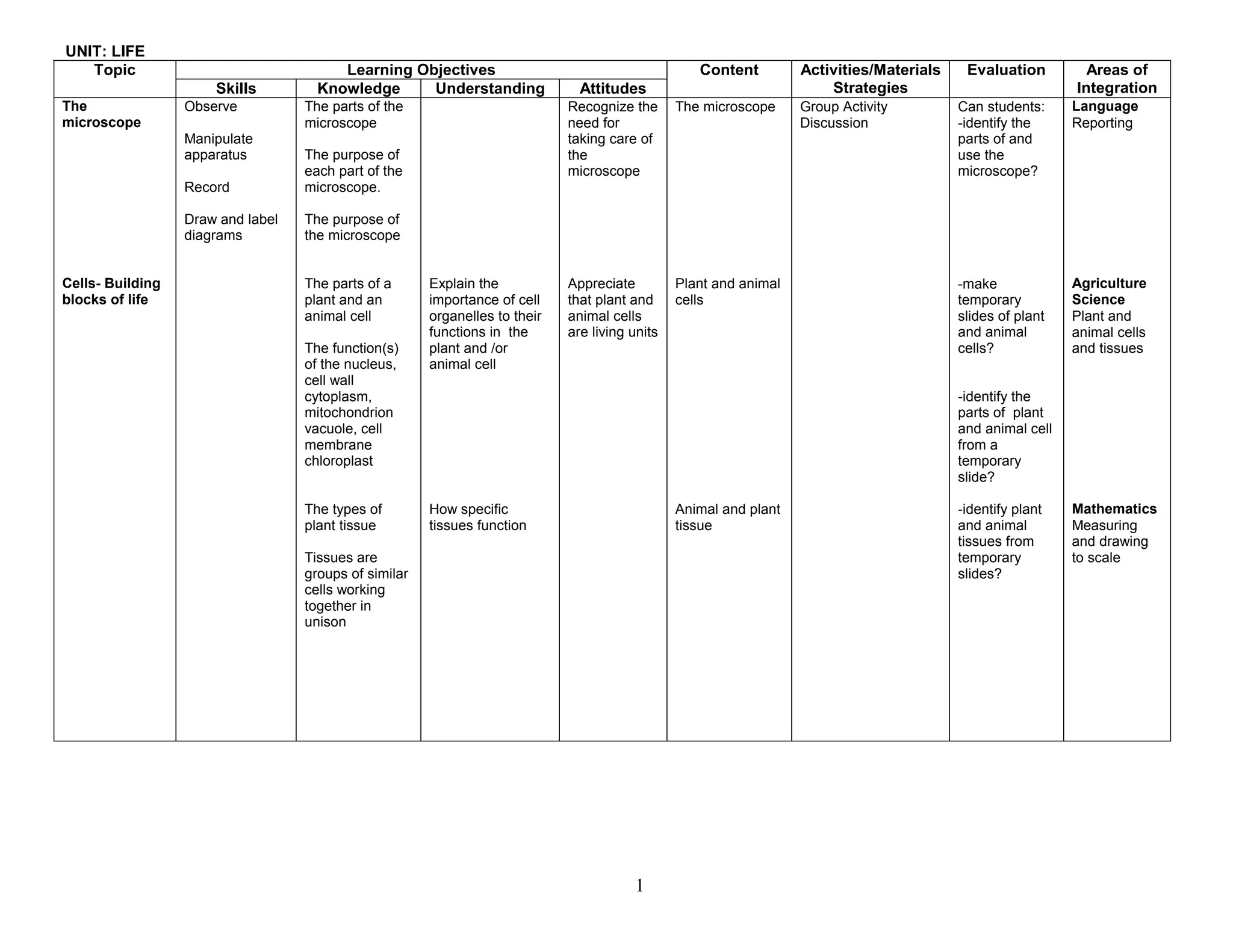
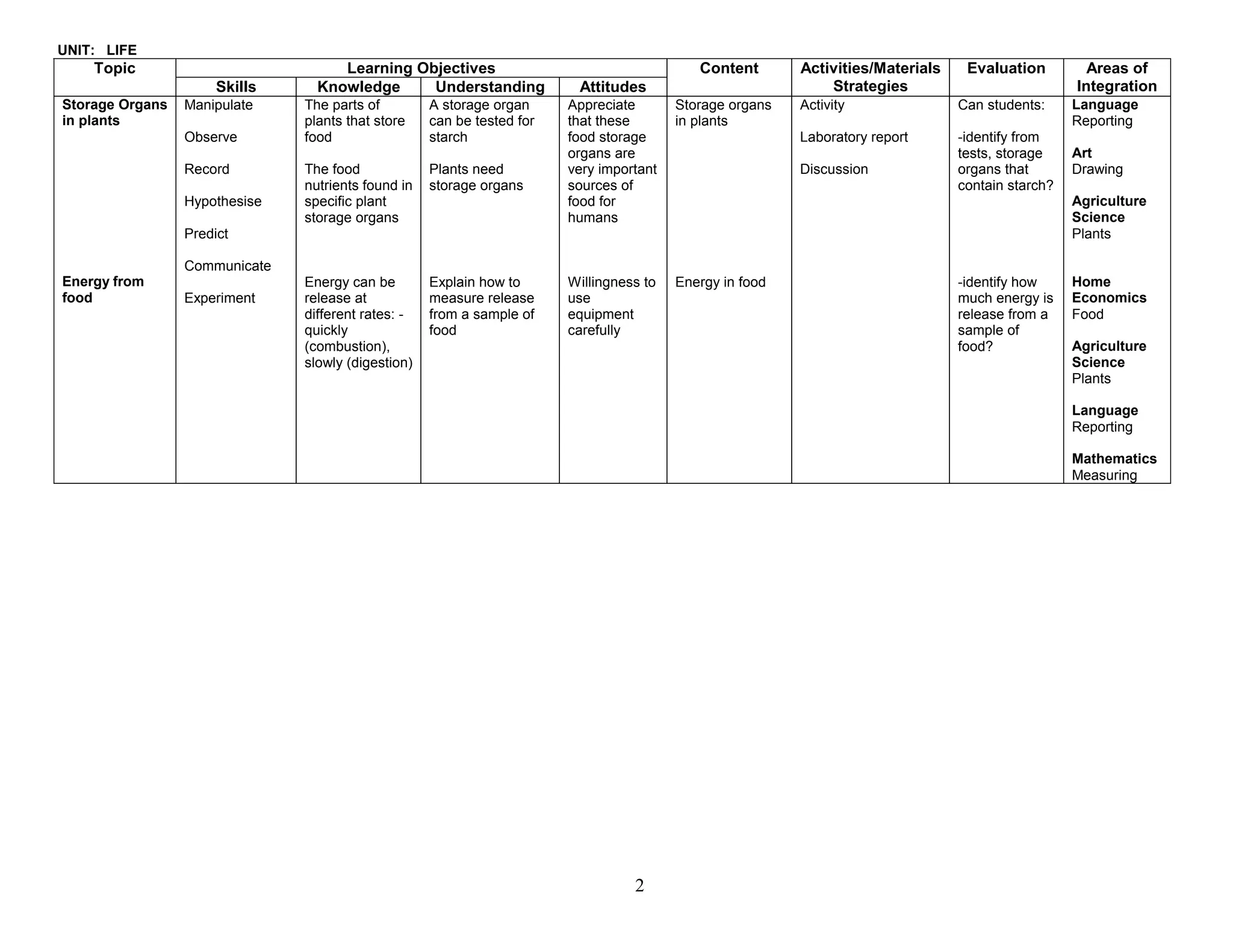
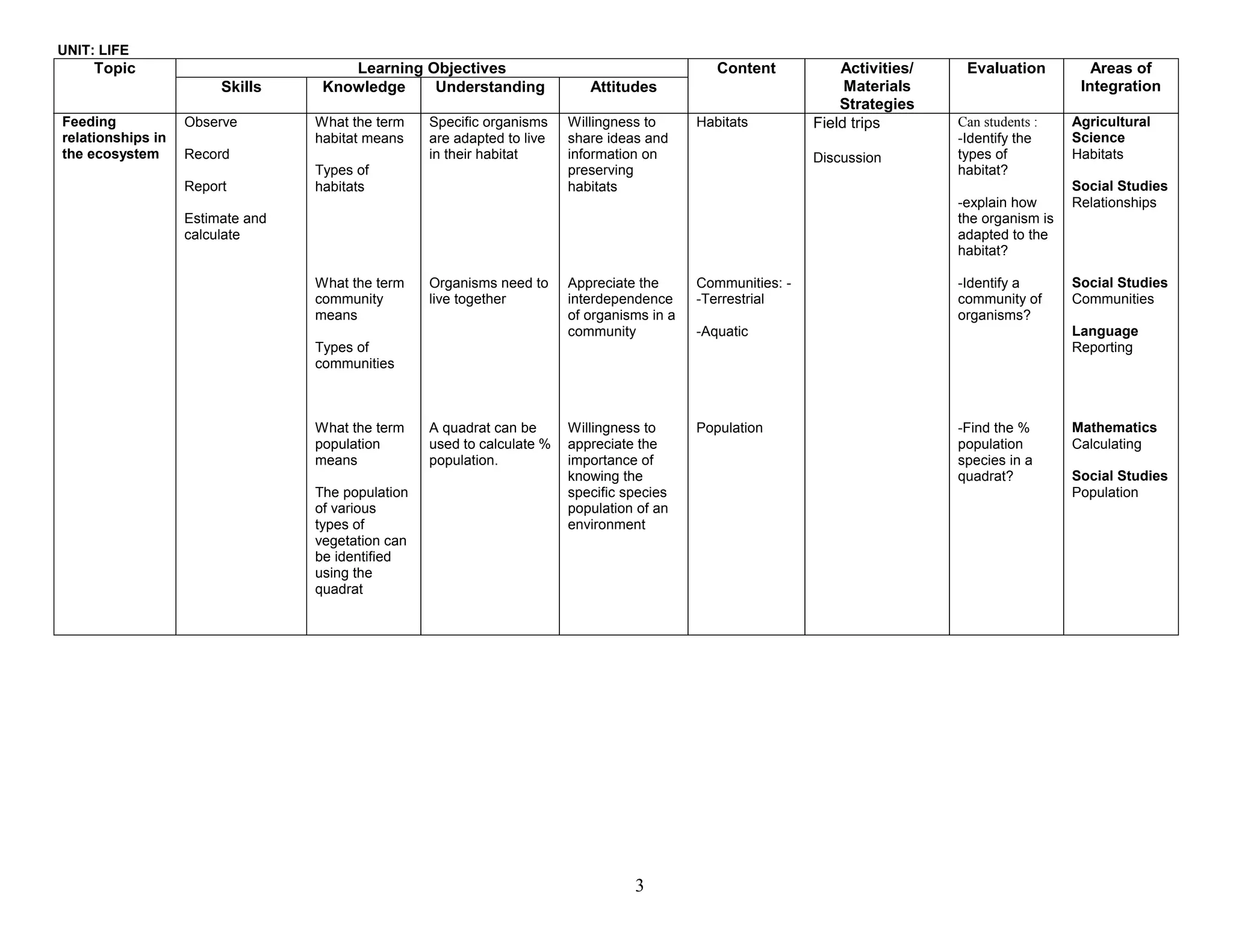
