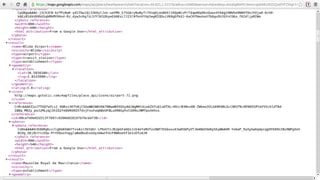
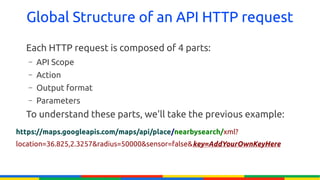
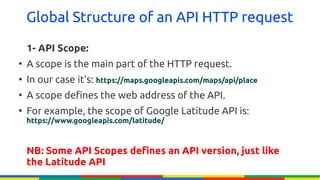
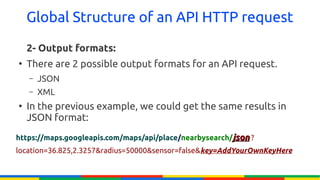
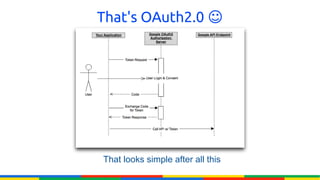
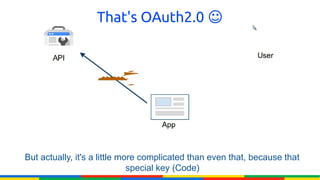
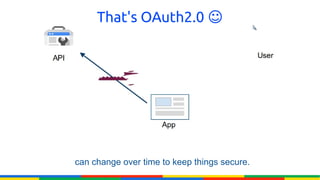
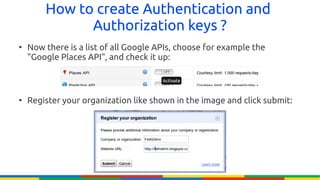
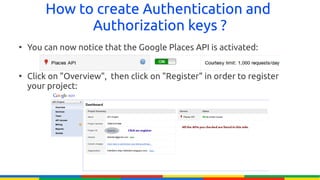
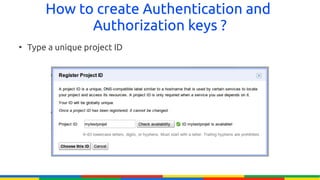
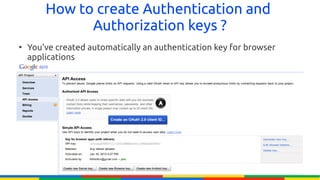
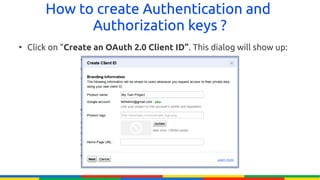
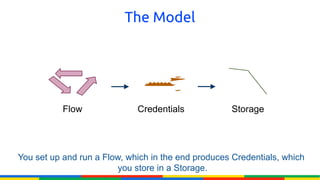
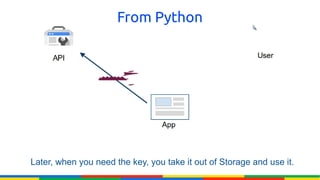
The document provides an overview of Google APIs, describing their types, functions, and usage, particularly focusing on public and private APIs, authentication, and authorization methods. It explains how to construct API requests, manage authentication keys, and utilize OAuth 2.0 for accessing user data securely. Additionally, it introduces Google API client libraries for simplifying API interaction and outlines the process for setting up authentication and authorization keys for applications.