The document provides an extensive overview of key Google interview questions, covering topics for software engineers, freshers, and programming languages. It includes eligibility criteria, types of interview questions (technical, behavioral, and system design), and coding challenges that candidates can practice. Additionally, it outlines the Google interview process, emphasizes cultural fit, and discusses Google Cloud services related to networking and application deployment.


![Output
Example
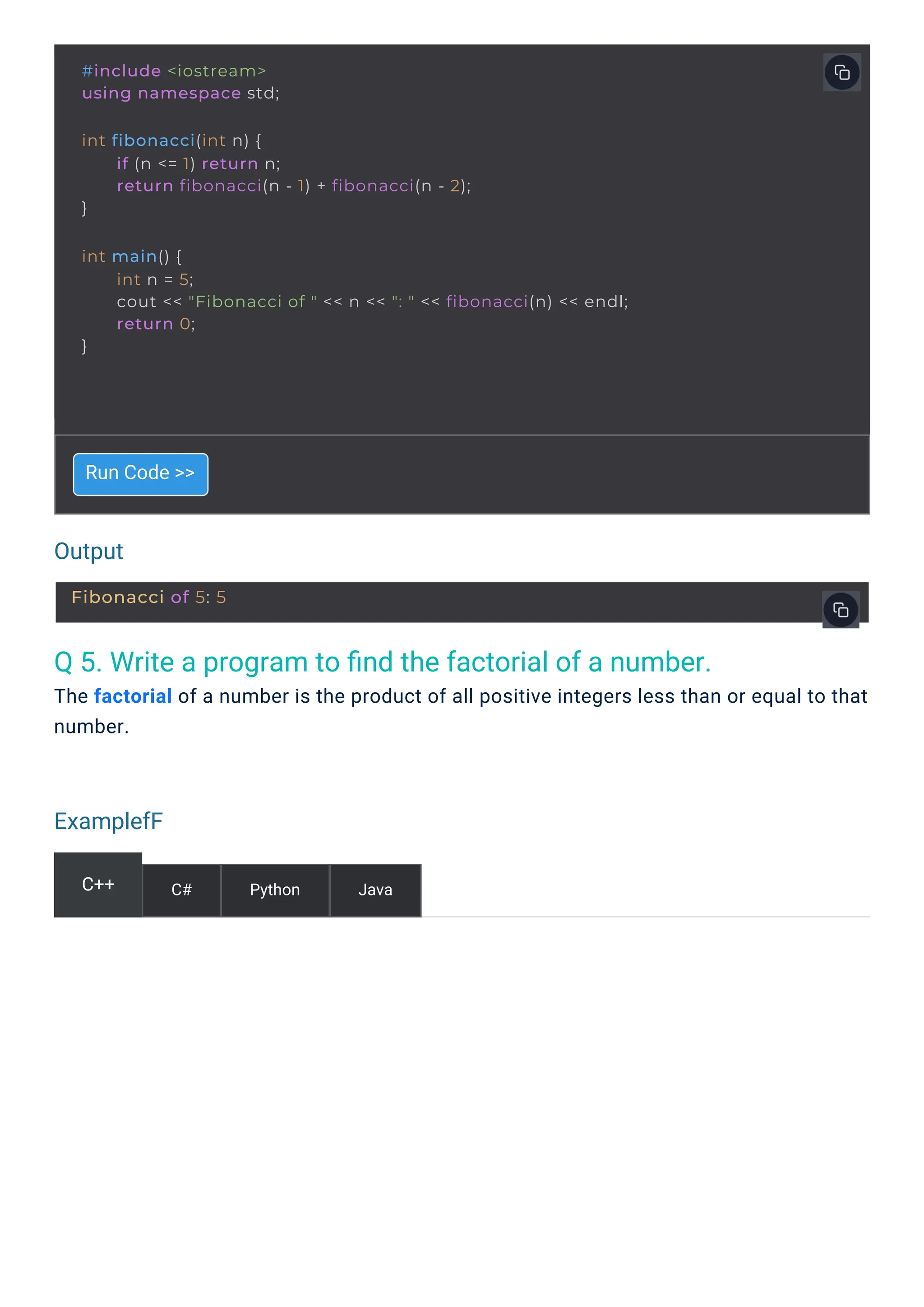
Q 4. Write a program to generate the nth Fibonacci number.
The Fibonacci sequence starts with 0 and 1, and each subsequent number is the sum of the
two preceding ones.
Run Code >>
Read more: How to Implement Fibonacci Series in C#
C++ C# Python Java
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace
std;
int findMax(int arr[], int size) {
}
return *max_element(arr, arr + size);
int main() {
}
int arr[] = {1, 5, 3, 9, 2};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Maximum element: " << findMax(arr, size) << endl;
return 0;
Maximum element: 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleinterviewquestionsbyscholarhat-241130215834-cdec9925/75/Google-Interview-Questions-By-Scholarhat-6-2048.jpg)
![Output
Google Programming Languages Interview Questions
Q 1. What are the differences between Java and C#?
Java and C# are both object-oriented languages but differ in their platform dependency. Java is
platform-independent at runtime and is used with the JVM, whereas C# is primarily used with
the .NET framework on Windows. C# has properties, events, and a for each loop for collection
traversal, while Java uses getter/setter methods and has a simpler event model.
Q 2. What is the difference between == and === in JavaScript?
In JavaScript, == checks for equality after type conversion, while === checks for strict equality
without type conversion. For instance, 5 == '5' is true because of type conversion, but 5 === '5' is
Run Code >>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int findMissingNumber(int arr[], int n) {
}
int totalSum = n * (n + 1) / 2;
int arrSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
arrSum += arr[i];
}
r e t u r n t o t a l S u m - a r r S u m ;
int main() {
}
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 4, 5, 6 };
int n = 6;
cout << "Missing number: " << findMissingNumber(arr, n) << endl;
return 0;
Missing number: 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleinterviewquestionsbyscholarhat-241130215834-cdec9925/75/Google-Interview-Questions-By-Scholarhat-9-2048.jpg)
![false.
The async and await are used in C# for asynchronous programming, allowing non-blocking
execution. An async method performs work on a separate thread without blocking the main
thread, and await is used to indicate where asynchronous operations pause and resume.
Q 6. Explain the map() function in Python.
The map() function in Python applies a given function to each item of an iterable (like a list)
and returns a map object. For example, map(lambda x: x*2, [1, 2, 3]) results in [2, 4, 6].
Python uses automatic garbage collection through reference counting and a cyclic garbage
collector. It manages memory allocation dynamically, using __del__ destructors less often
than languages like C++.
A virtual function in C++ is a function in a base class marked with the virtual keyword. This
allows derived classes to override the function, enabling polymorphism. The actual function
called depends on the object type.
An abstract class in Java can have method implementations, but an interface can only have
method declarations (prior to Java 8). Multiple interfaces can be implemented by a class, but
only one abstract class can be extended.
JavaScript uses prototype-based inheritance, meaning objects inherit directly from other
objects rather than classes. ES6 introduced classes syntactically, but they are still prototype-
based.
Q 5. Explain async and await in C#.
Q 8. What is a virtual function in C++?
Q 7. How is inheritance handled in JavaScript?
Q 3. How does Python handle memory management?
Q 4. What is the difference between an interface and an abstract
class in Java?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleinterviewquestionsbyscholarhat-241130215834-cdec9925/75/Google-Interview-Questions-By-Scholarhat-10-2048.jpg)