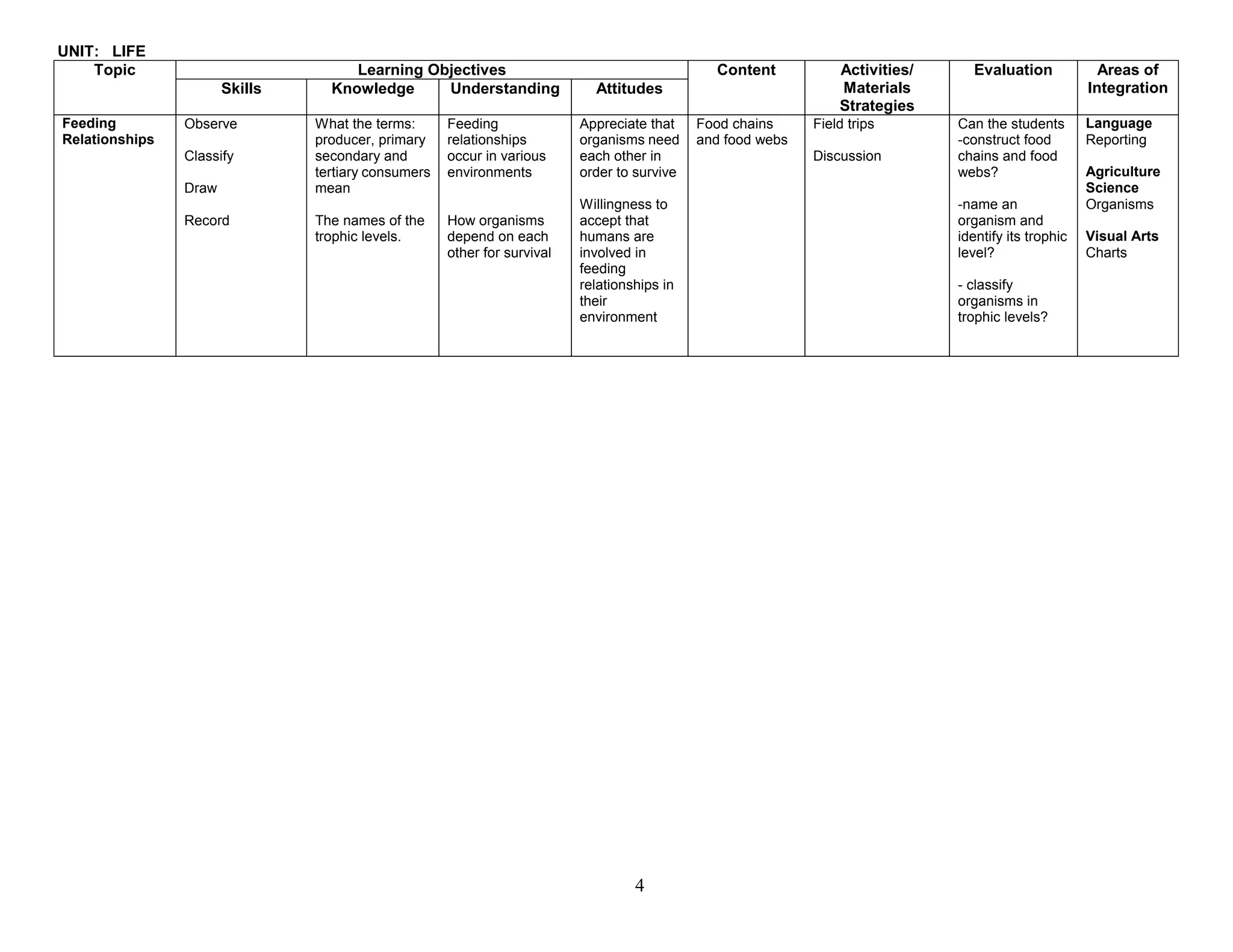
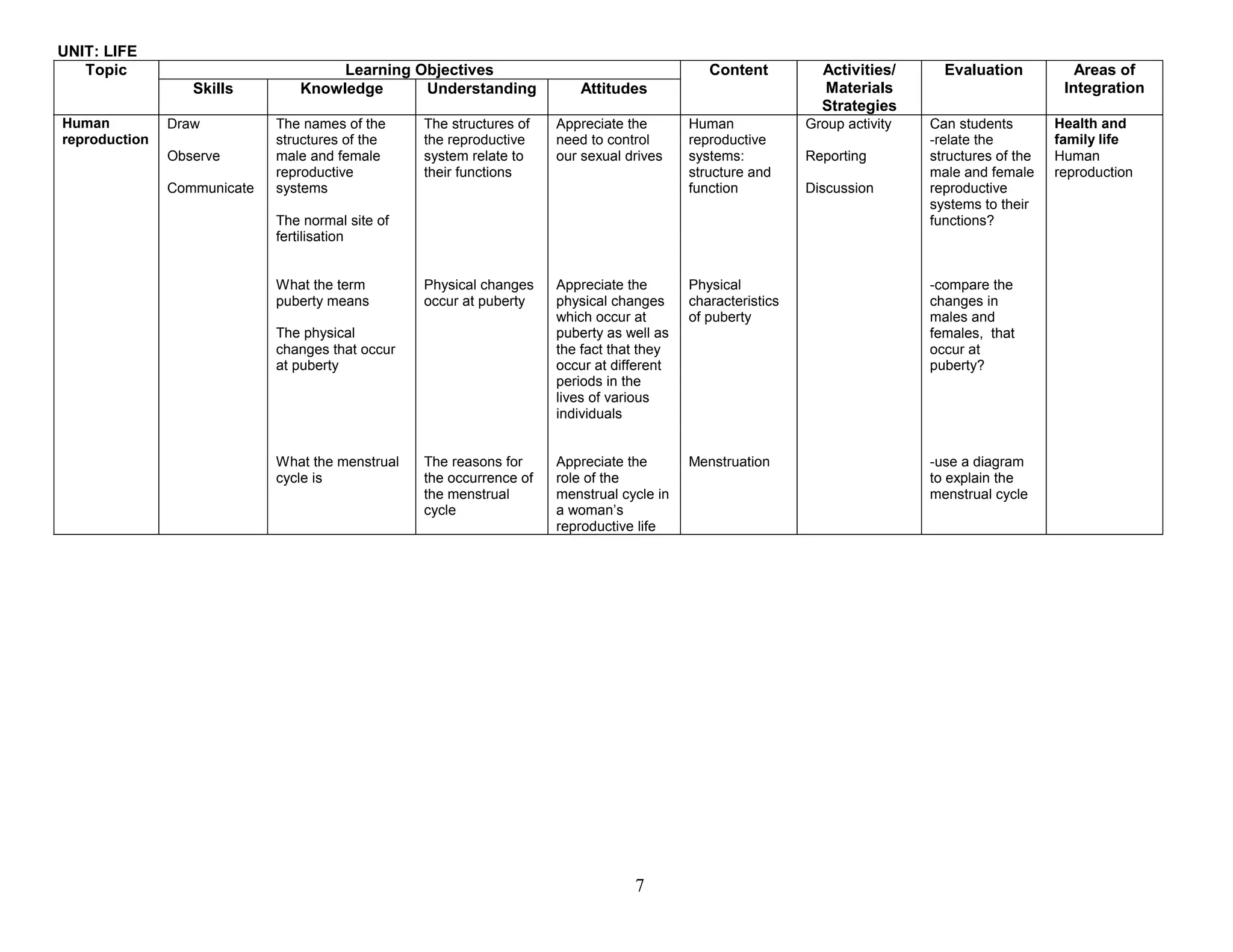
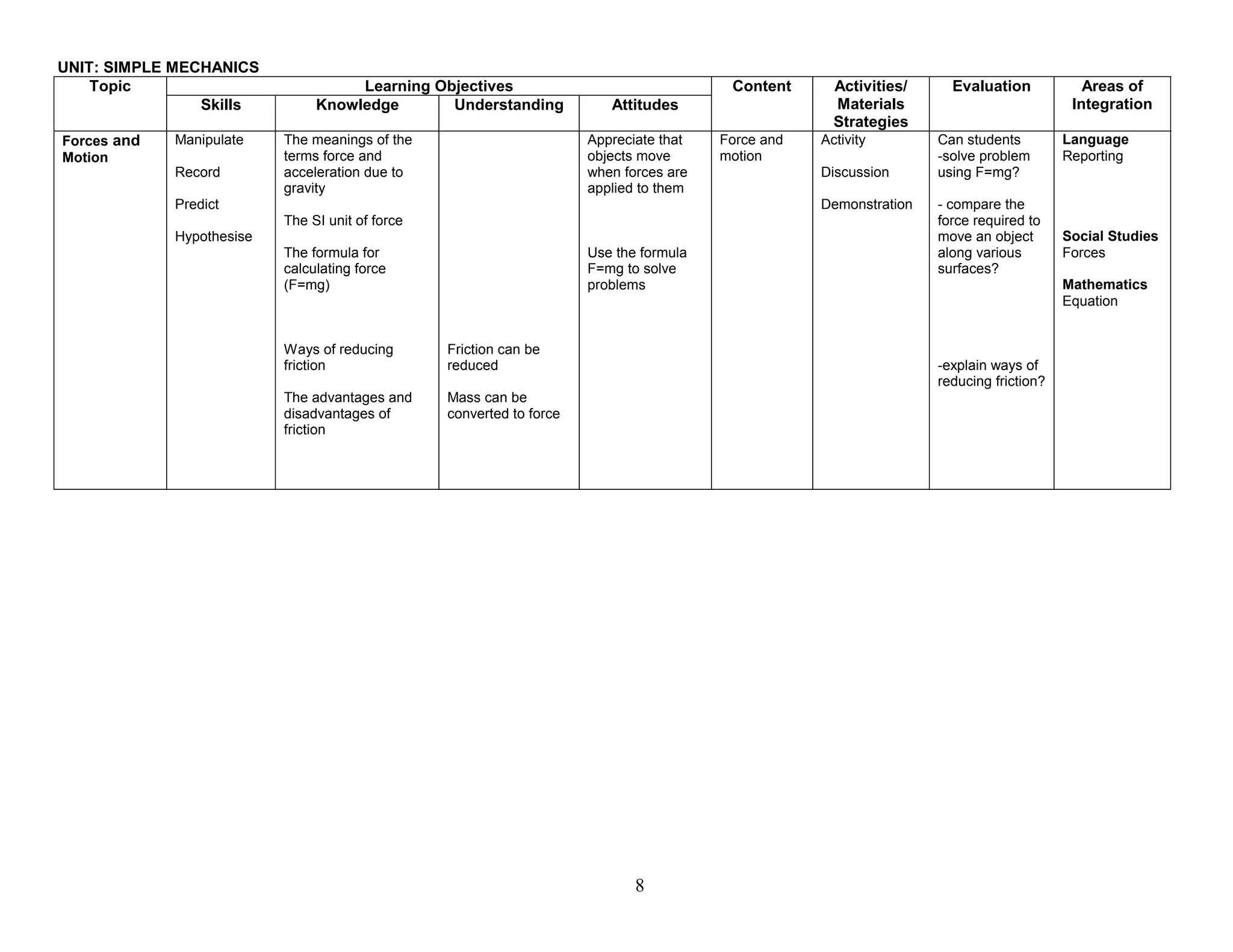
