✨ Unlock the Power of Connections: Graph Theory is EVERYWHERE! ✨
Think math is just equations? Think again! This deck reveals how Graph Theory—the science of networks—is the secret engine behind Google Maps, social media, and even the phone in your pocket. 🤯
🔮 What You’ll Discover:
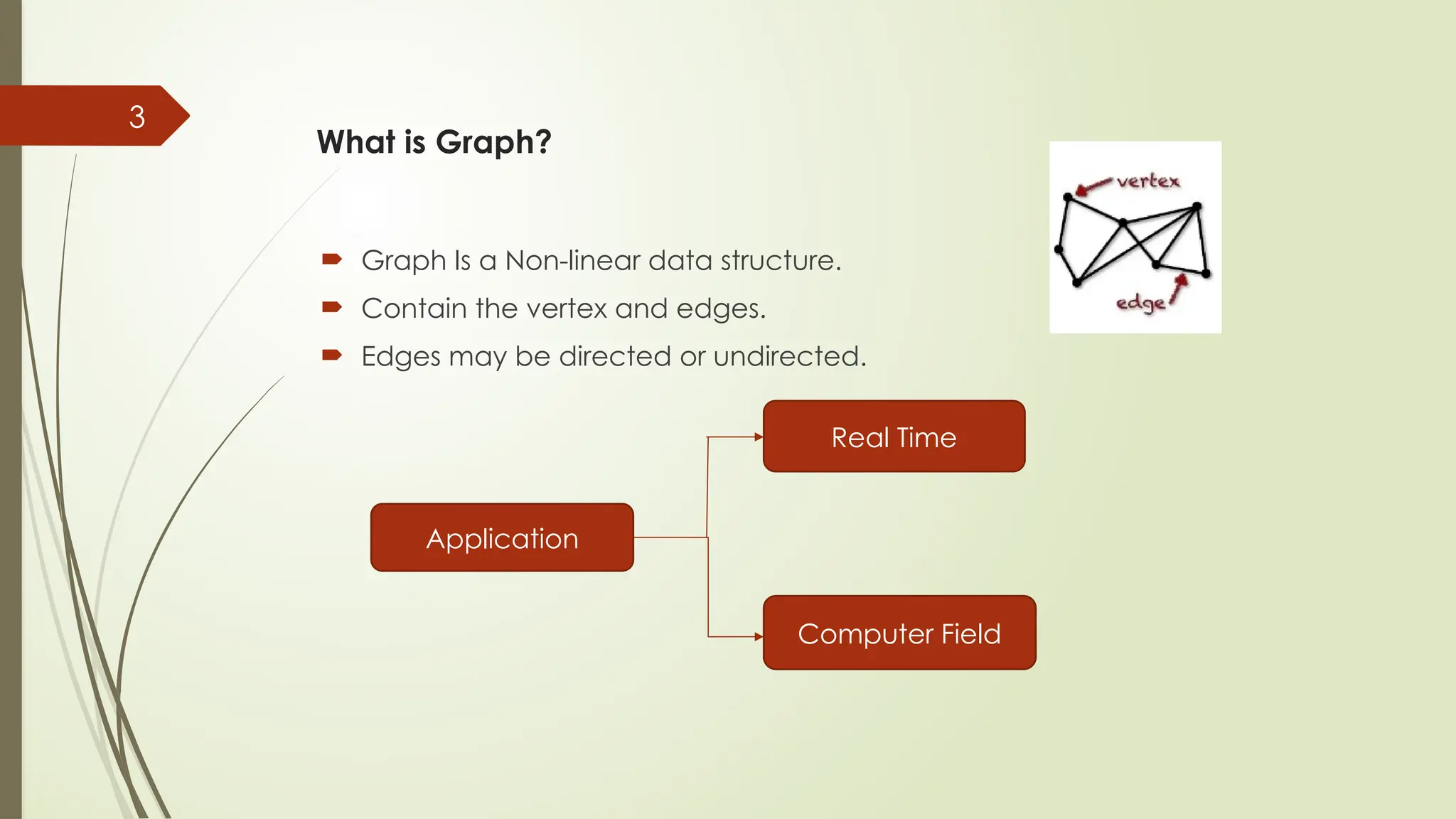
The Core Concept 🧠: What is a graph? It's simpler than you think: just vertices (points) and edges (lines connecting them). This simple idea powers the modern world.
