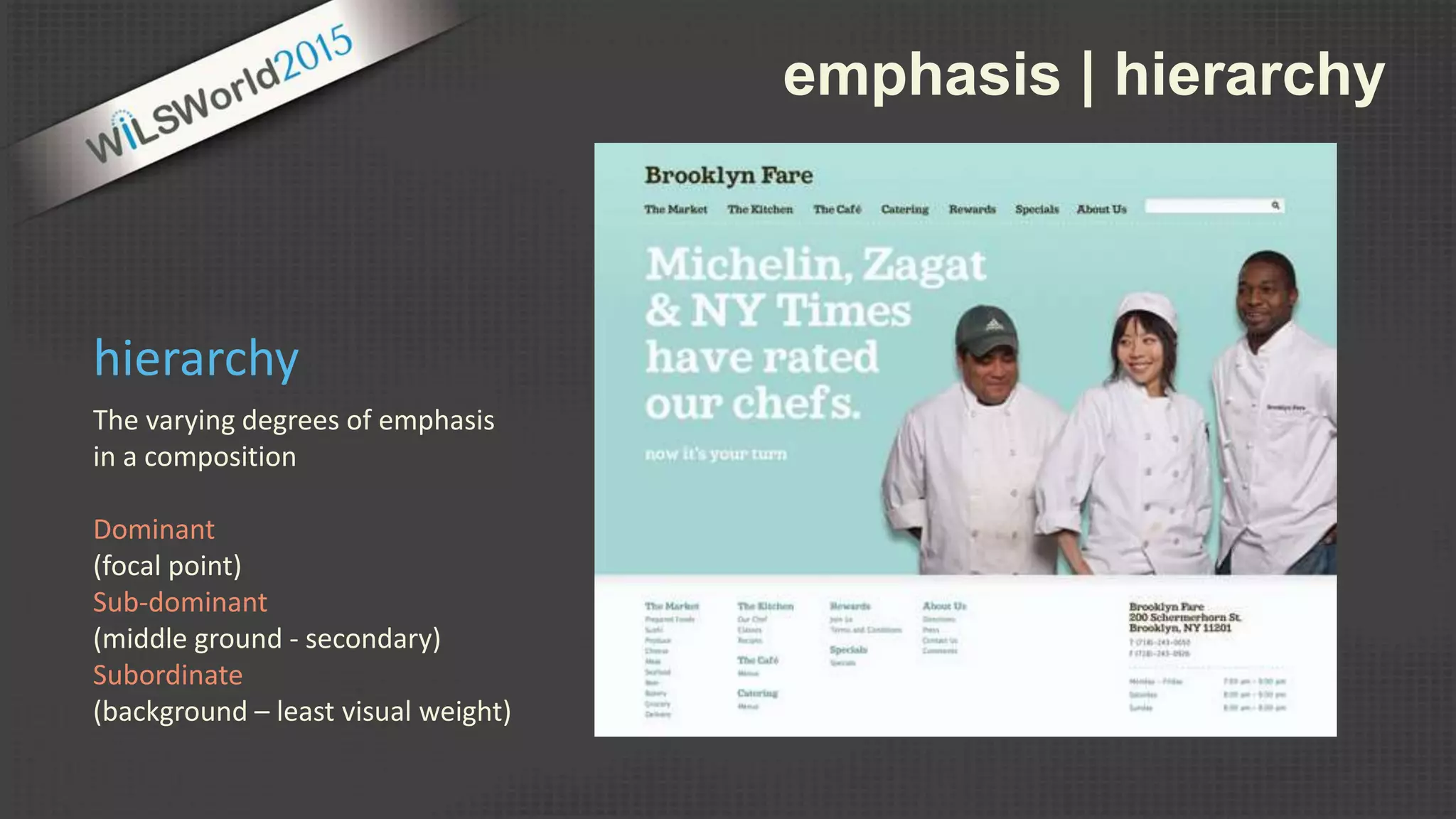
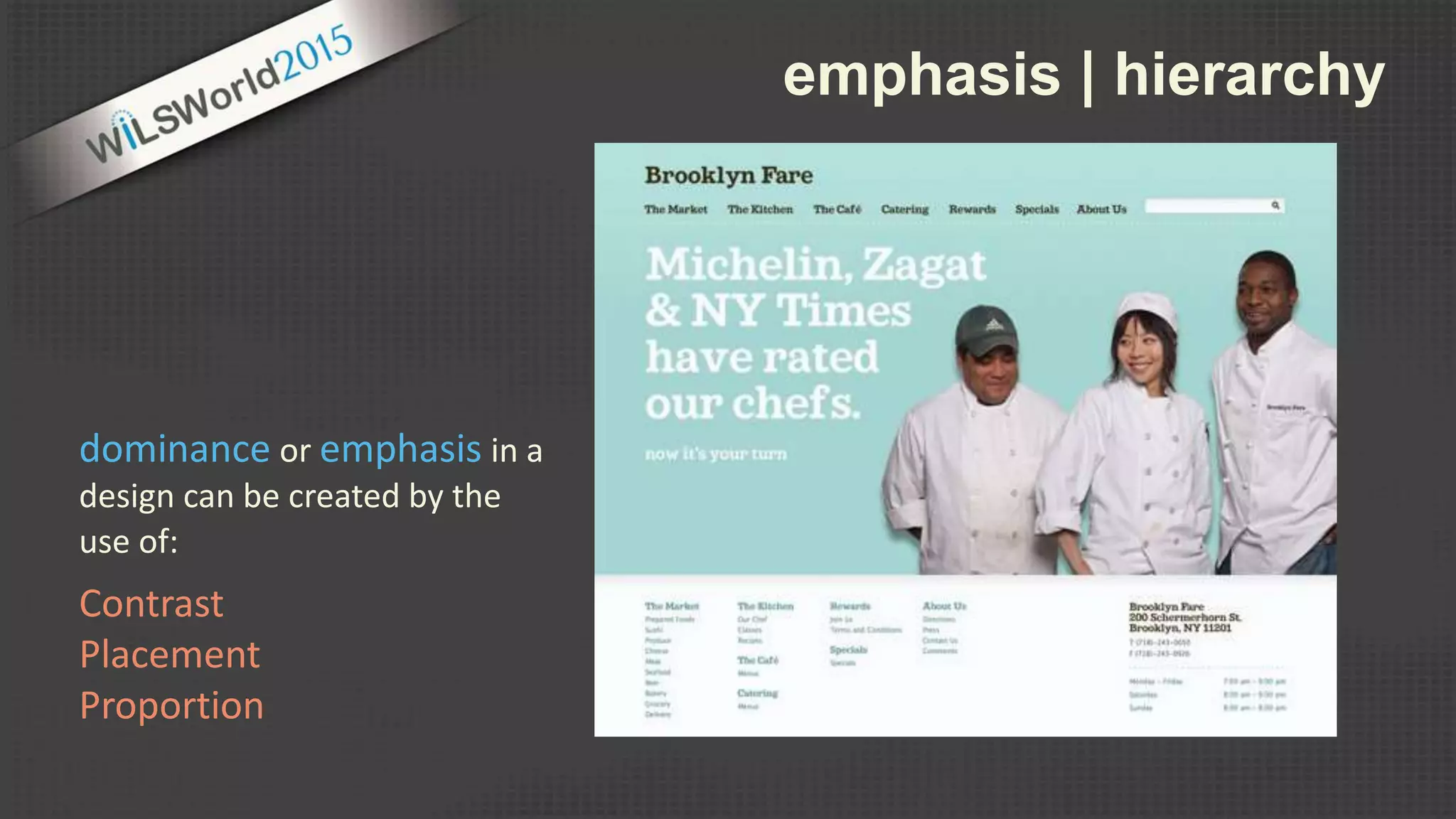