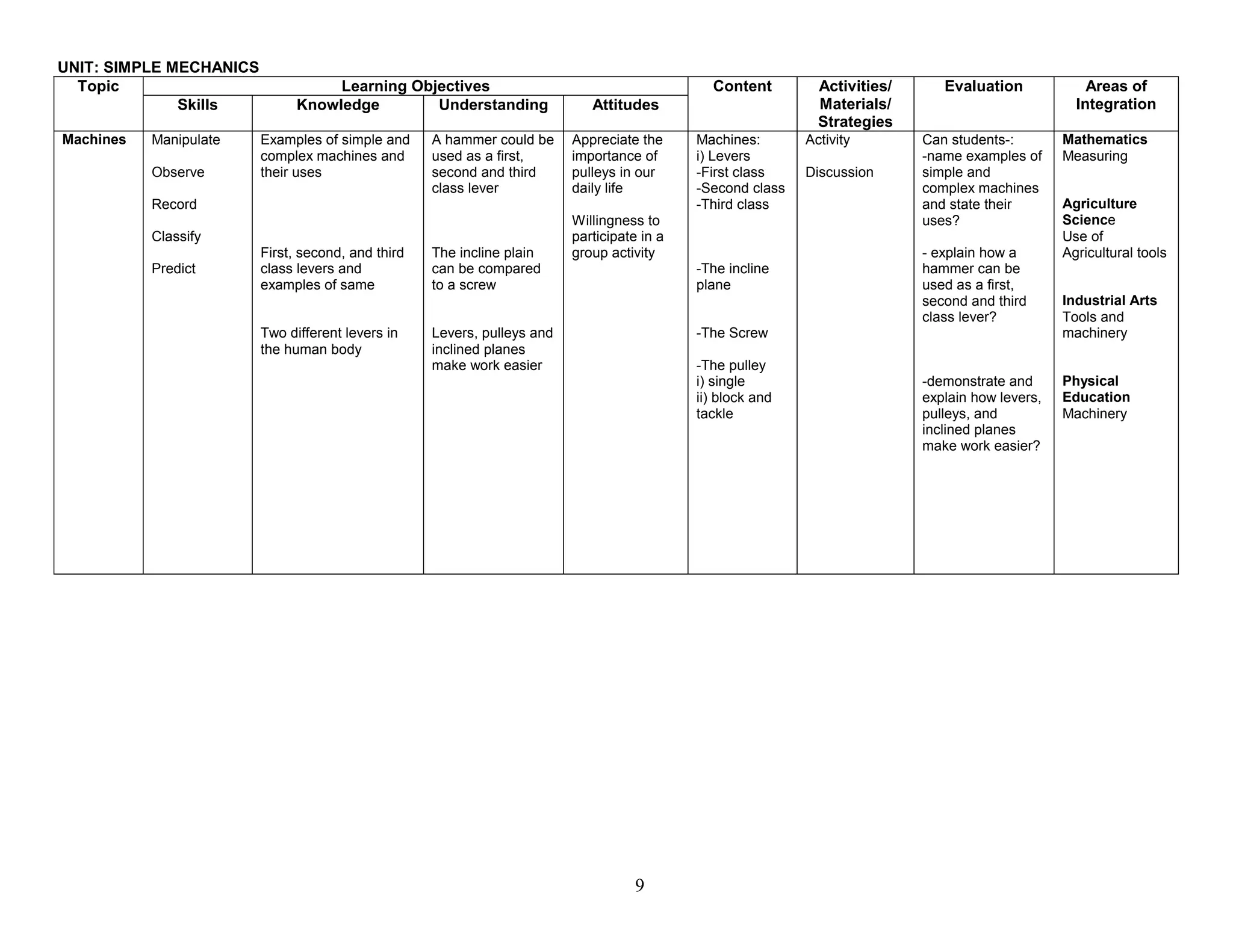
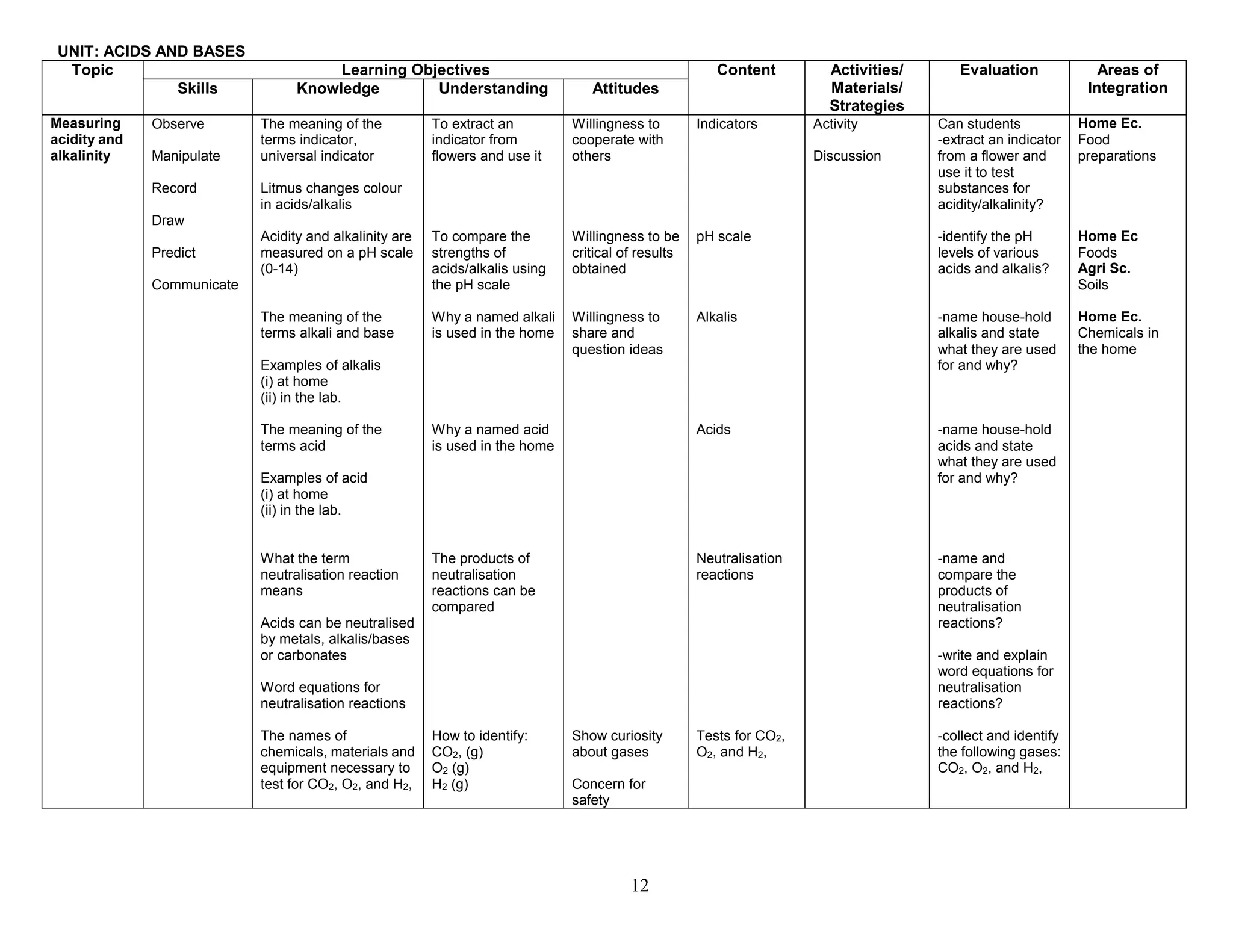
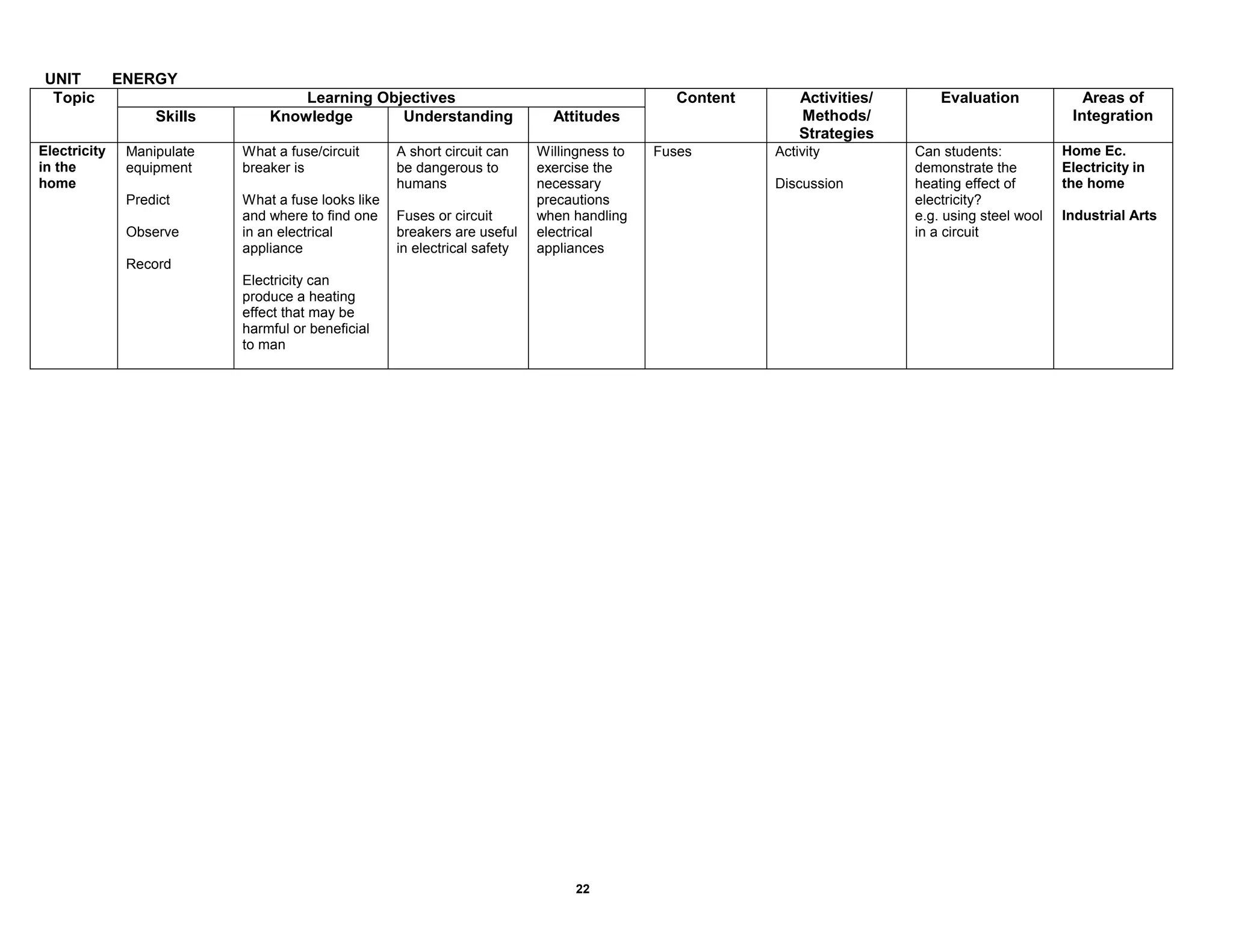
This document provides the table of contents and units for an Integrated Science Teacher's Guide for Grade 8. The guide contains 6 units covering various topics in life science, simple machines, acids and bases, senses, soil science, and energy. Each unit lists the learning objectives, topics, content, activities, strategies and areas of integration for each topic. It also includes acknowledgements, a foreword, preface and introduction providing background on the development of the curriculum guide. The level of detail provided for each topic aims to help teachers effectively plan their lessons to improve the quality of science teaching and learning.