Real-World Magic 🌍: See mind-blowing applications you use daily:
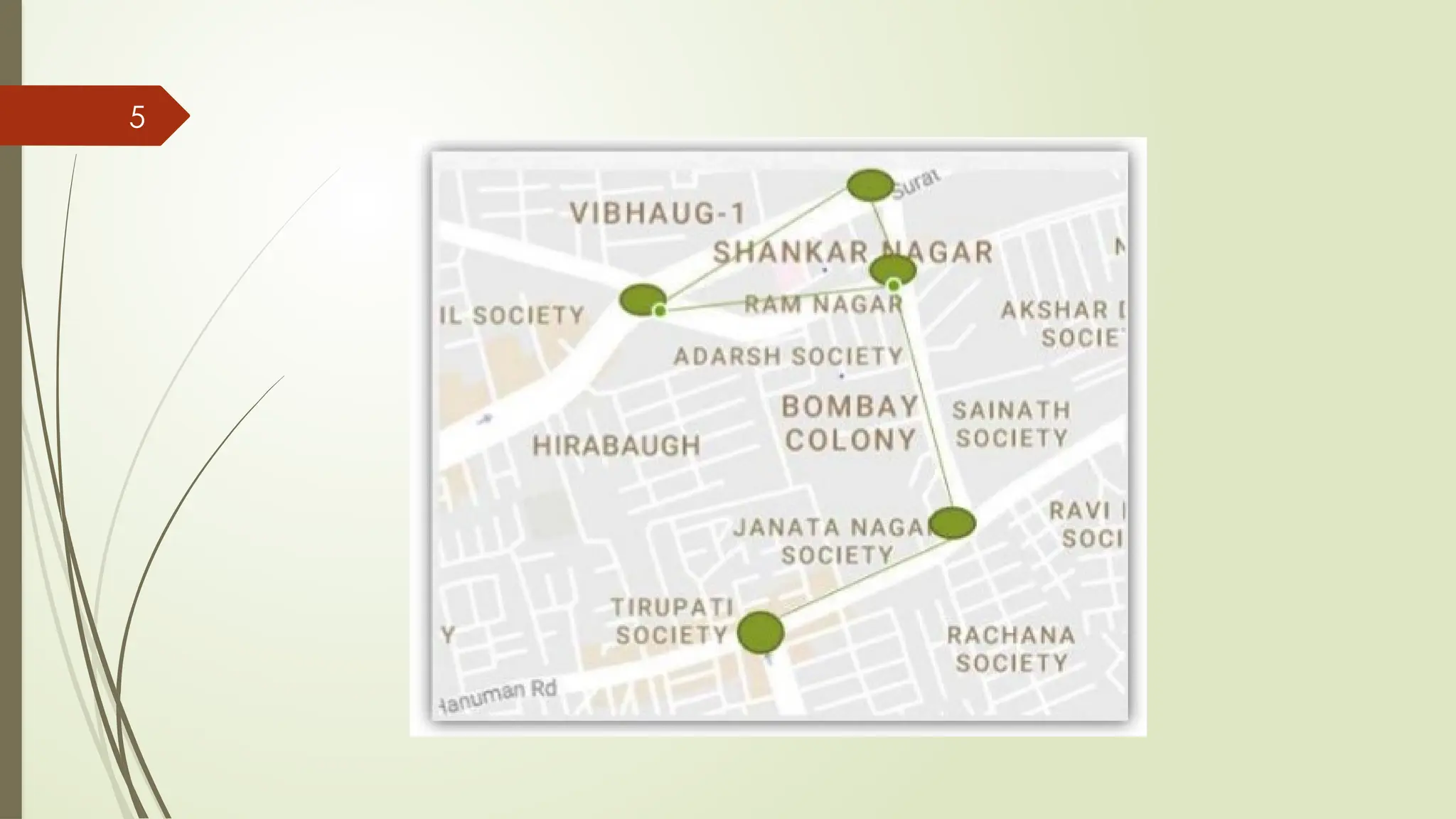
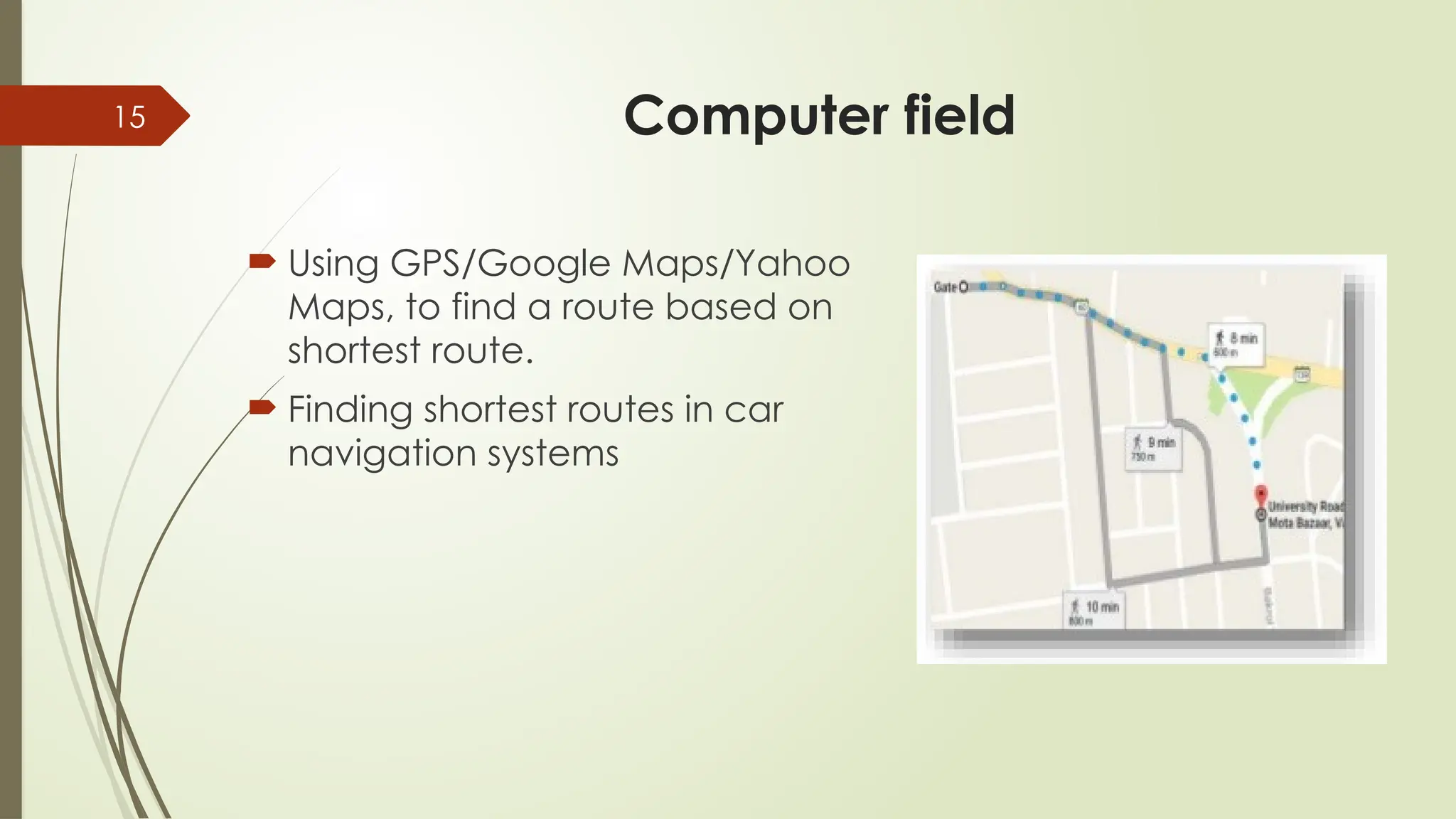
