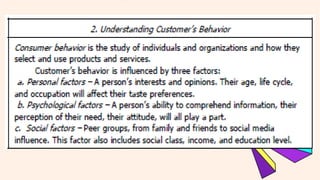
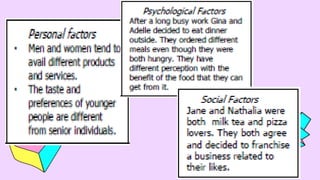
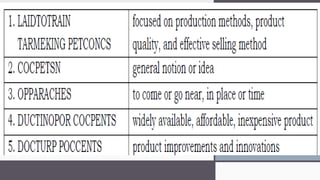
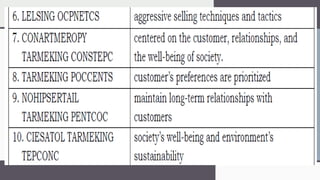
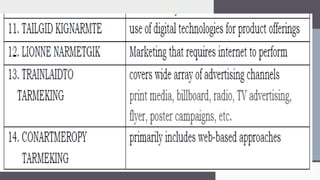
The document outlines key marketing principles, focusing on the roles of marketers, customers, and the importance of customer relationships in developing competitive advantages. It discusses marketing goals, emphasizing the need for understanding consumer needs, innovation, brand awareness, and effective marketing strategies in both traditional and contemporary contexts. Additionally, it addresses various marketing concepts, approaches, and channels, including digital marketing, social media, and event marketing, as well as the significance of adapting to changing customer preferences and societal well-being.