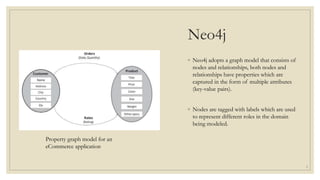
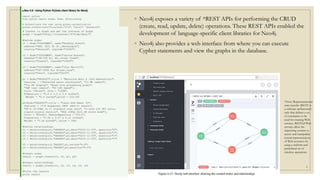
Graph databases model data as nodes and relationships. Nodes have attributes and represent entities, while relationships represent links between nodes. Querying for related entities is faster in graph databases than relational databases since they avoid complex join operations. Neo4j is a graph database that uses nodes, relationships, and properties to model data. It supports ACID and uses the Cypher query language and REST APIs for CRUD operations.