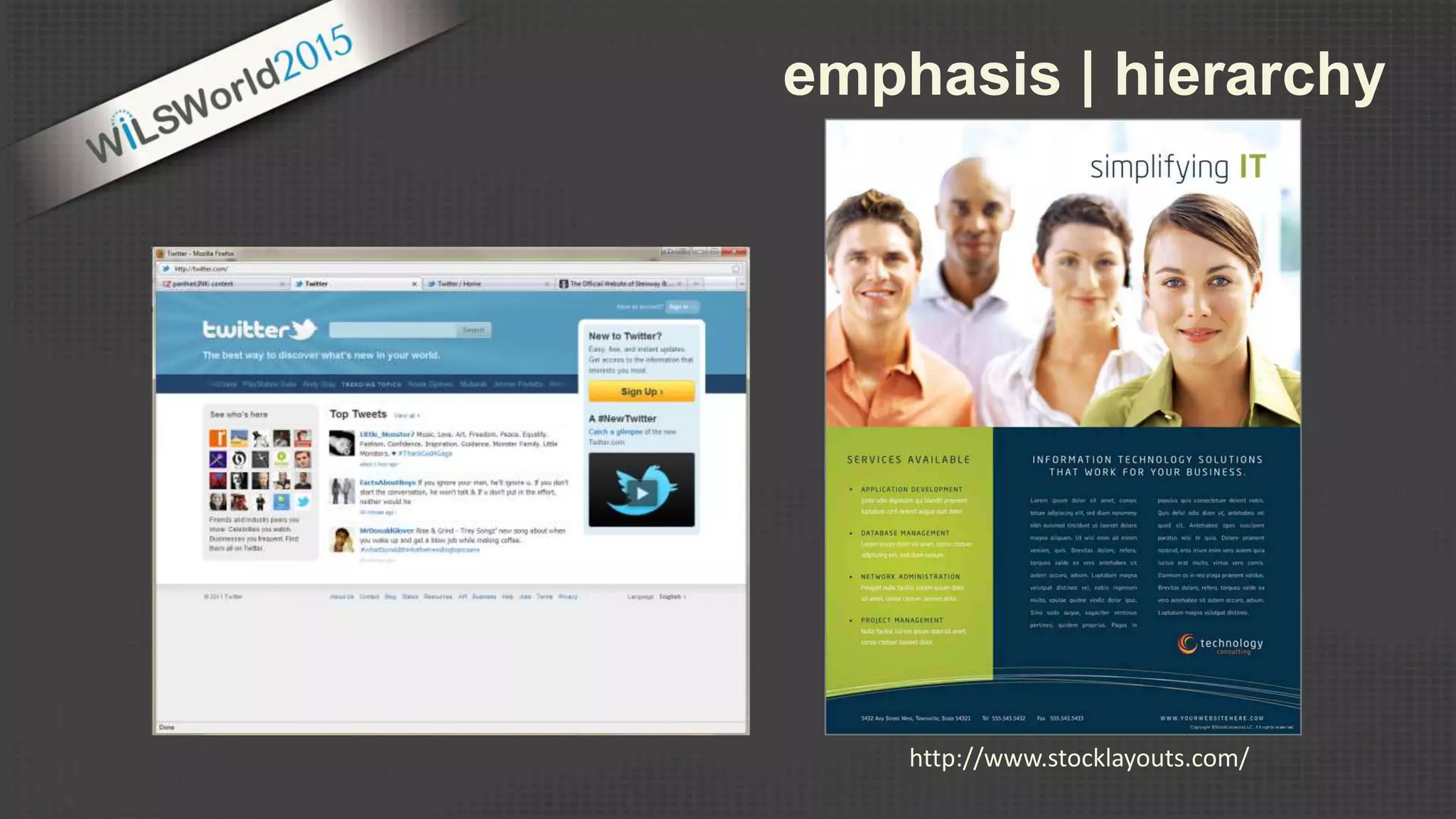
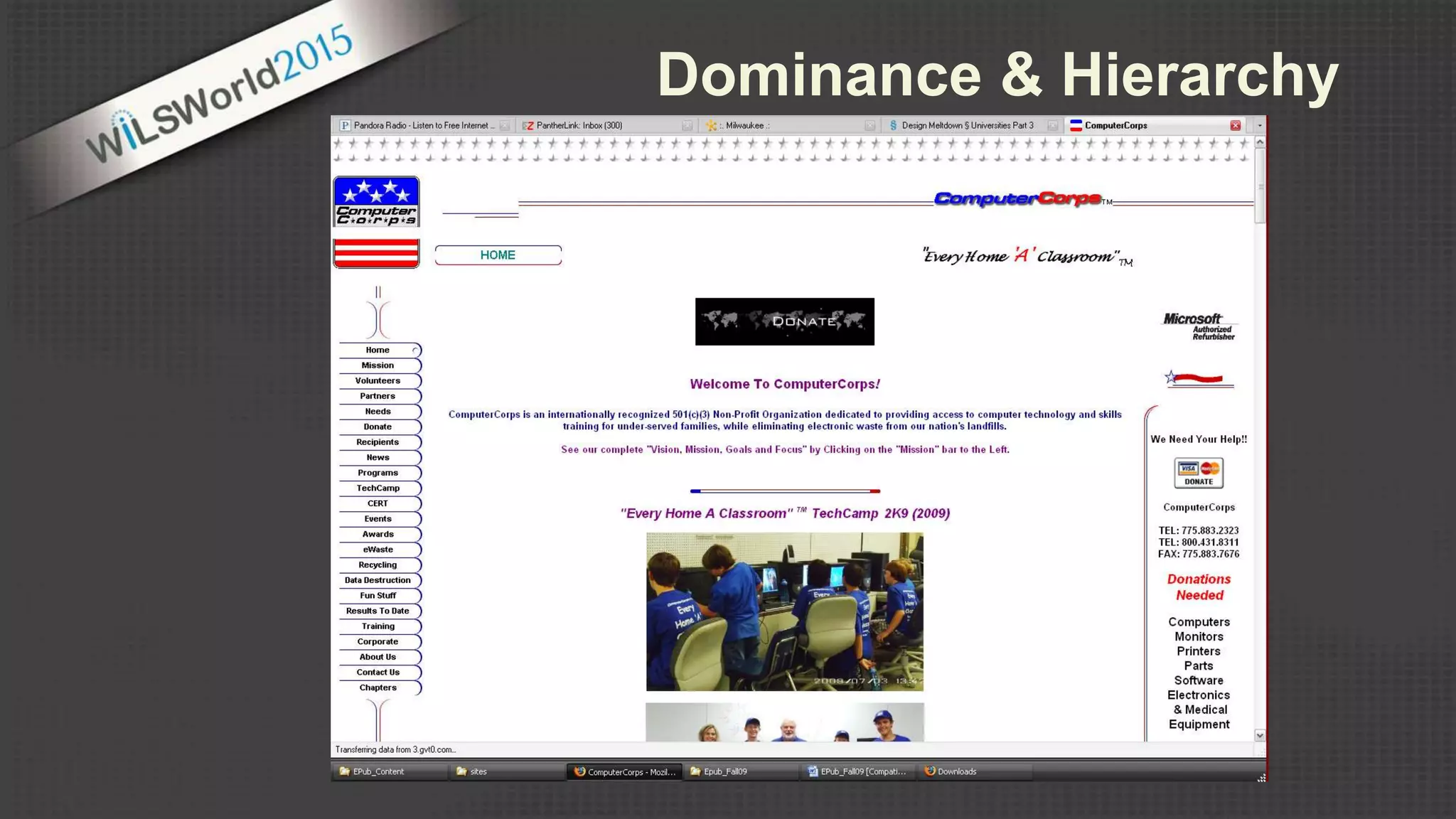
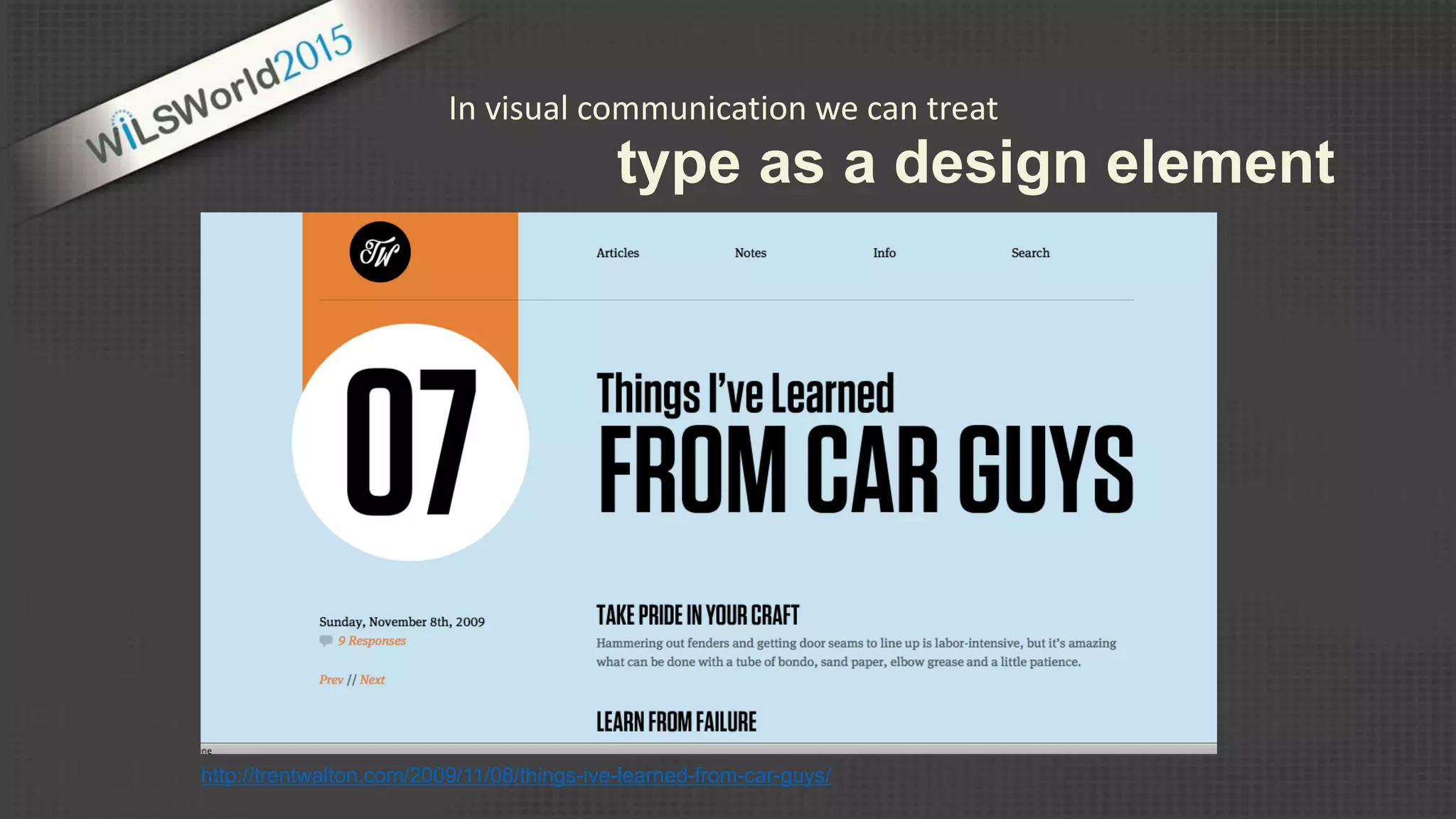