Google Maps: Finds the shortest path because roads are edges and intersections are vertices!
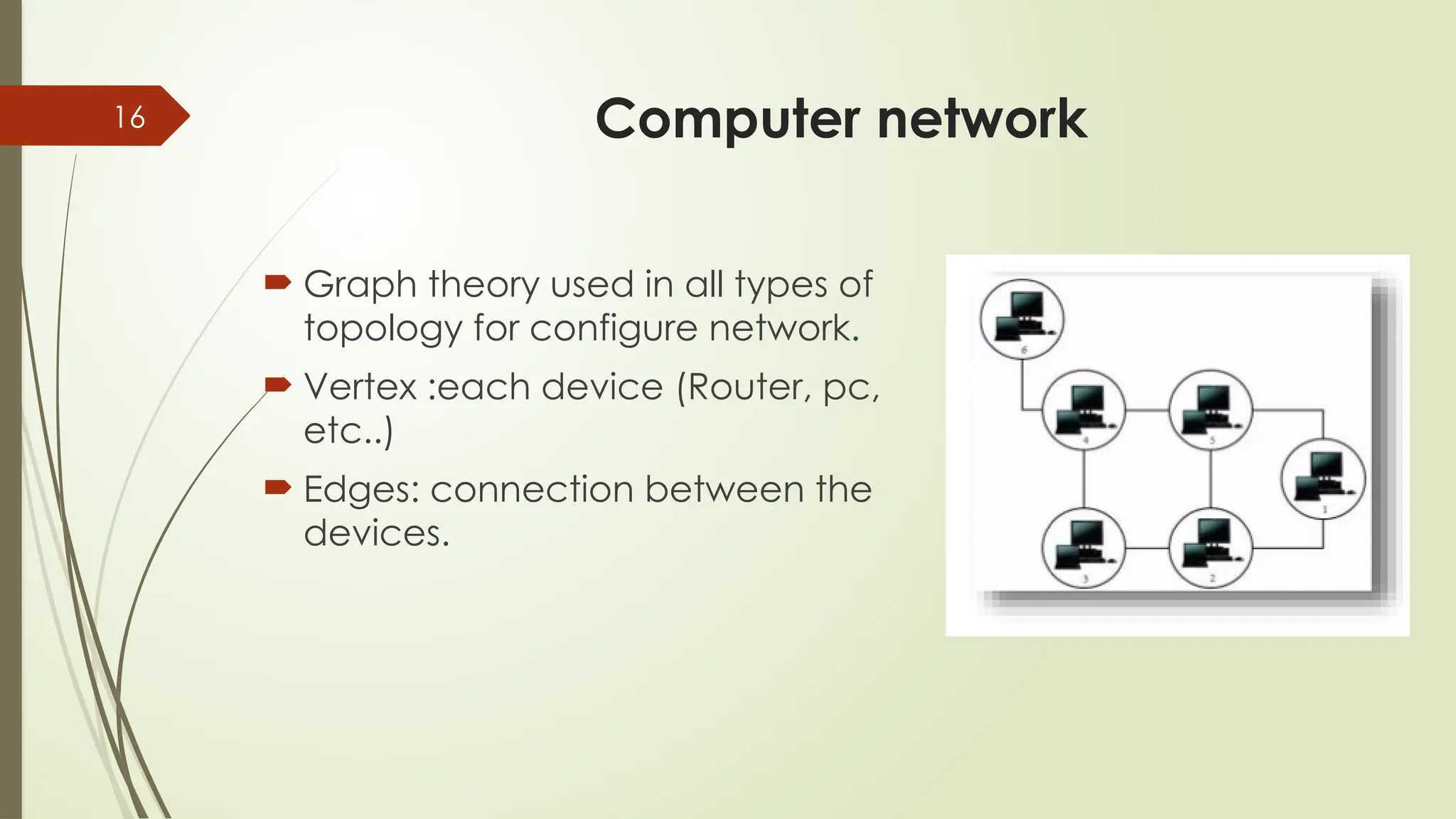
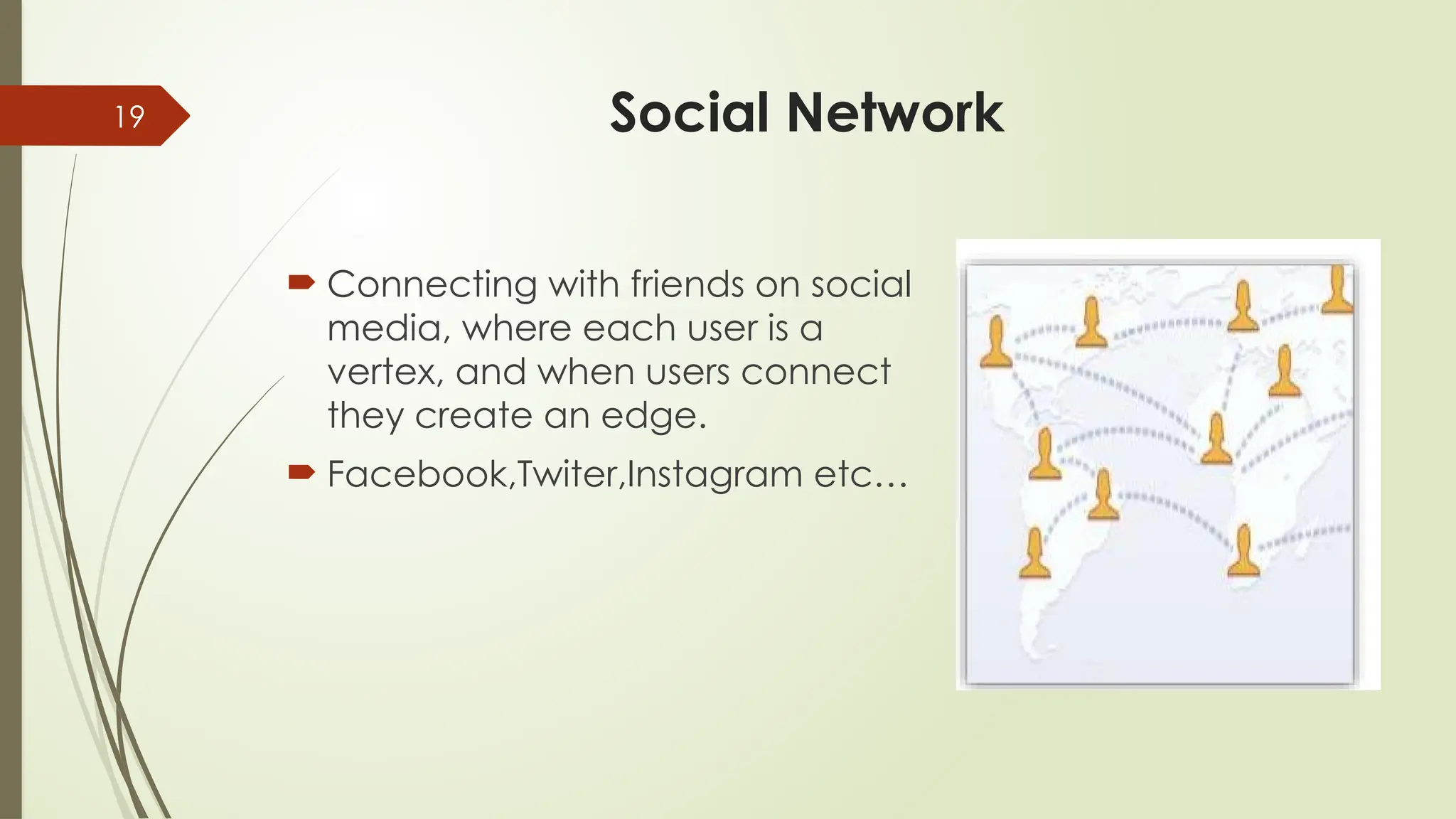
