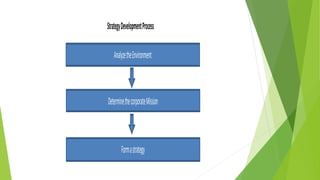
The document outlines six reasons for domestic operations to transition to international operations, including cost reduction, supply chain improvement, and global talent acquisition. It details various operational strategies such as international, multidomestic, global, and transnational, highlighting their traits and advantages. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of defining a corporate mission and strategy alongside recognizing key success factors and core competencies for competitive advantage.