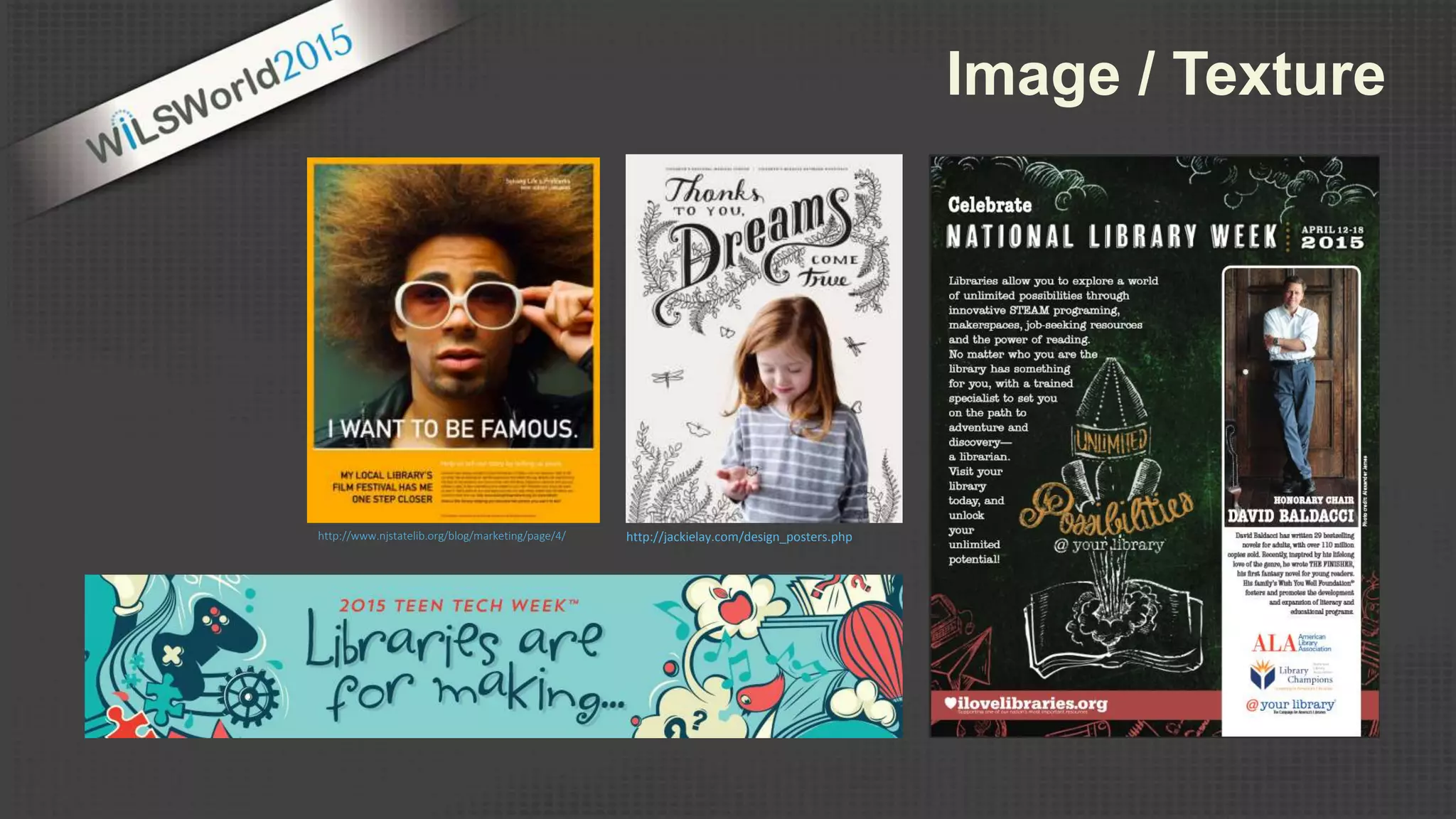
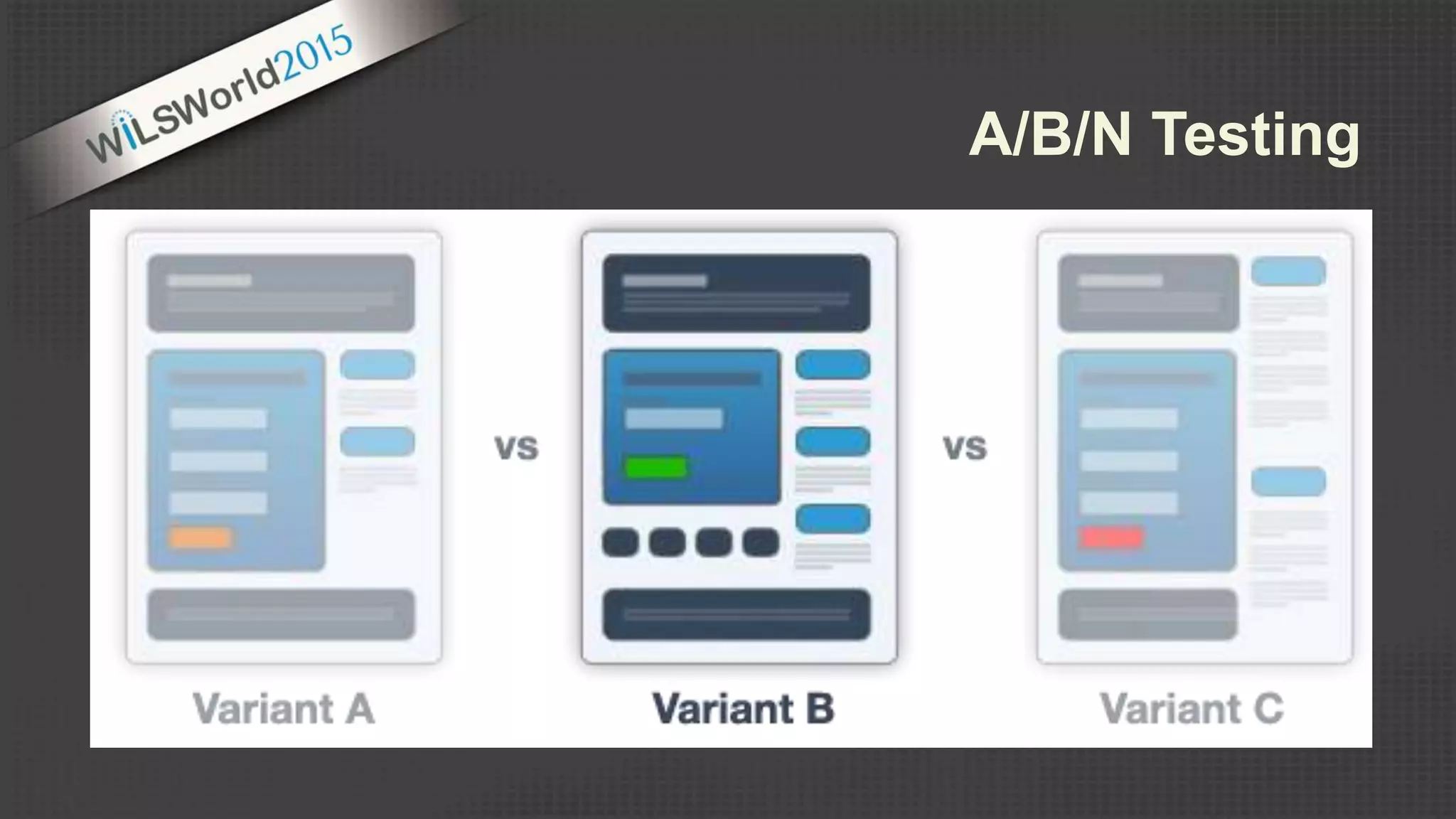