Social Networks: You are a vertex! Every friend is a connection (edge). Facebook & Instagram run on a giant graph.
The Internet: How Google ranks websites using the "web graph" of hyperlinks.
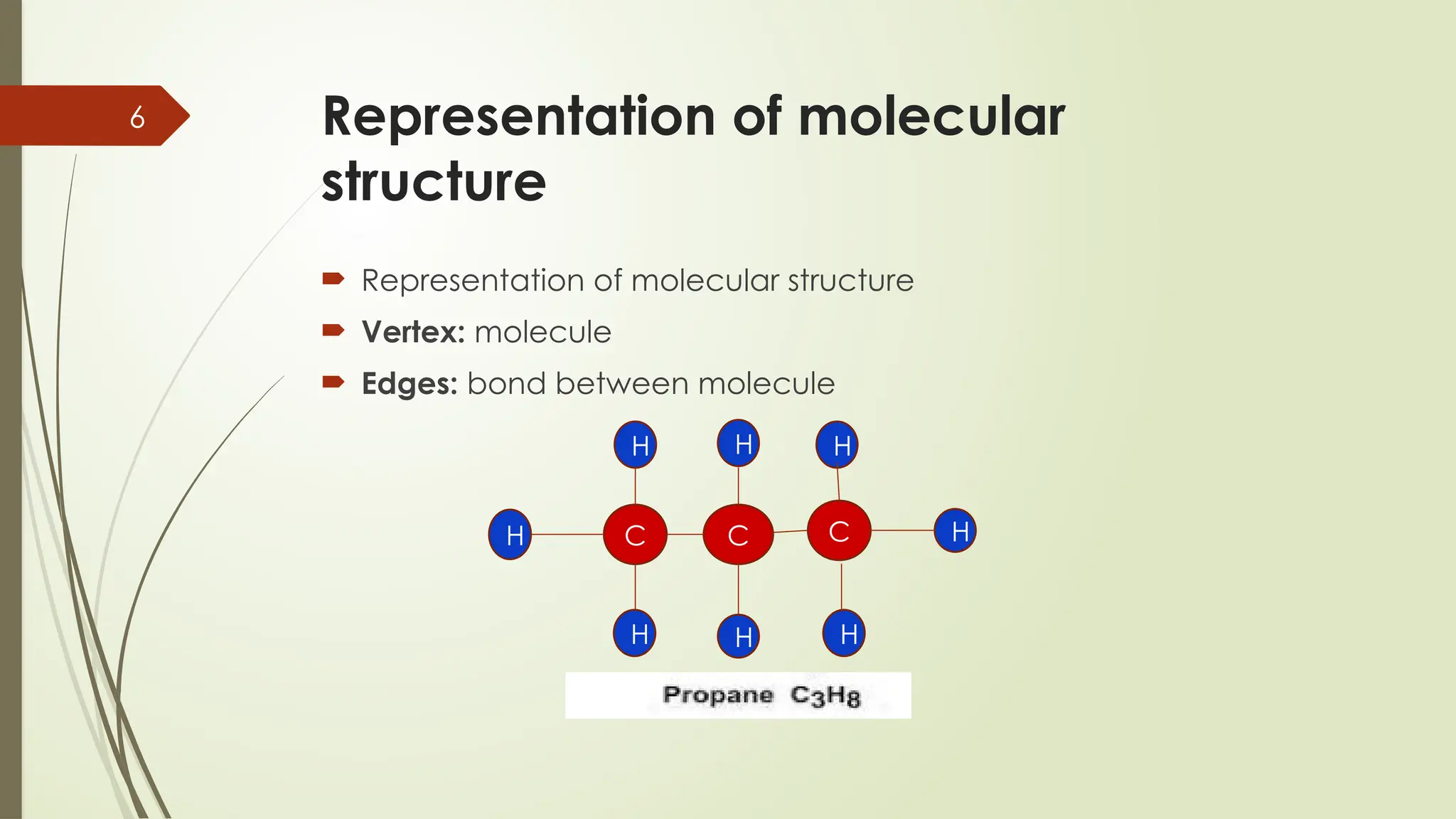
Chip Design: Optimizing millions of transistor connections inside your computer's CPU.
