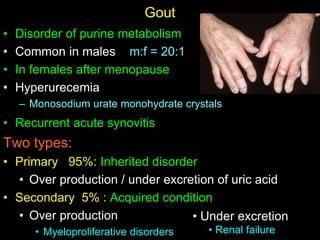
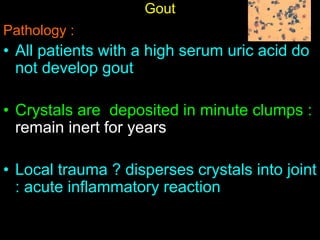
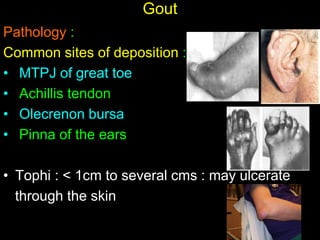
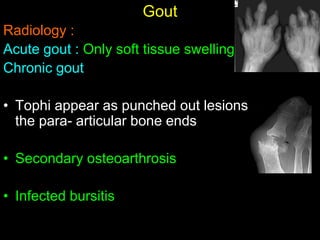
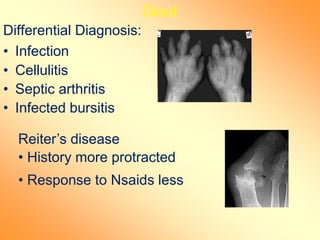
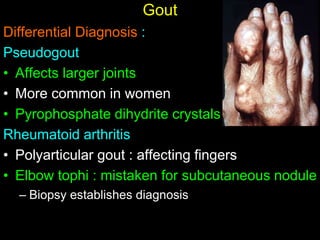
Crystal deposition diseases like gout result from the deposition of crystals like urate in joints and surrounding tissues. Gout is caused by elevated uric acid levels resulting from purine metabolism abnormalities. It usually affects middle-aged males and post-menopausal females, causing sudden, severe joint pain and inflammation. Diagnosis is confirmed by identifying urate crystals in joint fluid. Treatment involves lifestyle changes, medications like allopurinol and NSAIDs to prevent attacks and reduce uric acid levels.