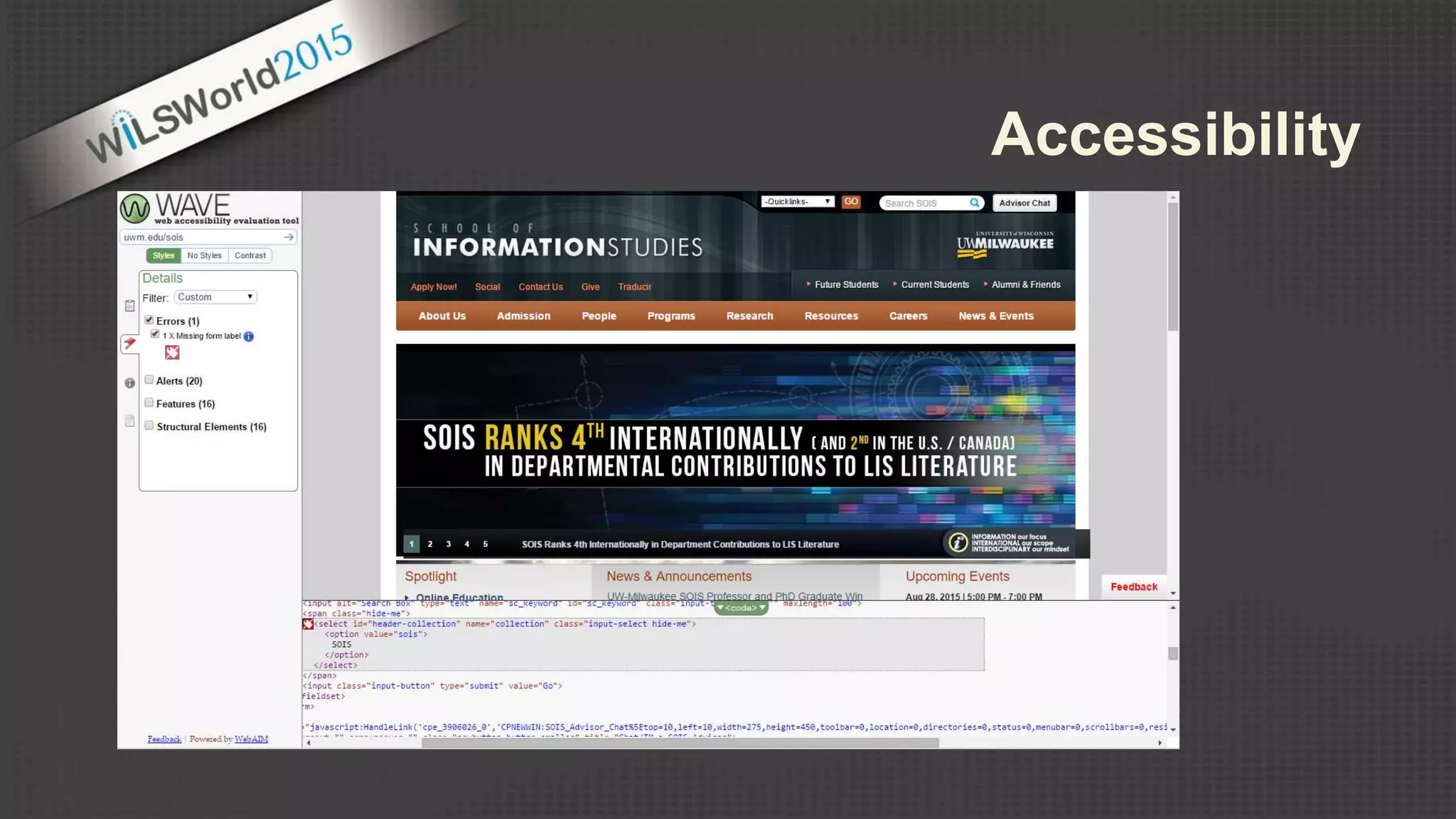
The document outlines principles and elements of design, covering topics such as unity, balance, hierarchy, and the use of color, type, and images in branding and identity. It emphasizes the importance of effective visual communication in various careers, marketing strategies, and the tools available for web design. The conclusion encourages familiarization with design principles, experimenting with tools, and maintaining consistency in branding.