Visual Learning 🎨: Complex ideas are broken down with clear examples and intuitive visuals. No heavy math, just clear logic.
Key Problems Solved ⚙️:
The Shortest Path problem (getting from A to B fastest).
The Travelling Salesman problem (the most efficient tour).
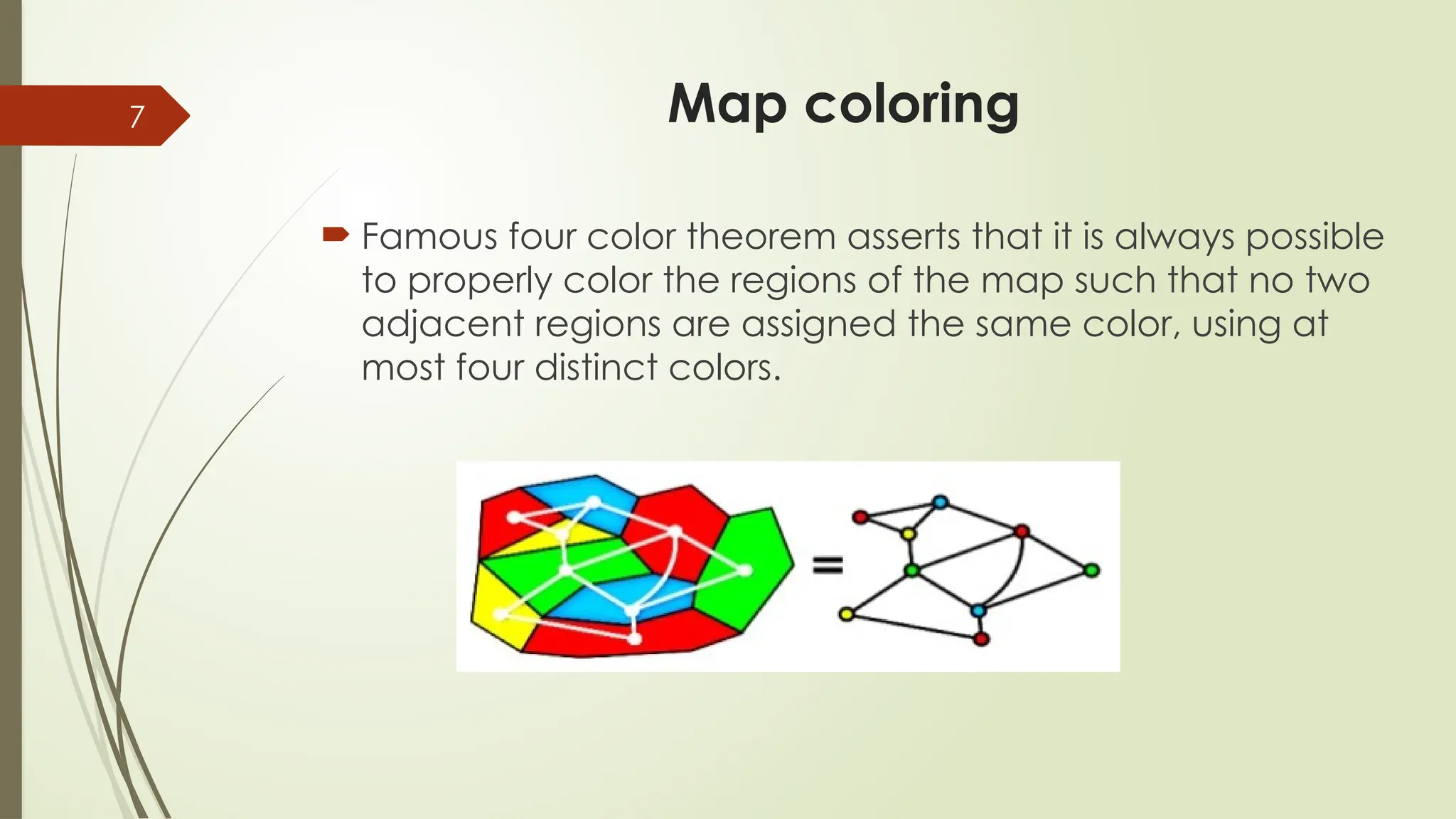
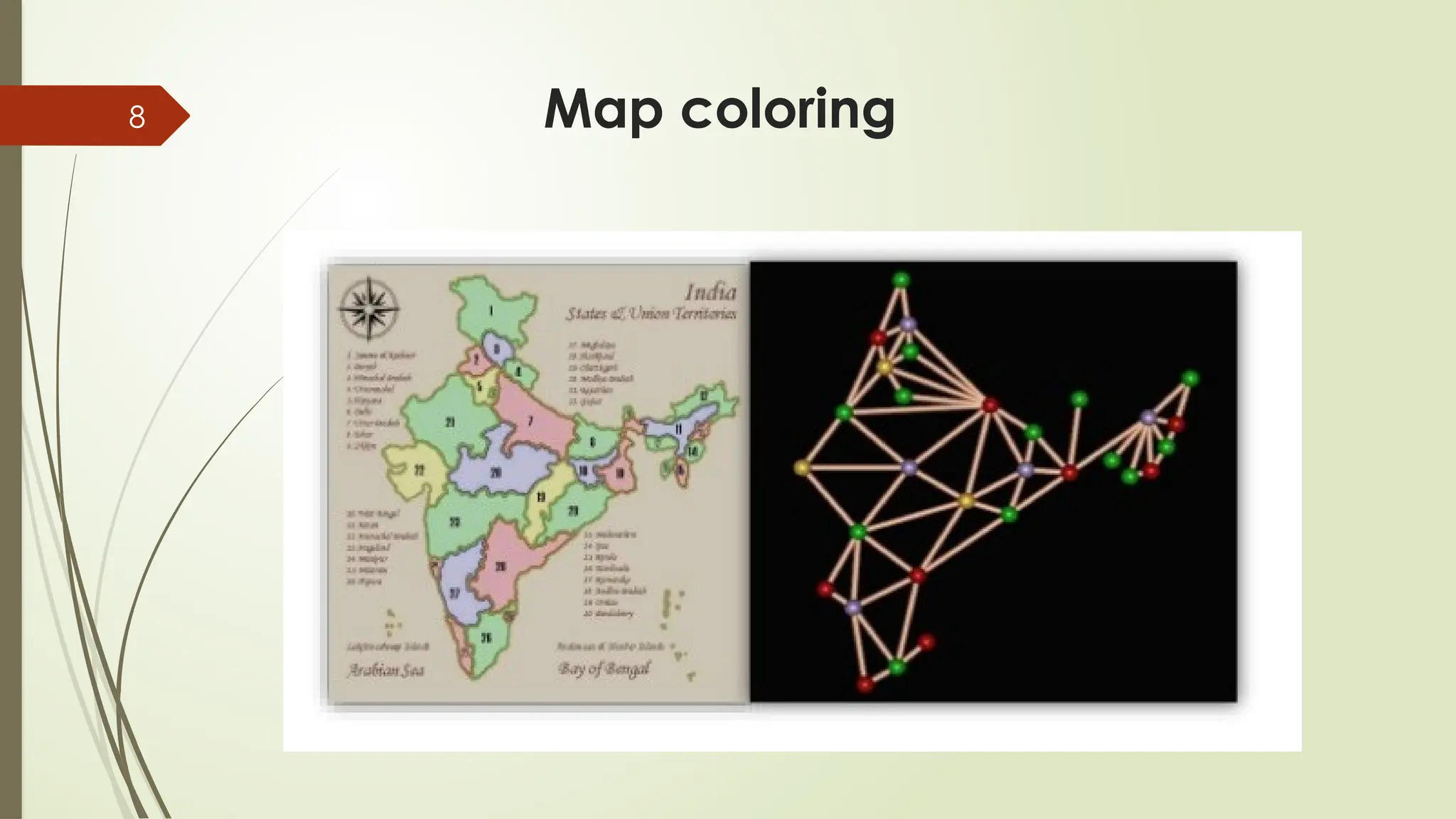
The Map Coloring theorem (how to color any map with no same-colored neighbors).
Pro Tip 💡: The #1 thing to remember? Graphs are about relationships, not just things. Master that, and you'll see networks everywhere!
💬 Key Quotes to Remember:
"Graph theory is the language of networks."
"From social media to silicon chips, everything is connected."
🚀 Ready to See the World Differently?
✅ SAVE this guide to finally get how tech really works!
✅ TAG your study buddy or tech-loving friend! #GraphTheory #ComputerScience #Tech
✅ FOLLOW for more content that turns complex topics into simple superpowers!
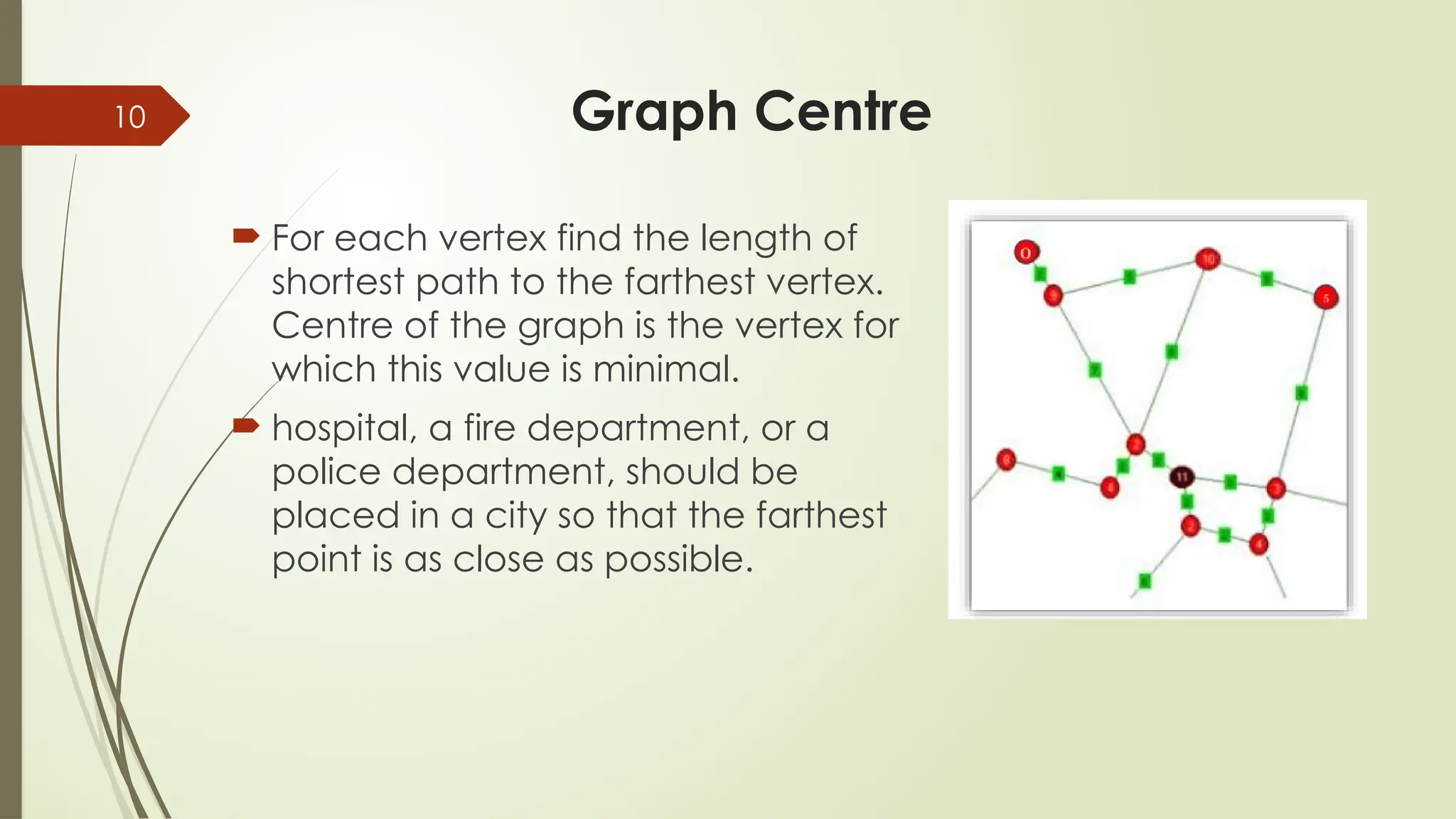
📌 BONUS: The slides reveal how a simple graph center algorithm decides the optimal spot for a new hospital or fire station in a city! 🚒